
One end of the light inelastic string is tied to a helium filled balloon and its other end is tied to the bottom of a water filled container at point O. The container lies on a fixed horizontal surface and is pulled horizontally towards the right with a constant horizontal acceleration of magnitude a. Assuming no relative motion of balloon and water with respect to a container, the string will be inclined with the vertical line passing through O by an angle:

A. \[\theta = {\tan ^{( - 1)}}\dfrac{a}{g}\]and the string will be on the right of the vertical line passing through O.
B. \[\theta = {\tan ^{( - 1)}}\dfrac{g}{a}\]and the string will be on the right of the vertical line passing through O.
C. \[\theta = {\tan ^{( - 1)}}\dfrac{a}{g}\]and the string will be on the left of the vertical line passing through O.
D. \[\theta = {\tan ^{( - 1)}}\dfrac{g}{a}\]and the string will be on the left of the vertical line passing through O.

Answer
565.8k+ views
Hint:Here, there are two forces acting upon the helium based balloon, one is the gravitational force, and other is the force applied to move the container. First, draw the vectors of the two forces of the balloons, draw the line joining these vectors, and using the triangle formed, find the tangent angle of the triangle.
Complete step by step answer:
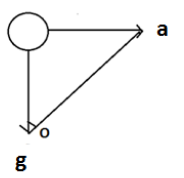
Above is the free body diagram of the helium filled balloon which is inside the water container. Now, the container is moving on the right side with a constant acceleration of magnitude a. The balloon also has force acting on it in the form of gravity. It acts towards the downward direction. Now, let the density of water\[{\rho _w}\]and the density of the helium gas is\[{\rho _g}\]. Let the volume enclosed inside the gas be V. Now, as shown from the diagram, if we form a line joining the two vectors, we get a triangle. The angle at the point O is given as\[\theta \]. Now, the tangent of this angle is obtained through the division of the opposite vector and the adjacent vector. Now, the force through the acceleration of the container and the acceleration due to gravity are as follows:
\[\
{F_a} = ({\rho _w} - {\rho _g})Va \\
\Rightarrow{F_g} = ({\rho _w} - {\rho _g})Vg \\
\]
Now, the tangent due to these forces is given as follows:
\[
\Rightarrow\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{F_a}}}{{{F_g}}} \\
\Rightarrow\tan \theta = \dfrac{{({\rho _w} - {\rho _g})Va}}{{({\rho _w} - {\rho _g})Vg}} \\
\therefore\tan \theta = \dfrac{a}{g} \\
\]
Now, the force due to the acceleration of the container is on the right, thus the string will move to the right of the vertical line passing through O.
Hence option A is the correct answer.
Note:Here, even if the gravitational acceleration overpowers the acceleration of the container, the direction of the final acceleration would be downwards but towards the right hand side of the container, so eventually, the direction would be towards the right side of the vertical line passing through the point O.
Complete step by step answer:

Above is the free body diagram of the helium filled balloon which is inside the water container. Now, the container is moving on the right side with a constant acceleration of magnitude a. The balloon also has force acting on it in the form of gravity. It acts towards the downward direction. Now, let the density of water\[{\rho _w}\]and the density of the helium gas is\[{\rho _g}\]. Let the volume enclosed inside the gas be V. Now, as shown from the diagram, if we form a line joining the two vectors, we get a triangle. The angle at the point O is given as\[\theta \]. Now, the tangent of this angle is obtained through the division of the opposite vector and the adjacent vector. Now, the force through the acceleration of the container and the acceleration due to gravity are as follows:
\[\
{F_a} = ({\rho _w} - {\rho _g})Va \\
\Rightarrow{F_g} = ({\rho _w} - {\rho _g})Vg \\
\]
Now, the tangent due to these forces is given as follows:
\[
\Rightarrow\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{F_a}}}{{{F_g}}} \\
\Rightarrow\tan \theta = \dfrac{{({\rho _w} - {\rho _g})Va}}{{({\rho _w} - {\rho _g})Vg}} \\
\therefore\tan \theta = \dfrac{a}{g} \\
\]
Now, the force due to the acceleration of the container is on the right, thus the string will move to the right of the vertical line passing through O.
Hence option A is the correct answer.
Note:Here, even if the gravitational acceleration overpowers the acceleration of the container, the direction of the final acceleration would be downwards but towards the right hand side of the container, so eventually, the direction would be towards the right side of the vertical line passing through the point O.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




