
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation produces
A. \[NA{{D}^{+}}\]
B. NADH
C. NADPH
D. \[NAD{{P}^{+}}\]
Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint: Photophosphorylation is a key process that occurs in the light reaction stage of photosynthesis. It involves the utilization of light energy to convert ADP into ATP. Non-cyclic photophosphorylation occurs when the movement of electrons in noncyclic for production of ATP along with a reduced form of \[NAD{{P}^{+}}\].
Complete answer:
Plants perform photosynthesis for synthesizing ATP molecules which provide energy for growth and development. Photosynthesis occurs in two major stages called light reaction stage and dark reaction stage. The light reaction is marked by the conversion of light energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP. This process utilizes light energy and adds phosphate to ADP to form ATP and hence it is known as photophosphorylation. This process is further of two types called cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
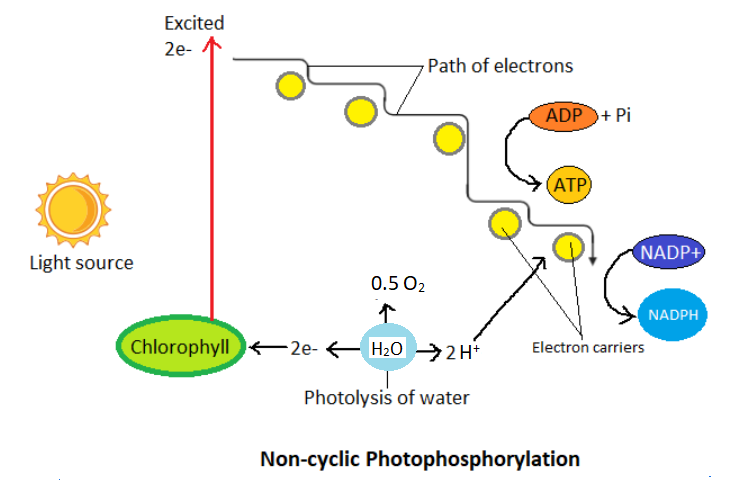
The cyclic photophosphorylation produces only ATP molecules for providing instant energy to plants. The non-cyclic photophosphorylation involves the production of ATP along with NADPH which is a reduced form of \[NAD{{P}^{+}}\]. This occurs through the non-cyclic movement of electrons. The movement of electrons is unidirectional in this process. The electrons combine with \[{{H}^{+}}\] that is obtained due to splitting of water molecules. This results in a reduction of \[NAD{{P}^{+}}\] to NADPH. This process involves both photosystems I and II. \[NAD{{P}^{+}}\] receives electrons from photosystem I. Oxygen is also synthesized as a by-product of the reaction. It is a predominant process in all green plants.
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: The photosystem I is able to absorb light of 700 nm and its active center is P700. Photosystem II, on the other hand, absorbs light of 680 nm and its active center is P680. In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, the electrons lost by P680 of photosystem II are attained by P700 of photosystem I. These are not reverted back in a cyclic manner to P680. This is the reason it is called non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Complete answer:
Plants perform photosynthesis for synthesizing ATP molecules which provide energy for growth and development. Photosynthesis occurs in two major stages called light reaction stage and dark reaction stage. The light reaction is marked by the conversion of light energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP. This process utilizes light energy and adds phosphate to ADP to form ATP and hence it is known as photophosphorylation. This process is further of two types called cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.

The cyclic photophosphorylation produces only ATP molecules for providing instant energy to plants. The non-cyclic photophosphorylation involves the production of ATP along with NADPH which is a reduced form of \[NAD{{P}^{+}}\]. This occurs through the non-cyclic movement of electrons. The movement of electrons is unidirectional in this process. The electrons combine with \[{{H}^{+}}\] that is obtained due to splitting of water molecules. This results in a reduction of \[NAD{{P}^{+}}\] to NADPH. This process involves both photosystems I and II. \[NAD{{P}^{+}}\] receives electrons from photosystem I. Oxygen is also synthesized as a by-product of the reaction. It is a predominant process in all green plants.
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: The photosystem I is able to absorb light of 700 nm and its active center is P700. Photosystem II, on the other hand, absorbs light of 680 nm and its active center is P680. In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, the electrons lost by P680 of photosystem II are attained by P700 of photosystem I. These are not reverted back in a cyclic manner to P680. This is the reason it is called non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




