
On mixing certain alkane with chlorine and irradiating with ultraviolet light, it forms only one mono chloroalkane. This alkane could be:
(A) propane
(B) pentane
(C) isopentane
(D) neopentane
Answer
546.6k+ views
Hint: When an alkane is reacted with a halogen in the presence of ultraviolet (UV) light or heat It leads to the formation of a haloalkane. This reaction is called halogenation of alkanes. These haloalkanes are also called alkyl halides.
Complete Step-by-step Answer:
In the process of halogenation, the derivative of hydrocarbon is produced in which one or more atoms of halogens are replaced for the H-atom present in the molecule. Alkanes are unreactive compounds as they are non-polar and do not have any functional group. Halogenation is a three-step process. The first process is the initiation step in which the halogen radical is formed when UV light falls on it. In the second step, the radical forms attacks the hydrogen present on the alkane to form an alkyl radical and a halogen atom. In the final step, the halogen radical binds with another radical to form the halogen molecule again.
Now, we will write the chlorination reaction of the given alkanes to check which alkane will yield only one mono chloroalkane.
Chlorination of propane is given as:
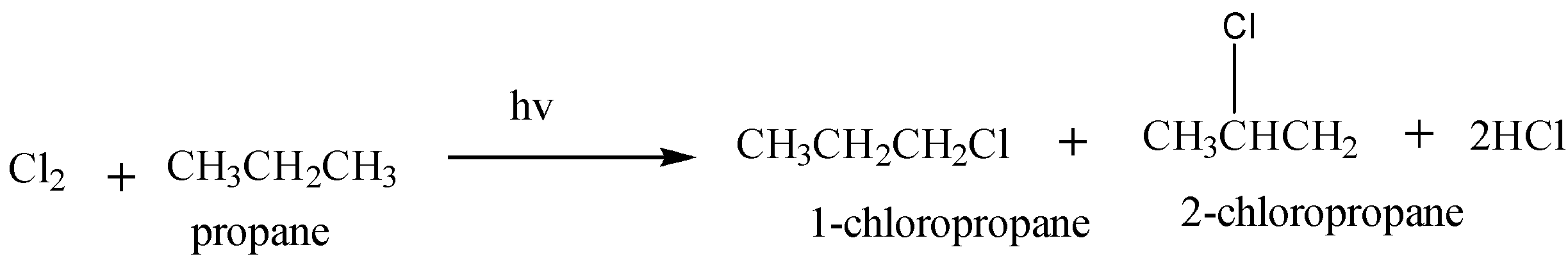
Hence, this reaction yields $ 2 $ mono chloroalkane.
Chlorination of pentane is given as:
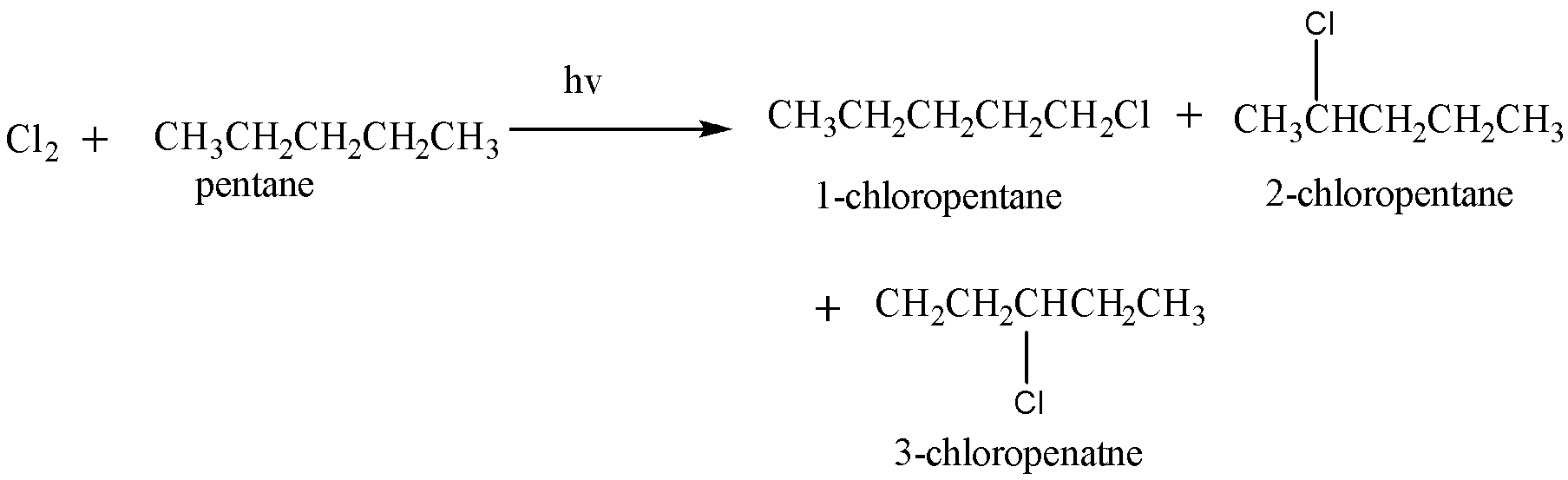
Hence, this reaction yields $ 3 $ mono chloroalkane.
Chlorination of isopentane is given as:
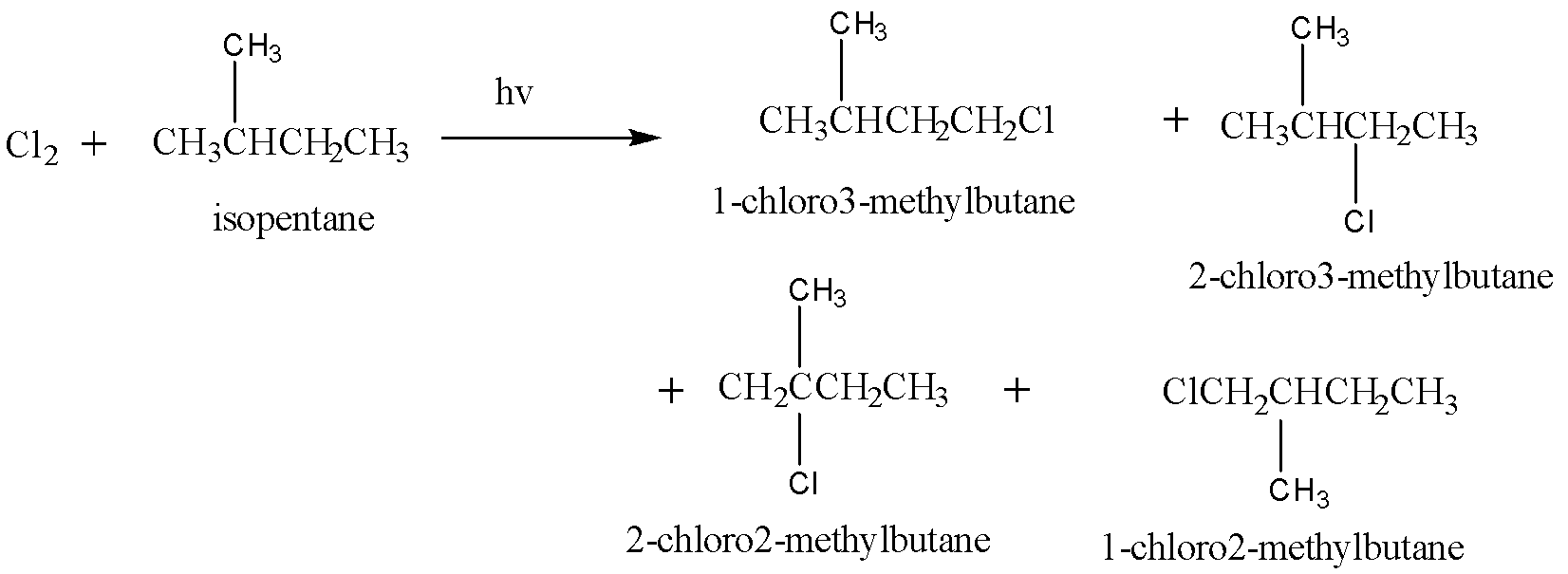
Hence, this reaction yields $ 4 $ mono chloroalkane.
Chlorination of neopentane is given as:
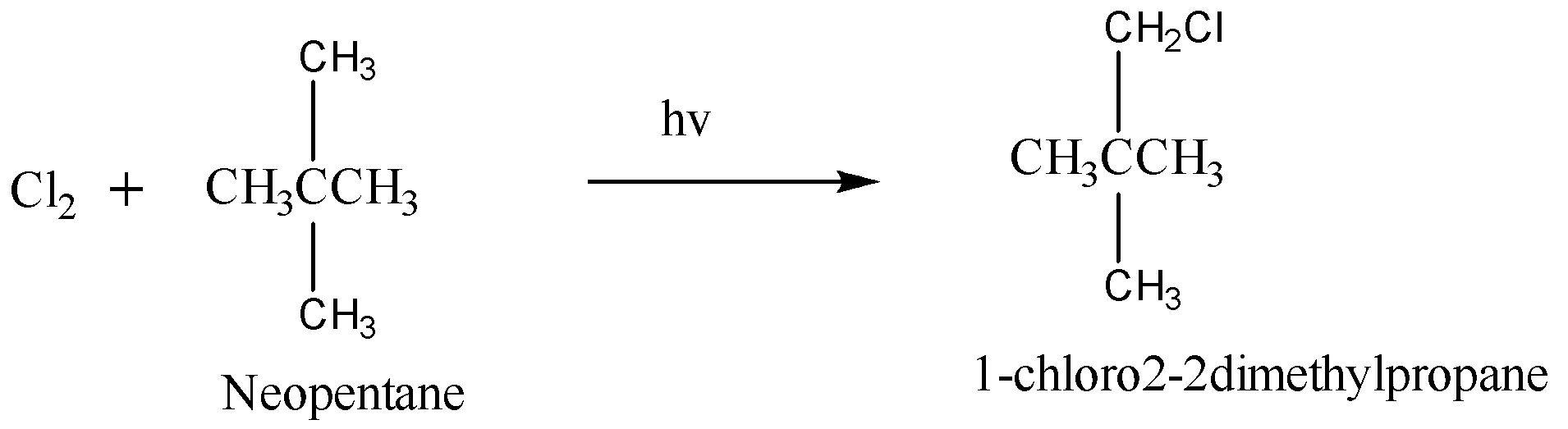
Hence, this reaction yields only one mono chloroalkane. Therefore we can say that option (D) is correct.
Note:
Halogenation is a reaction that happens when addition of one or more halogens is done to an alkane. In the periodic table, examples of halogens are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, etc. The substance that is formed from a halogenation reaction is known as a halogenated compound.
Complete Step-by-step Answer:
In the process of halogenation, the derivative of hydrocarbon is produced in which one or more atoms of halogens are replaced for the H-atom present in the molecule. Alkanes are unreactive compounds as they are non-polar and do not have any functional group. Halogenation is a three-step process. The first process is the initiation step in which the halogen radical is formed when UV light falls on it. In the second step, the radical forms attacks the hydrogen present on the alkane to form an alkyl radical and a halogen atom. In the final step, the halogen radical binds with another radical to form the halogen molecule again.
Now, we will write the chlorination reaction of the given alkanes to check which alkane will yield only one mono chloroalkane.
Chlorination of propane is given as:

Hence, this reaction yields $ 2 $ mono chloroalkane.
Chlorination of pentane is given as:

Hence, this reaction yields $ 3 $ mono chloroalkane.
Chlorination of isopentane is given as:

Hence, this reaction yields $ 4 $ mono chloroalkane.
Chlorination of neopentane is given as:

Hence, this reaction yields only one mono chloroalkane. Therefore we can say that option (D) is correct.
Note:
Halogenation is a reaction that happens when addition of one or more halogens is done to an alkane. In the periodic table, examples of halogens are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, etc. The substance that is formed from a halogenation reaction is known as a halogenated compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




