
On a bright sunny day, a diver of height $h$ stands at the bottom of a lake of depth $H$. Looking upward, he can see objects outside the lake in a circular region of radius $R$. Beyond this circle he sees the images of objects lying on the floor of the lake. If refractive index of water is $\dfrac{4}{3}$, then the value of $R$ is:
A. $3\left( {H - h} \right)/\sqrt 7 $
B. $\left( {H - h} \right)/\sqrt {7/3} $
C. $3h\sqrt 7 $
D. $3\left( {H - h} \right)/\sqrt {5/3} $
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Here first we have to assume and draw the observations given in the question, and then we have to find the critical angle to and use snell’s law to get the radius $R$
Complete step by step solution:
First let us see what refractive index is:
Refractive index is the ratio between the speed of light in vacuum and its speed in a given medium.
The refractive index does not have any dimension. It is a ratio representing the number of times slower a light wave would be in the given material than it is in a vacuum. The velocity of light in vacuum divided by the velocity of light in the medium is the refractive index.
Now let us observe the points given in the question.
Height of the diver $ = h$
Height of the lake $ = H$
Radius outside the lake $ = R$
Refractive index of water $ = \dfrac{4}{3}$
It is given that a diver of height $h$ stands at the bottom of a lake of depth $H$. Looking upward, he can see objects outside the lake in a circular region of radius $R$. Beyond this circle he sees the images of objects lying on the floor of the lake.
We have to find the value of $R$.
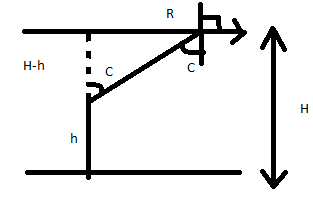
Let C be the critical angle of the refracted image formed with respect to the man.
Applying snell’s law on angle C we get-
$ {\mu _1}\sin C = {\mu _2}\sin {90^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}\sin C = 1 \times 1 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}\sin C = 1 \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \dfrac{3}{4} \\
$
(refractive index of ${\mu _1} = \dfrac{4}{3}$ and ${\mu _2} = 1$)
Therefore, $\tan C = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 7 }}$
From the figure we can see
Also,
$
\tan C = \dfrac{R}{{H - h}} \\
\dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 7 }} = \dfrac{R}{{H - h}} \\
R = \dfrac{{3\left( {H - h} \right)}}{{\sqrt 7 }} \\
$
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: Here we have to observe and assume how light is refracted in the figure with respect to the man. Also we have to keep in mind what snell’s law is and how it affects the refractive index.
Complete step by step solution:
First let us see what refractive index is:
Refractive index is the ratio between the speed of light in vacuum and its speed in a given medium.
The refractive index does not have any dimension. It is a ratio representing the number of times slower a light wave would be in the given material than it is in a vacuum. The velocity of light in vacuum divided by the velocity of light in the medium is the refractive index.
Now let us observe the points given in the question.
Height of the diver $ = h$
Height of the lake $ = H$
Radius outside the lake $ = R$
Refractive index of water $ = \dfrac{4}{3}$
It is given that a diver of height $h$ stands at the bottom of a lake of depth $H$. Looking upward, he can see objects outside the lake in a circular region of radius $R$. Beyond this circle he sees the images of objects lying on the floor of the lake.
We have to find the value of $R$.

Let C be the critical angle of the refracted image formed with respect to the man.
Applying snell’s law on angle C we get-
$ {\mu _1}\sin C = {\mu _2}\sin {90^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}\sin C = 1 \times 1 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}\sin C = 1 \\
\Rightarrow \sin C = \dfrac{3}{4} \\
$
(refractive index of ${\mu _1} = \dfrac{4}{3}$ and ${\mu _2} = 1$)
Therefore, $\tan C = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 7 }}$
From the figure we can see
Also,
$
\tan C = \dfrac{R}{{H - h}} \\
\dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 7 }} = \dfrac{R}{{H - h}} \\
R = \dfrac{{3\left( {H - h} \right)}}{{\sqrt 7 }} \\
$
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: Here we have to observe and assume how light is refracted in the figure with respect to the man. Also we have to keep in mind what snell’s law is and how it affects the refractive index.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




