
On ozonolysis, ethylene gives:
A. aldehyde
B. ketone
C. carboxylic acid
D. ether
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint:
Ozonolysis is the oxidative cleavage of carbon-carbon double bond using ozone as an oxidizing agent is called ozonolysis. The reaction is performed in organic solvents like dichloromethane, methanol or acetone at $ - {78^ \circ }{\text{C}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Ozone is the molecule containing three atoms of oxygen. Ozonolysis of ethylene or ethane involves the cleavage of the double bonds in the alkenes using ozone molecules $\left( {{{\text{O}}_3}} \right)$. Ozone is very reactive. Ozone acts as an oxidizing agent.
When ozone, in any of the solvents, is reacted with ethane, it forms an intermediate called ozonide molecule. Initially the electrophile of ozone is added to the carbon-carbon double bond which forms an intermediate. Then it breaks and forms carbonyl and carbonyl oxide molecules. This rearranges and makes a stable ozonide intermediate. This is followed by workup results in the formation of respective products. Thus it converts to corresponding carbonyl compounds. The reaction is given below:
${{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_4} + {{\text{O}}_3} \rightleftarrows $
 $ \rightleftarrows $
$ \rightleftarrows $
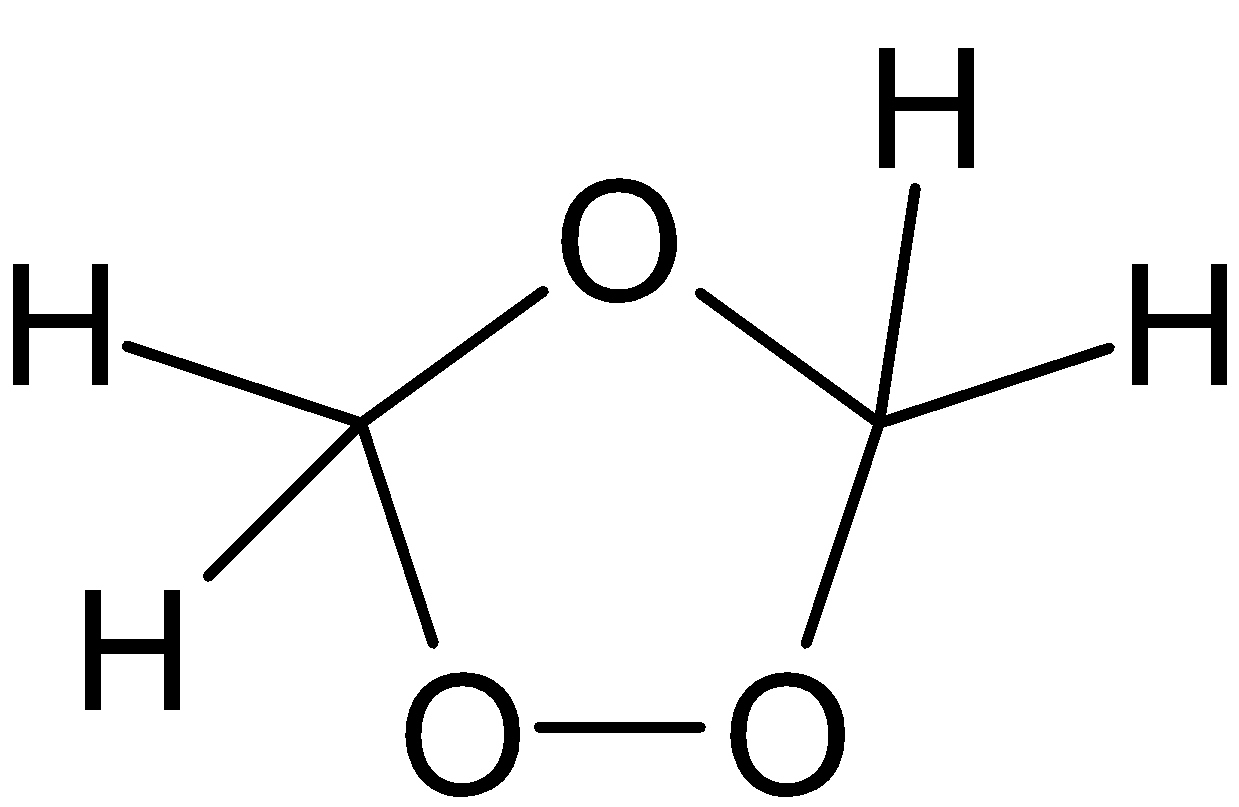 $ \to {\text{HCHO}}$
$ \to {\text{HCHO}}$
Hence aldehydes are formed.
Workup is divided into three types:
-Using mild reducing agents like ${\text{M}}{{\text{e}}_2}{\text{S}}$ or ${\text{PP}}{{\text{h}}_3}$ or zinc dust
It produces carbonyl compounds, particularly aldehyde or ketone.
-Strong reducing agents like ${\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_4}$ or ${\text{NaB}}{{\text{H}}_4}$.
It produces alcohol.
-Oxidizing agents like ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$ or ${{\text{O}}_2}$.
It produces carboxylic acids.
Hence option A is correct.
Note:
Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen. It breaks both $\sigma $ and $\pi $ bonds of alkene. Oxidizing or reducing agents are added to give corresponding carbonyl compounds. Alkynes may produce different types of acids on ozonolysis.
Ozonolysis is the oxidative cleavage of carbon-carbon double bond using ozone as an oxidizing agent is called ozonolysis. The reaction is performed in organic solvents like dichloromethane, methanol or acetone at $ - {78^ \circ }{\text{C}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Ozone is the molecule containing three atoms of oxygen. Ozonolysis of ethylene or ethane involves the cleavage of the double bonds in the alkenes using ozone molecules $\left( {{{\text{O}}_3}} \right)$. Ozone is very reactive. Ozone acts as an oxidizing agent.
When ozone, in any of the solvents, is reacted with ethane, it forms an intermediate called ozonide molecule. Initially the electrophile of ozone is added to the carbon-carbon double bond which forms an intermediate. Then it breaks and forms carbonyl and carbonyl oxide molecules. This rearranges and makes a stable ozonide intermediate. This is followed by workup results in the formation of respective products. Thus it converts to corresponding carbonyl compounds. The reaction is given below:
${{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_4} + {{\text{O}}_3} \rightleftarrows $


Hence aldehydes are formed.
Workup is divided into three types:
-Using mild reducing agents like ${\text{M}}{{\text{e}}_2}{\text{S}}$ or ${\text{PP}}{{\text{h}}_3}$ or zinc dust
It produces carbonyl compounds, particularly aldehyde or ketone.
-Strong reducing agents like ${\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_4}$ or ${\text{NaB}}{{\text{H}}_4}$.
It produces alcohol.
-Oxidizing agents like ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$ or ${{\text{O}}_2}$.
It produces carboxylic acids.
Hence option A is correct.
Note:
Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen. It breaks both $\sigma $ and $\pi $ bonds of alkene. Oxidizing or reducing agents are added to give corresponding carbonyl compounds. Alkynes may produce different types of acids on ozonolysis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




