
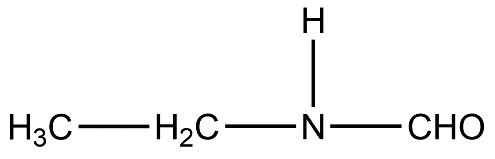
One among the following is the correct IUPAC name of the compound:
(A) N-formyl aminoethane
(B) N-ethyl formylamine
(C) N-ethyl methanamide
(D) ethalamino methanal

Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Find out the functional groups present in this compound. Then determine the parent carbon chain. Determine the substituents present in the compounds. Start by writing parent name followed by functional group according to IUPAC priority order as suffix and then accordingly add substituent as prefix.
Complete step by step solution:
- Let’s take a look at the given compound.
- According to IUPAC nomenclature, the functional group having the most priority will be the suffix for the parent name.
- Let’s first identify the functional group. The functional group present in this compound is an amide because nitrogen atom is directly bonded to the carbonyl group.
- The carbonyl group has one hydrogen atom attached to it so basically the parent chain is methane due to absence of carbon chain linked to carbonyl carbon.
- Now, we can see that nitrogen atoms have an ethyl chain attached to it. But according to IUPAC, carbonyl group has higher priority than amine, so ethyl will be the substituent on nitrogen atom of amide group. So, we get N-ethyl.
- Our functional group is amide and parent chain or root is methane so the IUPAC parent name will be methanamide.
- Putting everything together we get N-ethyl methanamide.
- Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is N-ethyl methanamide.
- Therefore, the answer is option (C).
Note: N-ethyl methyl amide is commonly known as N-ethyl formyl amide because one of the hydrogen of formaldehyde is replaced by ethyl amine group. Actually, N-ethyl methanamide is formed due to condensation reaction between ethyl amine and formic acid. IF –CHO group is a substituent due to presence of a main functional group like acid which has higher priority then –CHO is prefixed as formyl.
Complete step by step solution:
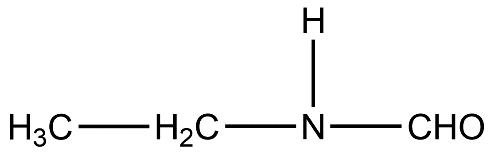
- Let’s take a look at the given compound.

- According to IUPAC nomenclature, the functional group having the most priority will be the suffix for the parent name.
- Let’s first identify the functional group. The functional group present in this compound is an amide because nitrogen atom is directly bonded to the carbonyl group.
- The carbonyl group has one hydrogen atom attached to it so basically the parent chain is methane due to absence of carbon chain linked to carbonyl carbon.
- Now, we can see that nitrogen atoms have an ethyl chain attached to it. But according to IUPAC, carbonyl group has higher priority than amine, so ethyl will be the substituent on nitrogen atom of amide group. So, we get N-ethyl.
- Our functional group is amide and parent chain or root is methane so the IUPAC parent name will be methanamide.
- Putting everything together we get N-ethyl methanamide.
- Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is N-ethyl methanamide.
- Therefore, the answer is option (C).
Note: N-ethyl methyl amide is commonly known as N-ethyl formyl amide because one of the hydrogen of formaldehyde is replaced by ethyl amine group. Actually, N-ethyl methanamide is formed due to condensation reaction between ethyl amine and formic acid. IF –CHO group is a substituent due to presence of a main functional group like acid which has higher priority then –CHO is prefixed as formyl.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




