
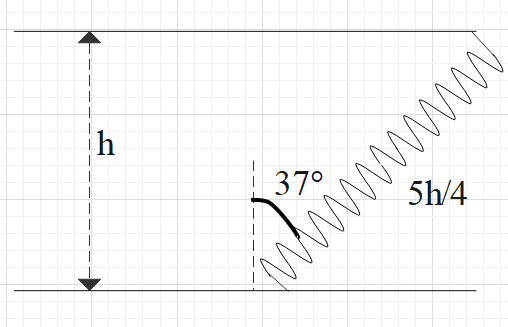
One end of a spring of natural length h and spring constant K is fixed on the ground and the other is fitted with a smooth ring of mass m which is allowed to slide on a horizontal rod fixed at a height h. Initially the spring makes an angle of ${{37}^{\circ }}$ with the vertical when the system is released from rest. Find out the speed of the ring when the spring becomes vertical.
a) \[v=\dfrac{h}{3}\sqrt{\dfrac{k}{m}}\]
b) \[v=\dfrac{h}{4}\sqrt{\dfrac{2k}{m}}\]
c) \[v=\dfrac{h}{4}\sqrt{\dfrac{k}{m}}\]
d) \[v=\dfrac{h}{4}\sqrt{\dfrac{k}{2m}}\]

Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: The initial length of the spring, when in equilibrium position is h. After the system is released from rest, let us assume that the spring is extended by x. So, the net length of spring is $\left( h+x \right)$ which is given as: $\dfrac{5h}{4}$. So, using this relation, find the value of x. Then apply, work energy theorem as: $\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$ where change in potential energy is equal to change in kinetic energy, to find the value of velocity.
Complete step by step answer:
As we have assumed that the extension in the system after it is released from the rest is x.
So, the final length can be given as:
$\begin{align}
& \left( h+x \right)=\dfrac{5h}{4} \\
& x=\dfrac{5h}{4}-h \\
& x=\dfrac{h}{4}......(1) \\
\end{align}$
Now, apply work-energy theorem to the system, we get:
Change in potential energy = Change in kinetic energy
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}k{{\left( \dfrac{h}{4} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{k}{m}{{\left( \dfrac{h}{4} \right)}^{2}}={{v}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\dfrac{h}{4}\sqrt{\dfrac{k}{m}} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, we get: \[v=\dfrac{h}{4}\sqrt{\dfrac{k}{m}}\].
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The work-energy theorem states that the net work done by the forces on an object equals the change in its kinetic energy, i.e. \[W=\Delta KE\]
So, for the spring system, work done is $W=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$
And we know that kinetic energy is given as: $KE=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$
Hence, work energy theorem for a spring system is: $\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
As we have assumed that the extension in the system after it is released from the rest is x.
So, the final length can be given as:
$\begin{align}
& \left( h+x \right)=\dfrac{5h}{4} \\
& x=\dfrac{5h}{4}-h \\
& x=\dfrac{h}{4}......(1) \\
\end{align}$
Now, apply work-energy theorem to the system, we get:
Change in potential energy = Change in kinetic energy
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}k{{\left( \dfrac{h}{4} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{k}{m}{{\left( \dfrac{h}{4} \right)}^{2}}={{v}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\dfrac{h}{4}\sqrt{\dfrac{k}{m}} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, we get: \[v=\dfrac{h}{4}\sqrt{\dfrac{k}{m}}\].
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The work-energy theorem states that the net work done by the forces on an object equals the change in its kinetic energy, i.e. \[W=\Delta KE\]
So, for the spring system, work done is $W=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$
And we know that kinetic energy is given as: $KE=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$
Hence, work energy theorem for a spring system is: $\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




