
No. of structural isomeric alkenes (molecular formula $ = \,{C_6}{H_{12}} $ ) which all give n-hexane on hydrogenation in presence of metal catalyst is:
$ (1)2 $
$ (2)3 $
$ (3)4 $
$ (4)5 $
Answer
514.2k+ views
Hint :Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. The general structural formula of alkenes is $ {C_n}{H_{2n}} $ . The given alkene, $ {C_6}{H_{12}} $ , contains six carbon atoms and one double bond between two carbon atoms. On hydrogenation, the alkene gets reduced i.e., hydrogen atoms get added to the double bond to form a saturated alkane.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To find out the possible number of structural isomers of $ {C_6}{H_{12}} $ that give n-hexane (straight chain of $ {C_6}{H_{14}} $ ) on hydrogenation, we must try out hydrogenation reactions with each isomer. For hydrogenation reactions, we can use Palladium (Pd) as a metal catalyst.
Let us start with $ hex - 1 - ene $ :
$ C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CH = C{H_2}\,\,\xrightarrow{{{H_2}/Pd}}\,C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CH{}_2 - C{H_3} $
$ hex - 1 - ene $ n-hexane
Hydrogenation of $ hex - 2 - ene $ gives:
$ C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CH = CH - C{H_3}\,\,\xrightarrow{{{H_2}/Pd}}\,C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CH{}_2 - C{H_3} $
$ hex - 2 - ene $ n-hexane
Hydrogenation of $ hex - 3 - ene $ :
$ C{H_3} - C{H_2} - CH = CH - C{H_2} - C{H_3}\,\,\xrightarrow{{{H_2}/Pd}}\,C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CH{}_2 - C{H_3} $
$ hex - 3 - ene $ n-hexane
These are the possible straight chain isomers of $ {C_6}{H_{12}} $ .
Now let us check the hydrogenation of a simple branched chain isomer of $ {C_6}{H_{12}} $ .
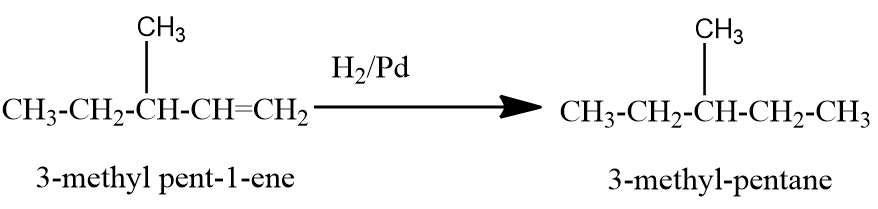
Here we can see that the end product is not n-hexane. Similarly, other branched chain isomers of $ {C_6}{H_{12}} $ will give branched chain alkanes only as a product. Therefore, the structural isomeric alkenes of $ {C_6}{H_{12}} $ that give n-hexane on hydrogenation in presence of metal catalysts are $ hex - 1 - ene $ , $ hex - 2 - ene $ and $ hex - 3 - ene $ .
The right option is $ (2)\,\,3 $ .
Note :
Hydrogenation reaction is an exothermic reaction between a hydrogen molecule - $ {H_2} $ and an organic compound in the presence of metal catalysts. Group $ 10 $ metals like NI, Pd and Pt are mainly used as catalysts in this reaction to reduce the compounds. It is a common method used to convert unsaturated organic compounds to saturated compounds.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To find out the possible number of structural isomers of $ {C_6}{H_{12}} $ that give n-hexane (straight chain of $ {C_6}{H_{14}} $ ) on hydrogenation, we must try out hydrogenation reactions with each isomer. For hydrogenation reactions, we can use Palladium (Pd) as a metal catalyst.
Let us start with $ hex - 1 - ene $ :
$ C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CH = C{H_2}\,\,\xrightarrow{{{H_2}/Pd}}\,C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CH{}_2 - C{H_3} $
$ hex - 1 - ene $ n-hexane
Hydrogenation of $ hex - 2 - ene $ gives:
$ C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CH = CH - C{H_3}\,\,\xrightarrow{{{H_2}/Pd}}\,C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CH{}_2 - C{H_3} $
$ hex - 2 - ene $ n-hexane
Hydrogenation of $ hex - 3 - ene $ :
$ C{H_3} - C{H_2} - CH = CH - C{H_2} - C{H_3}\,\,\xrightarrow{{{H_2}/Pd}}\,C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CH{}_2 - C{H_3} $
$ hex - 3 - ene $ n-hexane
These are the possible straight chain isomers of $ {C_6}{H_{12}} $ .
Now let us check the hydrogenation of a simple branched chain isomer of $ {C_6}{H_{12}} $ .

Here we can see that the end product is not n-hexane. Similarly, other branched chain isomers of $ {C_6}{H_{12}} $ will give branched chain alkanes only as a product. Therefore, the structural isomeric alkenes of $ {C_6}{H_{12}} $ that give n-hexane on hydrogenation in presence of metal catalysts are $ hex - 1 - ene $ , $ hex - 2 - ene $ and $ hex - 3 - ene $ .
The right option is $ (2)\,\,3 $ .
Note :
Hydrogenation reaction is an exothermic reaction between a hydrogen molecule - $ {H_2} $ and an organic compound in the presence of metal catalysts. Group $ 10 $ metals like NI, Pd and Pt are mainly used as catalysts in this reaction to reduce the compounds. It is a common method used to convert unsaturated organic compounds to saturated compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




