
Object A is completely immersed in water. True weight of object A is ${W_A}$, weight of water with beaker is ${W_B}$ . Let B be the buoyant force. ${W_1}$ and ${W_2}$ are scale reading of spring balance and weighing scale respectively:
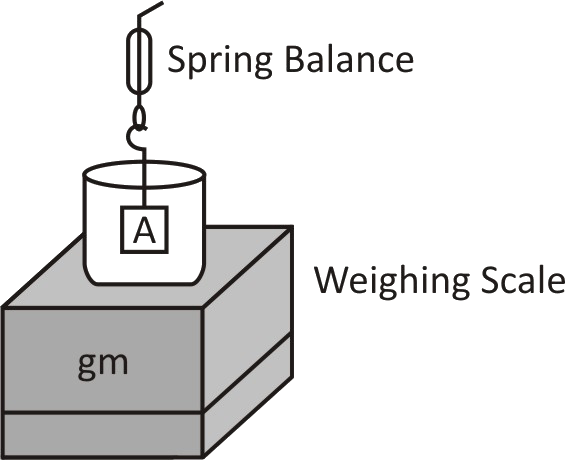
A. ${W_1} = {W_A}$
B. ${W_1} = {W_A} + B$
C. ${W_2} = {W_B}$
D. ${W_2} = {W_B} + B$

Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Here we have to use the relation between true weight and buoyant force and then find the reading of the weighing scale.
The object rises to the surface and floats if the buoyant force is greater than the weight of the object. The object sinks if the buoyant force is less than the weight of the object. The object can remain suspended at its current depth if the buoyant force equals the weight of the object.
Complete step by step answer:
The force that initiates objects to float is buoyancy. It is the force that is exerted on an object partially or entirely immersed in a fluid. The differences in pressure acting on opposite sides of an object immersed in a static fluid are the cause of buoyancy. It is referred to as the buoyant force as well.
True weight is the specific load of a body which is the amount of the mass and gravitational force following up on it.
Apparent weight is the heaviness of the body when it is inundated in a liquid so it feels a light power which makes its weight lesser than True weight.
Weight loss is the measure of weight reduction by a body when it's submerged in water which is equivalent to the measure of water dislodged by it.
Here scale reading of spring balance is:
$
{W_1} = true\,weight - buoyant\,force \\
= {W_A} - B \\
$
So, scale reading of weighing balance is:
$
{W_2} = weight\,of\,water\,with\,bea\ker + buoyant\,force \\
= {W_B} + B \\
$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Here we have to carefully observe the figure in the question and also see which one is apparent weight and which one is true weight. Also we have to see where buoyant force is added and where it is subtracted.The differences in pressure acting on opposite sides of an object immersed in a static fluid are the cause of buoyancy. It is referred to as the buoyant force as well.
The object rises to the surface and floats if the buoyant force is greater than the weight of the object. The object sinks if the buoyant force is less than the weight of the object. The object can remain suspended at its current depth if the buoyant force equals the weight of the object.
Complete step by step answer:
The force that initiates objects to float is buoyancy. It is the force that is exerted on an object partially or entirely immersed in a fluid. The differences in pressure acting on opposite sides of an object immersed in a static fluid are the cause of buoyancy. It is referred to as the buoyant force as well.
True weight is the specific load of a body which is the amount of the mass and gravitational force following up on it.
Apparent weight is the heaviness of the body when it is inundated in a liquid so it feels a light power which makes its weight lesser than True weight.
Weight loss is the measure of weight reduction by a body when it's submerged in water which is equivalent to the measure of water dislodged by it.
Here scale reading of spring balance is:
$
{W_1} = true\,weight - buoyant\,force \\
= {W_A} - B \\
$
So, scale reading of weighing balance is:
$
{W_2} = weight\,of\,water\,with\,bea\ker + buoyant\,force \\
= {W_B} + B \\
$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Here we have to carefully observe the figure in the question and also see which one is apparent weight and which one is true weight. Also we have to see where buoyant force is added and where it is subtracted.The differences in pressure acting on opposite sides of an object immersed in a static fluid are the cause of buoyancy. It is referred to as the buoyant force as well.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




