
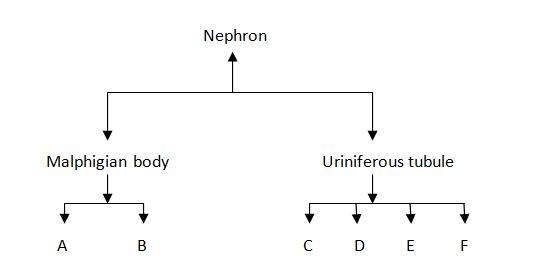
Observe the chart depicting the structure of a nephron.
(i) Mention the structures A to F
(ii) Explain the main function of a nephron.

Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: The renal corpuscle and the renal tubule consist of the nephron. For filtration, excretion and resorption, the nephron is responsible. It filters out small plasma molecules, reabsorbs much of the water and some of the molecules selectively, and even secrete some secretory compounds into the filtrate.
Complete answer:
A. Glomerulus - The blood from the afferent arteriole joins and travels into the efferent arteriole.
B. Capsule Bowman's
C. Convoluted Tubule Proximal
D. Henle Loop
E. Distal Tubule Convoluted
F. The Apparatus of the Juxtaglomerular (JGA)
The basic purpose of the nephron is to pump the blood and extract excess substances for different biochemical processes while maintaining important substances. The nephron may also affect the pH (acid-base balance) of the blood in the process, stabilize blood pressure, maintain the volume of blood and monitor the amount of electrolytes in the fluids of the body.
With regard to each component, the roles of the nephron can be discussed:
Bowman's Capsule - The incoming fluid from the glomerular capillaries is extracted.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule- Reabsorbing salt, potassium, water, glucose and amino acids (removed from the tubules). Acids and bases are secreted into the proximal tubule, such as bile salts, oxalate along with uric acid.
Henle's loop- In the descending limb and the thin portion of the ascending limb, water is mostly reabsorbed.
The thick section of the ascending limb deliberately reabsorbs sodium, calcium, chloride, magnesium and potassium.
Distal convoluted tubule- It regulates the blood supply of the nephron to which it corresponds through the glomerular capillaries and glomerular filtration. Reabsorption of sodium, potassium and chloride. Reabsorption of sodium, potassium and chloride. Secretion of hydrogen ions.
Note: Kidneys play an important role in osmoregulation by controlling the volume of water reabsorbed from glomerular filtrate in renal tubules, which is mediated by hormones such as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), aldosterone, and angiotensin II, the kidneys play a very significant role in human osmoregulation.
Complete answer:
A. Glomerulus - The blood from the afferent arteriole joins and travels into the efferent arteriole.
B. Capsule Bowman's
C. Convoluted Tubule Proximal
D. Henle Loop
E. Distal Tubule Convoluted
F. The Apparatus of the Juxtaglomerular (JGA)
The basic purpose of the nephron is to pump the blood and extract excess substances for different biochemical processes while maintaining important substances. The nephron may also affect the pH (acid-base balance) of the blood in the process, stabilize blood pressure, maintain the volume of blood and monitor the amount of electrolytes in the fluids of the body.
With regard to each component, the roles of the nephron can be discussed:
Bowman's Capsule - The incoming fluid from the glomerular capillaries is extracted.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule- Reabsorbing salt, potassium, water, glucose and amino acids (removed from the tubules). Acids and bases are secreted into the proximal tubule, such as bile salts, oxalate along with uric acid.
Henle's loop- In the descending limb and the thin portion of the ascending limb, water is mostly reabsorbed.
The thick section of the ascending limb deliberately reabsorbs sodium, calcium, chloride, magnesium and potassium.
Distal convoluted tubule- It regulates the blood supply of the nephron to which it corresponds through the glomerular capillaries and glomerular filtration. Reabsorption of sodium, potassium and chloride. Reabsorption of sodium, potassium and chloride. Secretion of hydrogen ions.
Note: Kidneys play an important role in osmoregulation by controlling the volume of water reabsorbed from glomerular filtrate in renal tubules, which is mediated by hormones such as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), aldosterone, and angiotensin II, the kidneys play a very significant role in human osmoregulation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




