
What is the number of ${{H}_{2}}O$ molecules surrounded by each water molecule of ice through hydrogen bonds?
Answer
575.4k+ views
Hint: In order to know about how many molecules are surrounded by each water molecule, we should first know about the structure of water molecule that how many bonds it can form easily and then, we will come to know about the number of surrounded molecules easily.
Complete answer:
Now , first of let’s discuss what is hydrogen bonding. By the hydrogen bonding, we mean the weak force of attraction between the hydrogen atom and the highly electronegative atom due to which the hydrogen atom becomes partially positively charged while the electronegative atom acquires partial negative charge.
The positively polarized hydrogen of one molecule attracts and is attracted by the negatively polarized electronegative atom of the second molecule.
Now, coming to the structure of the water molecule. A water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to the central metal i.e. the oxygen. We know that the water molecule has $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization and has bent V-shaped geometry. The structure of water molecule is as;
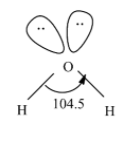
In this, there are two oxygen-hydrogen bonds and two lone pair of electrons are present on the oxygen atom. So, thus it means that the water molecules can form four bonds; two with the hydrogen and two with the lone pair of electrons i.e. the unshared electrons as;
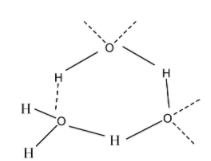
Hence, the number of ${{H}_{2}}O$ molecules surrounded by each water molecule of ice through hydrogen bonds is four.
Note:
There are two conditions for H-bonding. They are as;
1. High electronegativity of the atom:- The atom which is covalently bonded to the hydrogen atom should have high electronegativity so that it can attract the shared electron pair strongly towards itself.
2. Small size of the atom:- The size of the atom bonded to hydrogen atom should be small only then it will be able to develop strong electrostatic interaction with the neighboring molecule.
Complete answer:
Now , first of let’s discuss what is hydrogen bonding. By the hydrogen bonding, we mean the weak force of attraction between the hydrogen atom and the highly electronegative atom due to which the hydrogen atom becomes partially positively charged while the electronegative atom acquires partial negative charge.
The positively polarized hydrogen of one molecule attracts and is attracted by the negatively polarized electronegative atom of the second molecule.
Now, coming to the structure of the water molecule. A water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to the central metal i.e. the oxygen. We know that the water molecule has $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization and has bent V-shaped geometry. The structure of water molecule is as;

In this, there are two oxygen-hydrogen bonds and two lone pair of electrons are present on the oxygen atom. So, thus it means that the water molecules can form four bonds; two with the hydrogen and two with the lone pair of electrons i.e. the unshared electrons as;

Hence, the number of ${{H}_{2}}O$ molecules surrounded by each water molecule of ice through hydrogen bonds is four.
Note:
There are two conditions for H-bonding. They are as;
1. High electronegativity of the atom:- The atom which is covalently bonded to the hydrogen atom should have high electronegativity so that it can attract the shared electron pair strongly towards itself.
2. Small size of the atom:- The size of the atom bonded to hydrogen atom should be small only then it will be able to develop strong electrostatic interaction with the neighboring molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




