
Nucleic acids are polymer of:
A. Nucleotides
B. Nucleosides
C. Nuclei of heavy metal
D. Proteins
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint:Chromosomes, the particles responsible for heredity are made up of protein,nucleic acid. Nucleic acids are of two types.
-Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
-Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Complete step by step answer: A nucleic acid is a biopolymer i.e., polymers present in the living system. They are also called as polynucleotides since the repeating structural unit of nucleic acid is a nucleotide. Each nucleotide is made up of three parts i.e., a sugar molecule, a heterocyclic nitrogenous base, and a phosphoric acid. In general, a nucleotide may be represented as shown below:
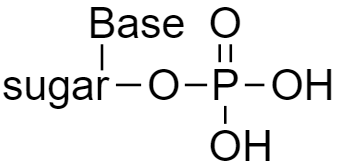
Hence the nucleic acid may be represented as below:
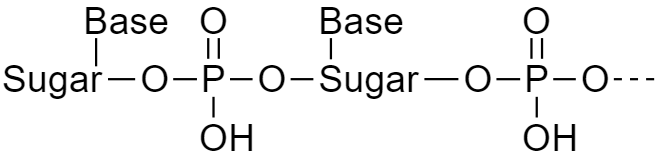
Chemical composition of nucleic acid contains:
-A pentose sugar
-The nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound also called nitrogenous base
-Phosphoric acid
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information: The structure of nucleic acid is discussed at the following two levels:
-Primary structure: The sequence in which the four nitrogen bases are attached to the sugar-phosphate backbone of a nucleotide chain is called the primary structure.
-Secondary structure: Secondary structure of nucleic acid is the set of interactions between bases. In DNA double helix, the two strands of DNA are held together by a hydrogen bond, the nucleotides on one strand base pair with the nucleotide on the other strand. It is responsible for the shape taken by the nucleic acid. In the case of RNA, its secondary structure consists of a single polynucleotide. Base pairing in RNA occurs when RNA folds between the complementarity regions.
Note: There are two different class of nitrogenous base found in nucleic acid:
Purines: the two purines which are most commonly found in nucleic acid are adenine (A) and guanine (G).
Pyrimidines: There are three most commonly occurring pyrimidines in nucleic acid.
-Uracil (U)
-Thymine (T)
-Cytosine (C)
-Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
-Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Complete step by step answer: A nucleic acid is a biopolymer i.e., polymers present in the living system. They are also called as polynucleotides since the repeating structural unit of nucleic acid is a nucleotide. Each nucleotide is made up of three parts i.e., a sugar molecule, a heterocyclic nitrogenous base, and a phosphoric acid. In general, a nucleotide may be represented as shown below:
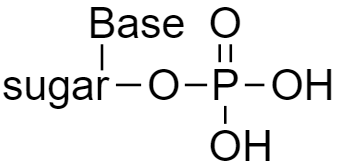
Hence the nucleic acid may be represented as below:
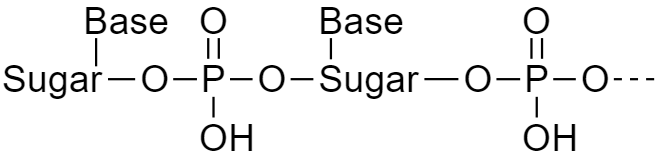
Chemical composition of nucleic acid contains:
-A pentose sugar
-The nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound also called nitrogenous base
-Phosphoric acid
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information: The structure of nucleic acid is discussed at the following two levels:
-Primary structure: The sequence in which the four nitrogen bases are attached to the sugar-phosphate backbone of a nucleotide chain is called the primary structure.
-Secondary structure: Secondary structure of nucleic acid is the set of interactions between bases. In DNA double helix, the two strands of DNA are held together by a hydrogen bond, the nucleotides on one strand base pair with the nucleotide on the other strand. It is responsible for the shape taken by the nucleic acid. In the case of RNA, its secondary structure consists of a single polynucleotide. Base pairing in RNA occurs when RNA folds between the complementarity regions.
Note: There are two different class of nitrogenous base found in nucleic acid:
Purines: the two purines which are most commonly found in nucleic acid are adenine (A) and guanine (G).
Pyrimidines: There are three most commonly occurring pyrimidines in nucleic acid.
-Uracil (U)
-Thymine (T)
-Cytosine (C)
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




