
On a straight line passing through the foot of the tower, two points C and D are at distances of 4 m and 16 m from the foot respectively. If the angles of elevation from C and D of the top of the tower are complementary, then find the height of the tower.
Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint: Use the formula for tangent of an angle,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{Opposite\,side}{Adjacent\,side}\]
Use properties of complementary angles. Complementary angles are angles that sum up to \[{{90}^{\circ }}\]. Let, A and B be two angles, they are said to be complementary angles of each other if$A+B={{90}^{\circ }}$.
Use the trigonometric formula, \[\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }\]
Draw diagrams for ease of understanding the question.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given, two points C and D are at distances of 4 m and 16 m from the foot respectively. We are also given that the angles of elevation from C and D of the top of the tower are complementary.
We are asked to find the height of the tower.
Taking AB to be the tower mentioned in the question (with a height $h$ ),
We can represent the scenario as,
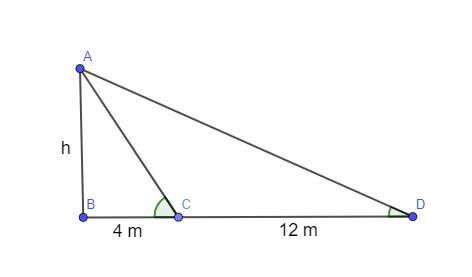
Here, \[\angle C\]and \[\angle D\] are complementary angles.
Hence,
\[\angle C={{90}^{\circ }}-\angle D\ and\,\angle D={{90}^{\circ }}-\angle C\]
From\[\Delta ABC\],
We know that \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{Opposite\,side}{Adjacent\,side}\]
\[\therefore \tan C=\dfrac{h}{4}\,...............(1)\]
From \[\Delta ABD\],
We know that \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{Opposite\,side}{Adjacent\,side}\]
\[\tan D=\tan ({{90}^{\circ }}-C)=\dfrac{h}{12+4}\]
\[\cot C=\dfrac{h}{16}..............(2)\]
We know the trigonometric equation,
\[\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }\]
Hence, using this trigonometric equation, equation (2) becomes,
\[\tan C=\dfrac{16}{h}..............(3)\]
On equating equation (1) and (2), we obtain,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{16}{h}=\dfrac{h}{4} \\
& \\
\end{align}\]
On cross-multiplying,
\[\begin{align}
& {{h}^{2}}=64 \\
& \\
\end{align}\]
On taking square root of both the side,
\[h=\pm 8\]
Since, measurement of lengths cannot be a negative value, we reject the value of \[h=-8\].
\[\therefore h=8m\]
Hence, the height of the tower is 8m.
Note:
The same question could have been asked keeping the distance of points from the foot of the perpendicular as unknowns and to find those distances (Height would be given in this case). Nevertheless, the method would remain the same.
You have to keep in mind the difference between angle of elevation and angle of depression. Do not confuse it with each other.
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{Opposite\,side}{Adjacent\,side}\]
Use properties of complementary angles. Complementary angles are angles that sum up to \[{{90}^{\circ }}\]. Let, A and B be two angles, they are said to be complementary angles of each other if$A+B={{90}^{\circ }}$.
Use the trigonometric formula, \[\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }\]
Draw diagrams for ease of understanding the question.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given, two points C and D are at distances of 4 m and 16 m from the foot respectively. We are also given that the angles of elevation from C and D of the top of the tower are complementary.
We are asked to find the height of the tower.
Taking AB to be the tower mentioned in the question (with a height $h$ ),
We can represent the scenario as,

Here, \[\angle C\]and \[\angle D\] are complementary angles.
Hence,
\[\angle C={{90}^{\circ }}-\angle D\ and\,\angle D={{90}^{\circ }}-\angle C\]
From\[\Delta ABC\],
We know that \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{Opposite\,side}{Adjacent\,side}\]
\[\therefore \tan C=\dfrac{h}{4}\,...............(1)\]
From \[\Delta ABD\],
We know that \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{Opposite\,side}{Adjacent\,side}\]
\[\tan D=\tan ({{90}^{\circ }}-C)=\dfrac{h}{12+4}\]
\[\cot C=\dfrac{h}{16}..............(2)\]
We know the trigonometric equation,
\[\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }\]
Hence, using this trigonometric equation, equation (2) becomes,
\[\tan C=\dfrac{16}{h}..............(3)\]
On equating equation (1) and (2), we obtain,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{16}{h}=\dfrac{h}{4} \\
& \\
\end{align}\]
On cross-multiplying,
\[\begin{align}
& {{h}^{2}}=64 \\
& \\
\end{align}\]
On taking square root of both the side,
\[h=\pm 8\]
Since, measurement of lengths cannot be a negative value, we reject the value of \[h=-8\].
\[\therefore h=8m\]
Hence, the height of the tower is 8m.
Note:
The same question could have been asked keeping the distance of points from the foot of the perpendicular as unknowns and to find those distances (Height would be given in this case). Nevertheless, the method would remain the same.
You have to keep in mind the difference between angle of elevation and angle of depression. Do not confuse it with each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




