
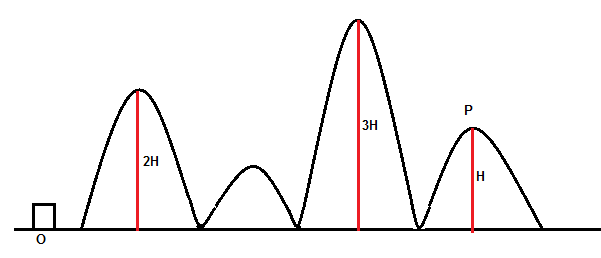
On a smooth curved track shown in the diagram, a small particle is projected from the point O, and that it just manages to reach the point P. Assume that particles always remain in contact with the track. The velocity of the particle on reaching the point P will be equal to:
(A) $ zero $
(B) $ \sqrt {2gH} $
(C) $ \sqrt {6gH} $
(D) $ \sqrt {4gH} $

Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint :O is the given particle as shown in the figure, it moves along the described trajectory and it is in contact with the track. We have to find out the velocity of particle O to reach the particle at the position named as P in the figure. Here we have the height of the particle at a different position and P is at the height $ H $ . Let us use the concept of kinetic energy to be used here.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here, the particle should have the initial velocity such that the particle should reach the maximum height $ 3H $ and velocity $ v = 0 $ at the highest point.
Now, here it is known that the point P is at the height of $ H $ and we have to consider the velocity at point P as $ {v_p} $ .
From this information we can be able to find out the work done by the gravity from highest point to Point P, such that $ {W_g} $ is given by
$ {W_g} = 2mg(3H - H) $
$ \Rightarrow {W_g} = 2mgH $
Since, here on particle O the gravity is acting so we have to use the work energy theorem to find out the velocity of O at point P.
Applying, work energy theorem, we get
$ \Delta K.E. = {W_g} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{m}{2}(v_p^2 - {0^2}) = 2mgH $ (here, we have to use initial and final velocities of the particle)
$ \Rightarrow v_p^2 = 4gH $
$ \Rightarrow {v_p} = \sqrt {4gH} $
Hence, velocity of particle at point P is $ \sqrt {4gH} $ .
Thus, the correct option is D.
Note :
We have used the concept of work energy theorem as we observed that the work done here is under the influence of gravity and we have initial and final velocities of the particle. The formula we used here was: $ \Delta K.E. = {W_g} \Rightarrow \dfrac{m}{2}(velocity_{final}^2 - velocity_{initial}^2) = {W_g} $ .
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here, the particle should have the initial velocity such that the particle should reach the maximum height $ 3H $ and velocity $ v = 0 $ at the highest point.
Now, here it is known that the point P is at the height of $ H $ and we have to consider the velocity at point P as $ {v_p} $ .
From this information we can be able to find out the work done by the gravity from highest point to Point P, such that $ {W_g} $ is given by
$ {W_g} = 2mg(3H - H) $
$ \Rightarrow {W_g} = 2mgH $
Since, here on particle O the gravity is acting so we have to use the work energy theorem to find out the velocity of O at point P.
Applying, work energy theorem, we get
$ \Delta K.E. = {W_g} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{m}{2}(v_p^2 - {0^2}) = 2mgH $ (here, we have to use initial and final velocities of the particle)
$ \Rightarrow v_p^2 = 4gH $
$ \Rightarrow {v_p} = \sqrt {4gH} $
Hence, velocity of particle at point P is $ \sqrt {4gH} $ .
Thus, the correct option is D.
Note :
We have used the concept of work energy theorem as we observed that the work done here is under the influence of gravity and we have initial and final velocities of the particle. The formula we used here was: $ \Delta K.E. = {W_g} \Rightarrow \dfrac{m}{2}(velocity_{final}^2 - velocity_{initial}^2) = {W_g} $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




