
On a linear escalator running between two points A and B, a boy takes time\[{{t}_{1}}\], to move from A to B, if the boy runs with a constant speed on the escalator. If the boy runs from B to A, he takes time\[{{t}_{2}}\] to reach B to A. The time taken by the boy to move from A to B if he stands still on the escalator will be (The escalator moves from A to B)
\[\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. }\dfrac{{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}{{{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}} \\
& \text{B}\text{. }\dfrac{2{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}{{{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}} \\
& \text{C}\text{. }\dfrac{t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}}{{{t}_{2}}{{t}_{1}}} \\
& \text{D}\text{. }\dfrac{t_{1}^{2}-t_{2}^{2}}{{{t}_{2}}{{t}_{1}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: For the given question we have to find the time taken by a boy standing still on the escalator to cover a distance from A to B when time taken by a boy running on escalator from A to B and B to A is given. So we need to find the time the escalator takes moving from A to B. By using the formula of time given as distance divided by speed we can solve the given question.
Formula used:
\[\text{time=}\dfrac{\text{distance}}{\text{speed}}\]
Complete answer:
Let us assume that the distance from A to B is d. Now according to data given a boy is running from A to B with constant speed, say u. He covers the distance d in time \[{{t}_{1}}\]. Also the escalator is moving from A to B with some constant speed, say v. So the actual speed with which the boy covers the distance will be \[u+v\]. Because the boy and the escalator are moving in the same direction, the speed of the escalator is added with the speed of the boy. Below is the diagram to show distance and the movement of the boy in direction A to B and B to A.
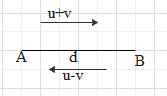
We know time is given as ratio of distance to speed, hence we can write \[{{t}_{1}}\]in terms of d, u and v as given below
\[{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{d}{u+v}\text{ }...................\text{(i)}\]
Now the boy runs back from B to A and time taken to cover the distance d is \[{{t}_{2}}\]as now he is moving in the opposite direction of the motion of the escalator (escalator moves from A to B). The speed of the boy and the escalator will be the same but the actual speed with which he covers distance d now will be \[u-v\]. Because the boy and the escalator are moving in opposite directions, the speed of the escalator is subtracted from the speed of the boy.
So we can write \[{{t}_{2}}\] as follows
\[{{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{d}{u-v}\text{ }...................\text{(ii)}\]
Here we have to find the time taken by the boy to cover distance d moving from A to B when he stands still on the escalator that means his speed will be zero. Therefore time taken by boy will be equal to time taken by escalator which will be given as
\[t=\dfrac{d}{v}\text{ }.................\text{(iii)}\]
Now we want t in terms of \[{{t}_{1}}\text{ and }{{t}_{2}}\], so let us subtract equation (i) from equation (ii) we get
\[\begin{align}
& {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{d}{u-v}-\dfrac{d}{u+v} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{d(u+v)-d(u-v)}{(u-v)(u+v)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{d(u+v-u+v)}{(u-v)(u+v)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{2dv}{{{d}^{2}}}}{\dfrac{(u-v)(u+v)}{{{d}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{2v}{d}}{\left[ \dfrac{(u-v)}{d} \right]\left[ \dfrac{(u+v)}{d} \right]} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{2}{t}}{\dfrac{1}{{{t}_{2}}}\dfrac{1}{{{t}_{1}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{2{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}{t} \\
& \Rightarrow t=\dfrac{2{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}{{{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}} \\
\end{align}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
The boy took different time covering the same distance because he is moving with respect to the escalator which is also in motion. Also in the first case he is moving in the same direction whereas in other cases he is moving in the opposite direction with respect to the escalator due to which time taken is changed.
Formula used:
\[\text{time=}\dfrac{\text{distance}}{\text{speed}}\]
Complete answer:
Let us assume that the distance from A to B is d. Now according to data given a boy is running from A to B with constant speed, say u. He covers the distance d in time \[{{t}_{1}}\]. Also the escalator is moving from A to B with some constant speed, say v. So the actual speed with which the boy covers the distance will be \[u+v\]. Because the boy and the escalator are moving in the same direction, the speed of the escalator is added with the speed of the boy. Below is the diagram to show distance and the movement of the boy in direction A to B and B to A.

We know time is given as ratio of distance to speed, hence we can write \[{{t}_{1}}\]in terms of d, u and v as given below
\[{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{d}{u+v}\text{ }...................\text{(i)}\]
Now the boy runs back from B to A and time taken to cover the distance d is \[{{t}_{2}}\]as now he is moving in the opposite direction of the motion of the escalator (escalator moves from A to B). The speed of the boy and the escalator will be the same but the actual speed with which he covers distance d now will be \[u-v\]. Because the boy and the escalator are moving in opposite directions, the speed of the escalator is subtracted from the speed of the boy.
So we can write \[{{t}_{2}}\] as follows
\[{{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{d}{u-v}\text{ }...................\text{(ii)}\]
Here we have to find the time taken by the boy to cover distance d moving from A to B when he stands still on the escalator that means his speed will be zero. Therefore time taken by boy will be equal to time taken by escalator which will be given as
\[t=\dfrac{d}{v}\text{ }.................\text{(iii)}\]
Now we want t in terms of \[{{t}_{1}}\text{ and }{{t}_{2}}\], so let us subtract equation (i) from equation (ii) we get
\[\begin{align}
& {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{d}{u-v}-\dfrac{d}{u+v} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{d(u+v)-d(u-v)}{(u-v)(u+v)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{d(u+v-u+v)}{(u-v)(u+v)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{2dv}{{{d}^{2}}}}{\dfrac{(u-v)(u+v)}{{{d}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{2v}{d}}{\left[ \dfrac{(u-v)}{d} \right]\left[ \dfrac{(u+v)}{d} \right]} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{2}{t}}{\dfrac{1}{{{t}_{2}}}\dfrac{1}{{{t}_{1}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{2{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}{t} \\
& \Rightarrow t=\dfrac{2{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}{{{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}} \\
\end{align}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
The boy took different time covering the same distance because he is moving with respect to the escalator which is also in motion. Also in the first case he is moving in the same direction whereas in other cases he is moving in the opposite direction with respect to the escalator due to which time taken is changed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




