
Ohm’s law is applicable to –
A) Diode
B) Transistor
C) Electrolyte
D) Conductor
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: We need to understand the use of Ohm’s law and its relation with the material under consideration. The Ohm’s law is a direct relation between the potential drop of a resistor and the current flowing through it. We need to compare these for each quantity.
Complete answer:
The Ohm’s law is one of the most basic laws in current electricity. It relates the potential difference of a resistor to the current flowing through it. According to Ohm’s law, the potential difference across a resistor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it. It is mathematically given as –
\[\begin{align}
& V\propto I \\
& \Rightarrow V=IR \\
\end{align}\]
Where, V is the potential drop, I is the current and R is the resistance of the resistor.
We know from the equation that the V-I characteristics for a material which obeys Ohm’s law must have a straight-line graph with the slope equal to the resistance as shown below.
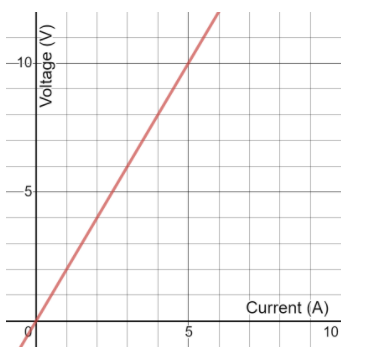
The above graph shows the V-I characteristics of a \[2\Omega \] resistor.
We know that this characteristic is only observed for Ohmic materials which are conductors.
We can compare the V-I characteristics of a diode, transistor and an electrolyte to prove this.
For diode: The V-I characteristic of diode is given below.
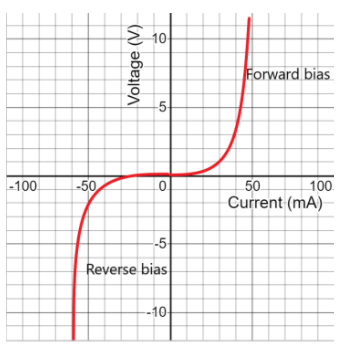
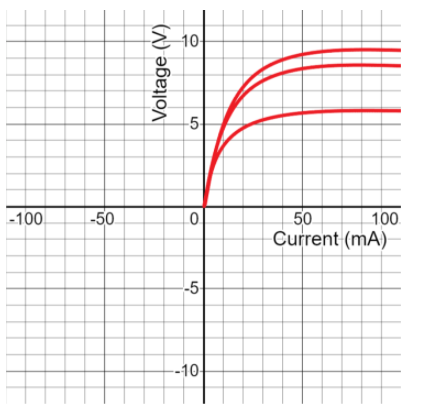
For transistor: The below is the output characteristics of a transistor. The input characteristics are similar to the diode characteristics.
The V-I relation in electrolytes is not linear and therefore, doesn’t obey Ohm’s law.
The conductors are the materials which obey the Ohm’s law.
The correct answer is option D.
Note:
The conductors, generally called as resistors, follow Ohm's law to a great-extend. They tend to deviate from the linear condition when the temperature becomes too much higher than normal conditions. Most of the conductors are Ohmic in normal conditions.
Complete answer:
The Ohm’s law is one of the most basic laws in current electricity. It relates the potential difference of a resistor to the current flowing through it. According to Ohm’s law, the potential difference across a resistor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it. It is mathematically given as –
\[\begin{align}
& V\propto I \\
& \Rightarrow V=IR \\
\end{align}\]
Where, V is the potential drop, I is the current and R is the resistance of the resistor.
We know from the equation that the V-I characteristics for a material which obeys Ohm’s law must have a straight-line graph with the slope equal to the resistance as shown below.

The above graph shows the V-I characteristics of a \[2\Omega \] resistor.
We know that this characteristic is only observed for Ohmic materials which are conductors.
We can compare the V-I characteristics of a diode, transistor and an electrolyte to prove this.
For diode: The V-I characteristic of diode is given below.

For transistor: The below is the output characteristics of a transistor. The input characteristics are similar to the diode characteristics.

The V-I relation in electrolytes is not linear and therefore, doesn’t obey Ohm’s law.
The conductors are the materials which obey the Ohm’s law.
The correct answer is option D.
Note:
The conductors, generally called as resistors, follow Ohm's law to a great-extend. They tend to deviate from the linear condition when the temperature becomes too much higher than normal conditions. Most of the conductors are Ohmic in normal conditions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




