
OABC is a rectangle inscribed in a quadrant of a circle of radius \[10\;cm\]. If OA = \[2\sqrt 5 \;cm\]. Find the area of the rectangle.
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: First draw an appropriate diagram for the given question. Use the Pythagoras theorem for the triangle formed by the sides and diagonal of the rectangle and then find the breadth of the rectangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
OABC is a rectangle inscribed in a quadrant of a circle of radius \[10\;cm\]. If OA = \[2\sqrt 5 \;cm\].
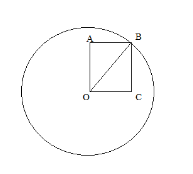
When we are solving this type of question, we need to follow the steps provided in the hint part above.
As we are given OA = \[2\sqrt 5 \;cm\]
In Rectangle \[\angle A = \angle B = \angle C = \angle O = {90^0}\]
So, \[\Delta OAB\]is a Right Angle triangle we can apply to Pythagoras Theorem.
OB = radius of circle that is given
OB = \[10\;cm\]
OA = given
Hypotenuse = OB = \[10\;cm\]
Base = OA = \[2\sqrt 5 \;cm\]
Perpendicular = AB =?
By Pythagoras Theorem
\[{(OB)^2} = {(OA)^2} + {(AB)^2}\]
Substitute OB = \[10\;cm\]and OA = \[2\sqrt 5 \;cm\]
\[
\Rightarrow {(10)^2} = {(2\sqrt 5 )^2} + {(AB)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {(AB)^2} = {(10)^2} - {(2\sqrt 5 )^2} \
= 100 - 20 \\
\Rightarrow {(AB)^2} = 80 \\
\Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {80} = 4\sqrt 5 \;cm \
\]
Now area of rectangle OABC = \[length \times width\]
length = OA
width = OB
$ \Rightarrow $ Area = \[OA{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}AB\]
OA = \[2\sqrt 5 cm\], AB = \[4\sqrt 5 \;cm\]
$ \Rightarrow $ Area = \[2\sqrt 5 \times {\text{4}}\sqrt 5 = 8 \times 5 = 40\;c{m^2}\]
Hence, the area of the rectangle is \[40\;c{m^2}\].
Note: Please take care of the calculations in the Pythagoras theorem to evaluate the square roots and also take care that the diagram is appropriate for the question and one end of the rectangle is on the center of the circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
OABC is a rectangle inscribed in a quadrant of a circle of radius \[10\;cm\]. If OA = \[2\sqrt 5 \;cm\].

When we are solving this type of question, we need to follow the steps provided in the hint part above.
As we are given OA = \[2\sqrt 5 \;cm\]
In Rectangle \[\angle A = \angle B = \angle C = \angle O = {90^0}\]
So, \[\Delta OAB\]is a Right Angle triangle we can apply to Pythagoras Theorem.
OB = radius of circle that is given
OB = \[10\;cm\]
OA = given
Hypotenuse = OB = \[10\;cm\]
Base = OA = \[2\sqrt 5 \;cm\]
Perpendicular = AB =?
By Pythagoras Theorem
\[{(OB)^2} = {(OA)^2} + {(AB)^2}\]
Substitute OB = \[10\;cm\]and OA = \[2\sqrt 5 \;cm\]
\[
\Rightarrow {(10)^2} = {(2\sqrt 5 )^2} + {(AB)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {(AB)^2} = {(10)^2} - {(2\sqrt 5 )^2} \
= 100 - 20 \\
\Rightarrow {(AB)^2} = 80 \\
\Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {80} = 4\sqrt 5 \;cm \
\]
Now area of rectangle OABC = \[length \times width\]
length = OA
width = OB
$ \Rightarrow $ Area = \[OA{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}AB\]
OA = \[2\sqrt 5 cm\], AB = \[4\sqrt 5 \;cm\]
$ \Rightarrow $ Area = \[2\sqrt 5 \times {\text{4}}\sqrt 5 = 8 \times 5 = 40\;c{m^2}\]
Hence, the area of the rectangle is \[40\;c{m^2}\].
Note: Please take care of the calculations in the Pythagoras theorem to evaluate the square roots and also take care that the diagram is appropriate for the question and one end of the rectangle is on the center of the circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





