
Number of oxygen molecules required during glycolysis on glucose molecule is
A. 38
B. 36
C. 2
D. Zero
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: The word glycolysis is composed of two words glycos means sugar and lysis meaning splitting. It is a ten-step process that occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell which breaks glucose (sugar) into pyruvic acid.
Step by step answer:Glycolysis is the process of conversion of glucose into ATP or adenosine triphosphate in a living cell. It is a vital process for all human beings.
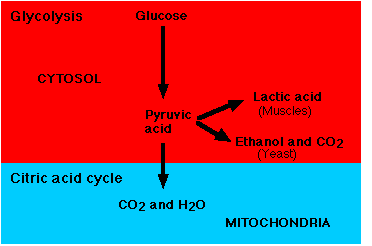
1. In the very first step of glycolysis, the glucose is phosphorylated at the ${C_6}$ carbon. The process includes the transfer of phosphate from the ATP to glucose, making the Glucose-6-phosphate in the presence of the enzymes hexokinase and glucokinase. In this step, energy is lost.
2. In the next step, Glucose 6-phosphate is reversibly isomerized to fructose 6-phosphate by the enzyme phosphohexoisomerase. This happens by the shift of the carbonyl oxygen from ${C_1}$to\[{{\text{C}}_2}\] which converts an aldose into a ketose.
3. In the next step, fructose-6-phosphate is converted into fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate in the presence of the enzyme called phosphofructokinase. Again, the energy is lost in the form of ATP.
4. In the next step, fructose diphosphate aldolase, an enzyme, cleaves of fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate. The bond between C3 and C4 is broken. This results in two glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
5. In the successive step, dihydroxyacetone phosphate isomerizes into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate instead in the presence of triose phosphate isomerase. The glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is converted into 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate by the enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. In this process,\[{\text{NA}}{{\text{D}}^ + }\] gets reduced to NADH by the \[{{\text{H}}^-}\] given by glyceraldehydes 3-phosphate. Two NADH is produced in this step.
6. In the next step, transfer of phosphate group from the 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP by the enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase takes place, thus producing 2 ATP molecules and 3-phosphoglycerate. The 3-phosphoglycerate gets converted into 2-phosphoglycerate due to the shift of phosphoryl group from ${C_3}$to ${C_2}$ which is facilitated by the enzyme phosphoglycerate mutase.
7. In the next step, dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate takes place in the presence of phosphopyruvate hydratase.
8. In the very last step, phosphoenolpyruvate changes into an enol form of pyruvate using the enzyme pyruvate kinase. The enol pyruvate rearranges quickly to form keto form of pyruvate. The enzyme facilitates the transfer of the phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP, thus generating ATP.
So the process of glycolysis does not require any oxygen.
Hence option D is correct.
Note: The equation of glycolysis is : \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}} + {\text{2ADP}} + {\text{2Pi}} + {\text{ 2NA}}{{\text{D}}^ + } \to {\text{2}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} + {\text{2ATP}} + {\text{2NADH}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}^ + }\], where \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\] is chemical formula of glucose, \[{\text{ADP}}\] is the chemical compound adenosine phosphate, \[{\text{Pi }}\] is phosphate, is Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\] is pyruvate, \[{\text{NADH}}\] is Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
Step by step answer:Glycolysis is the process of conversion of glucose into ATP or adenosine triphosphate in a living cell. It is a vital process for all human beings.

1. In the very first step of glycolysis, the glucose is phosphorylated at the ${C_6}$ carbon. The process includes the transfer of phosphate from the ATP to glucose, making the Glucose-6-phosphate in the presence of the enzymes hexokinase and glucokinase. In this step, energy is lost.
2. In the next step, Glucose 6-phosphate is reversibly isomerized to fructose 6-phosphate by the enzyme phosphohexoisomerase. This happens by the shift of the carbonyl oxygen from ${C_1}$to\[{{\text{C}}_2}\] which converts an aldose into a ketose.
3. In the next step, fructose-6-phosphate is converted into fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate in the presence of the enzyme called phosphofructokinase. Again, the energy is lost in the form of ATP.
4. In the next step, fructose diphosphate aldolase, an enzyme, cleaves of fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate. The bond between C3 and C4 is broken. This results in two glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
5. In the successive step, dihydroxyacetone phosphate isomerizes into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate instead in the presence of triose phosphate isomerase. The glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is converted into 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate by the enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. In this process,\[{\text{NA}}{{\text{D}}^ + }\] gets reduced to NADH by the \[{{\text{H}}^-}\] given by glyceraldehydes 3-phosphate. Two NADH is produced in this step.
6. In the next step, transfer of phosphate group from the 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP by the enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase takes place, thus producing 2 ATP molecules and 3-phosphoglycerate. The 3-phosphoglycerate gets converted into 2-phosphoglycerate due to the shift of phosphoryl group from ${C_3}$to ${C_2}$ which is facilitated by the enzyme phosphoglycerate mutase.
7. In the next step, dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate takes place in the presence of phosphopyruvate hydratase.
8. In the very last step, phosphoenolpyruvate changes into an enol form of pyruvate using the enzyme pyruvate kinase. The enol pyruvate rearranges quickly to form keto form of pyruvate. The enzyme facilitates the transfer of the phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP, thus generating ATP.
So the process of glycolysis does not require any oxygen.
Hence option D is correct.
Note: The equation of glycolysis is : \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}} + {\text{2ADP}} + {\text{2Pi}} + {\text{ 2NA}}{{\text{D}}^ + } \to {\text{2}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} + {\text{2ATP}} + {\text{2NADH}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}^ + }\], where \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\] is chemical formula of glucose, \[{\text{ADP}}\] is the chemical compound adenosine phosphate, \[{\text{Pi }}\] is phosphate, is Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\] is pyruvate, \[{\text{NADH}}\] is Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




