
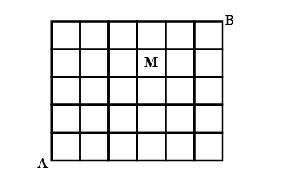
Number of different paths of the shortest distance from A to B in the grid which do not pass through M is,

Answer
558k+ views
Hint:To find the total probability required to cross the path or grid from A to B is by counting the total number of grids both horizontal and vertical and by removing a single line of block from both the vertical and horizontal, column and rows respectively by using the formula as:
\[{}^{\text{Total rows and column}}{{C}_{\text{Number of ways passing through M}}}\].
Complete step by step solution:
The total number of short distance path that can be used when crossing through M is given down below:
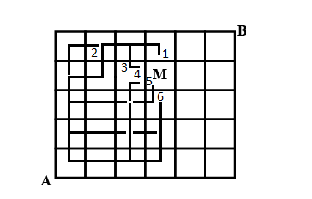
Now as we can see in the above diagram the number of ways the line passes through M to get to B is by six different ways.
To find the total number of ways in which the path from A to B can be taken is first we need to establish the total number of paths without avoiding M.
So let us see that the width and the length of the grid is given as \6\times 6\hence, the total number of paths from A to B is \[6+6=12\]and now the total number of ways while avoiding M is 12-1=11as whenever we will move we will avoid at least one cell at a time either a column cell or a row cell thereby making the total number of paths \[11\].
Therefore, the total number of paths one can take to go from A to B while avoiding M is by using the combination formula of \[{}^{\text{Total rows and column}}{{C}_{\text{Number of ways passing through
M}}}\]:
\[\Rightarrow {}^{11}{{C}_{\text{6}}}=\dfrac{11!}{6!5!}\]
After deducting the factorial value of \[5\] on both numerator and denominator:
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{11\times 10\times 9\times 8\times 7\times 6}{6\times 5\times 4\times 3\times
2\times 1}\]
\[\Rightarrow 462\] ways
Therefore, the total number of ways of crossing from A to B while avoiding M is \[462\] ways.
Note: Another method to solve the question is by permutation method where we use the formula as:
\[{}^{\text{Total rows and column}}{{P}_{\text{Number of ways passing through M}}}\]
And placing the value of total number of rows as \[11\] and total number of ways passing through M as \[6\]. We get the total number of ways passing going from A to B skipping M is:
\[{}^{\text{Total rows and column}}{{P}_{\text{Number of ways passing through M}}}=\dfrac{n!}{\left( n-r \right)!}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{11!}{\left( 11-6 \right)!}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{11!}{5!}=\dfrac{11\times 10\times 9\times 8\times 7}{5\times 4\times 3\times
2\times 1}\]
\[\Rightarrow 462\] ways
Therefore, the total number of ways of crossing from A to B while avoiding M is \[462\] ways.
\[{}^{\text{Total rows and column}}{{C}_{\text{Number of ways passing through M}}}\].
Complete step by step solution:
The total number of short distance path that can be used when crossing through M is given down below:

Now as we can see in the above diagram the number of ways the line passes through M to get to B is by six different ways.
To find the total number of ways in which the path from A to B can be taken is first we need to establish the total number of paths without avoiding M.
So let us see that the width and the length of the grid is given as \6\times 6\hence, the total number of paths from A to B is \[6+6=12\]and now the total number of ways while avoiding M is 12-1=11as whenever we will move we will avoid at least one cell at a time either a column cell or a row cell thereby making the total number of paths \[11\].
Therefore, the total number of paths one can take to go from A to B while avoiding M is by using the combination formula of \[{}^{\text{Total rows and column}}{{C}_{\text{Number of ways passing through
M}}}\]:
\[\Rightarrow {}^{11}{{C}_{\text{6}}}=\dfrac{11!}{6!5!}\]
After deducting the factorial value of \[5\] on both numerator and denominator:
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{11\times 10\times 9\times 8\times 7\times 6}{6\times 5\times 4\times 3\times
2\times 1}\]
\[\Rightarrow 462\] ways
Therefore, the total number of ways of crossing from A to B while avoiding M is \[462\] ways.
Note: Another method to solve the question is by permutation method where we use the formula as:
\[{}^{\text{Total rows and column}}{{P}_{\text{Number of ways passing through M}}}\]
And placing the value of total number of rows as \[11\] and total number of ways passing through M as \[6\]. We get the total number of ways passing going from A to B skipping M is:
\[{}^{\text{Total rows and column}}{{P}_{\text{Number of ways passing through M}}}=\dfrac{n!}{\left( n-r \right)!}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{11!}{\left( 11-6 \right)!}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{11!}{5!}=\dfrac{11\times 10\times 9\times 8\times 7}{5\times 4\times 3\times
2\times 1}\]
\[\Rightarrow 462\] ways
Therefore, the total number of ways of crossing from A to B while avoiding M is \[462\] ways.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




