
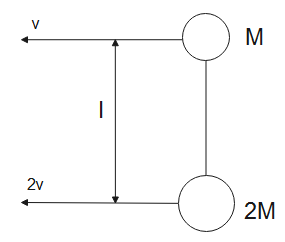
On a smooth level ground we keep a light rod to which 2 masses M and 2M are attached. The velocity of these masses at the moment is shown here choose the INCORRECT statement.
(A). the velocities of masses remain constant
(B). the angular velocities of the rod is $\dfrac{v}{l}$ clockwise
(C). the rod is under tension
(D). the centre of mass will move in a straight line

Answer
558k+ views
Hint: When an object moves across a rough surface it decelerates due to the force of friction, which reduces the speed of the object until it has completed its course over the rough surface. When the object crosses onto the smooth surface it no longer decelerates.
Formulas used:
$v=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
Complete step by step solution:
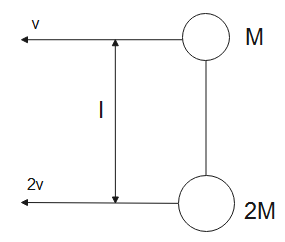
Given, two masses $M$ and $2M$ are attached to a light rod kept on a smooth surface. The velocities of the masses are $v$ and $2v$ respectively. The formula for velocity of centre of mass is-
$v=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
Here, ${{m}_{1}}$ and ${{m}_{2}}$ are masses of the bodies
${{v}_{1}}$ and ${{v}_{2}}$ are their velocities
In the above equation we substitute values to get,
$\begin{align}
& v'=\dfrac{M\times v+2M\times 2v}{M+2M} \\
& \Rightarrow v'=\dfrac{3Mv}{3M} \\
& \therefore v'=v \\
\end{align}$
The velocity of centre of mass is $v$.
The angular velocity is $\omega =\dfrac{v}{l}$.
As the system is moving in a straight line, the centre of mass will also move in a straight line. The rod is under tension because of the normal forces acting between the rods and masses.
No external forces are acting on the system but there are internal forces like normal reaction between rods and masses due to which the velocities of the masses will change but the momentum of the system will be conserved.
Therefore, the velocities of the masses will not remain constant, so it is the incorrect statement. Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: Normal reaction acts between two bodies in order to prevent them from passing through each other. It acts perpendicular to the surfaces. Since the system is isolated, the velocity of the centre of mass will remain constant. The position of centre of mass will lie more towards the heavier body.
Formulas used:
$v=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
Complete step by step solution:

Given, two masses $M$ and $2M$ are attached to a light rod kept on a smooth surface. The velocities of the masses are $v$ and $2v$ respectively. The formula for velocity of centre of mass is-
$v=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
Here, ${{m}_{1}}$ and ${{m}_{2}}$ are masses of the bodies
${{v}_{1}}$ and ${{v}_{2}}$ are their velocities
In the above equation we substitute values to get,
$\begin{align}
& v'=\dfrac{M\times v+2M\times 2v}{M+2M} \\
& \Rightarrow v'=\dfrac{3Mv}{3M} \\
& \therefore v'=v \\
\end{align}$
The velocity of centre of mass is $v$.
The angular velocity is $\omega =\dfrac{v}{l}$.
As the system is moving in a straight line, the centre of mass will also move in a straight line. The rod is under tension because of the normal forces acting between the rods and masses.
No external forces are acting on the system but there are internal forces like normal reaction between rods and masses due to which the velocities of the masses will change but the momentum of the system will be conserved.
Therefore, the velocities of the masses will not remain constant, so it is the incorrect statement. Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: Normal reaction acts between two bodies in order to prevent them from passing through each other. It acts perpendicular to the surfaces. Since the system is isolated, the velocity of the centre of mass will remain constant. The position of centre of mass will lie more towards the heavier body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




