
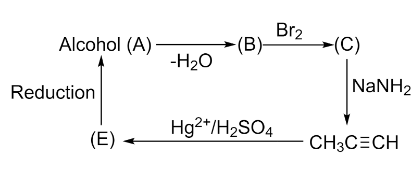
Observe the following sequence of reactions and find the structure of A.

Answer
535.5k+ views
Hint: An alkyne reacts with the ${{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{4}}$ in presence of $\text{H}{{\text{g}}^{2+}}$ catalyst to form an enol product which tautomerizes to produce a ketone. The ketone on further reduction yields alcohol.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To identify the structure of A we need to follow the sequence provided. Let’s start with the known compound given in the sequence, that is, propyne.
Propyne undergoes hydration reaction when reacts with ${{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{4}}$ in the presence of $\text{H}{{\text{g}}^{2+}}$ catalyst following Markovnikov’s rule and forms a ketone after tautomerization. According to Markovnikov’s rule, the hydrogen gets attached to the triply bonded carbon in an alkene that possesses a higher number of H-atoms. The reaction involved in this step is given below:
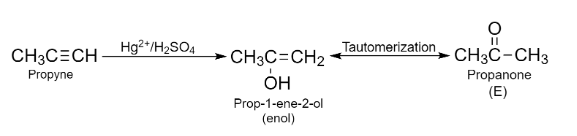
The ketone formed (E) on reduction gives secondary alcohol. So, the propanone on reduction will produce Propan-2-ol.

To check the product formed in the above reaction, we need to write reactions for the further process given in the question.
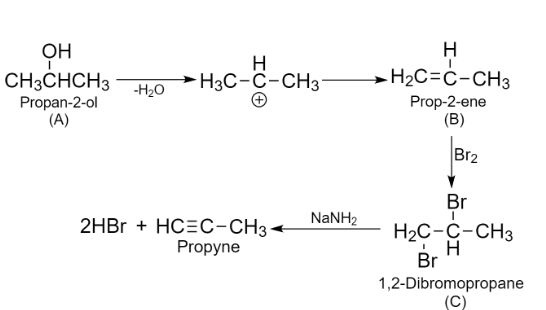
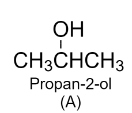
Here we can see that we end up with the propyne as the product. Hence, compound A is secondary alcohol and its structure is as follows:
Note: Not all alkynes produce ketone upon hydration. There is an exceptional case of ethyne which produces ethanal, an aldehyde, upon hydration. Also, the addition of a bromine molecule to alkene results in the formation of a vicinal dibromide in which bromine atoms get attached to opposite sides of an adjacent carbon atom.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To identify the structure of A we need to follow the sequence provided. Let’s start with the known compound given in the sequence, that is, propyne.
Propyne undergoes hydration reaction when reacts with ${{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{4}}$ in the presence of $\text{H}{{\text{g}}^{2+}}$ catalyst following Markovnikov’s rule and forms a ketone after tautomerization. According to Markovnikov’s rule, the hydrogen gets attached to the triply bonded carbon in an alkene that possesses a higher number of H-atoms. The reaction involved in this step is given below:

The ketone formed (E) on reduction gives secondary alcohol. So, the propanone on reduction will produce Propan-2-ol.

To check the product formed in the above reaction, we need to write reactions for the further process given in the question.

Here we can see that we end up with the propyne as the product. Hence, compound A is secondary alcohol and its structure is as follows:

Note: Not all alkynes produce ketone upon hydration. There is an exceptional case of ethyne which produces ethanal, an aldehyde, upon hydration. Also, the addition of a bromine molecule to alkene results in the formation of a vicinal dibromide in which bromine atoms get attached to opposite sides of an adjacent carbon atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




