
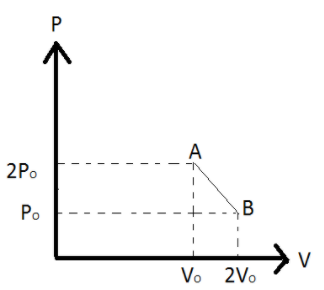
$n$moles of an ideal gas undergoes a process $A \to B$ is shown in figure. The maximum temperature of gas during the process will be
A. $\dfrac{{9{P_o}{V_o}}}{{nR}}$
B. $\dfrac{{9{P_o}{V_o}}}{{4nR}}$
C. $\dfrac{{3{P_o}{V_o}}}{{2nR}}$
D. $\dfrac{{9{P_o}{V_o}}}{{2nR}}$

Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint:In the given question we have to find the temperature of a gas in an ongoing reaction. We will find it by solving the equation of line. An ideal gas is a hypothetical gas which is composed of many randomly moving point particles that are not subject to interparticle interactions.
Formula used:
Equation of line: $Y - {Y_1} = \dfrac{{{Y_2} - {Y_1}}}{{{X_2} - {X_1}}}(X - {X_1})$
Ideal gas equation $PV = nRT$
Complete step by step solution:
From the given diagram the maximum temperature will be $T$ and the product of it will be maximum.
From the equation of line we have;
$Y - {Y_1} = \dfrac{{{Y_2} - {Y_1}}}{{{X_2} - {X_1}}}(X - {X_1})$
Where
$ Y:P \\
{Y_1}:{P_ \circ } \\
{Y_2}:2{P_ \circ } \\
X:V \\
{X_1}:2{V_ \circ } \\
{X_2}:{V_ \circ } $
By putting values, we get;
\[\Rightarrow P - {P_ \circ } = \dfrac{{2{P_ \circ } - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ } - 2{V_ \circ }}}(V - 2{V_ \circ })\]
$\Rightarrow P - {P_ \circ } = \dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}\left( {V - 2{V_ \circ }} \right)$
\[\Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}V + 3{P_ \circ }\]
$\Rightarrow PV = \dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}{V_2} + 3{P_ \circ }V$
According to ideal gas equation $PV = nRT$ , therefore
$\Rightarrow nRT = \dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}{V_2} + 3{P_ \circ }V$
$\Rightarrow T = \dfrac{1}{{nR}}\left[ {\dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}{V_2} + 3{P_ \circ }V} \right]$
For maximum temperature $\dfrac{{\partial T}}{{\partial V}} = 0$
So, $\dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}(2V) + 3{P_ \circ } = 0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}(2V) = - 3{P_ \circ }$
$\Rightarrow V = \dfrac{3}{2}V_\circ $ This is the condition for the maximum temperature.
So, the maximum temperature of the gas during the process
\[T_max = \dfrac{1}{{nR}}\left( {\dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}} \times \dfrac{9}{4}V{2_ \circ } + 3{P_ \circ } \times \dfrac{3}{2}{V_ \circ }} \right)\]
$ = \dfrac{1}{{nR}}\left( { - \dfrac{9}{4}{P_ \circ }{V_ \circ } + \dfrac{9}{2}{P_ \circ }{V_ \circ }} \right) = \dfrac{9}{4}\dfrac{{{P_ \circ }{V_ \circ }}}{{nR}}$
Hence, the maximum temperature of gas during the process is option D. $\dfrac{9}{4}\dfrac{{{P_ \circ }{V_ \circ }}}{{nR}}$ .
Additional information:
The ideal gas law was made by combining the gas law and Avogadro law. The gas law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to volume and directly proportional to temperature whereas Avogadro's Law states that volume or pressure is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas.
Note:
The temperature of a gas is a measure of the average translational kinetic energy of the molecules in a process. The ideal gas equation relates with all the components like the pressure, volume, temperature, and also number of moles of an ideal gas. When we have to find the temperature of a particular line then one has to use the line equation formula.
Formula used:
Equation of line: $Y - {Y_1} = \dfrac{{{Y_2} - {Y_1}}}{{{X_2} - {X_1}}}(X - {X_1})$
Ideal gas equation $PV = nRT$
Complete step by step solution:
From the given diagram the maximum temperature will be $T$ and the product of it will be maximum.
From the equation of line we have;
$Y - {Y_1} = \dfrac{{{Y_2} - {Y_1}}}{{{X_2} - {X_1}}}(X - {X_1})$
Where
$ Y:P \\
{Y_1}:{P_ \circ } \\
{Y_2}:2{P_ \circ } \\
X:V \\
{X_1}:2{V_ \circ } \\
{X_2}:{V_ \circ } $
By putting values, we get;
\[\Rightarrow P - {P_ \circ } = \dfrac{{2{P_ \circ } - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ } - 2{V_ \circ }}}(V - 2{V_ \circ })\]
$\Rightarrow P - {P_ \circ } = \dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}\left( {V - 2{V_ \circ }} \right)$
\[\Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}V + 3{P_ \circ }\]
$\Rightarrow PV = \dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}{V_2} + 3{P_ \circ }V$
According to ideal gas equation $PV = nRT$ , therefore
$\Rightarrow nRT = \dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}{V_2} + 3{P_ \circ }V$
$\Rightarrow T = \dfrac{1}{{nR}}\left[ {\dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}{V_2} + 3{P_ \circ }V} \right]$
For maximum temperature $\dfrac{{\partial T}}{{\partial V}} = 0$
So, $\dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}(2V) + 3{P_ \circ } = 0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}}(2V) = - 3{P_ \circ }$
$\Rightarrow V = \dfrac{3}{2}V_\circ $ This is the condition for the maximum temperature.
So, the maximum temperature of the gas during the process
\[T_max = \dfrac{1}{{nR}}\left( {\dfrac{{ - {P_ \circ }}}{{{V_ \circ }}} \times \dfrac{9}{4}V{2_ \circ } + 3{P_ \circ } \times \dfrac{3}{2}{V_ \circ }} \right)\]
$ = \dfrac{1}{{nR}}\left( { - \dfrac{9}{4}{P_ \circ }{V_ \circ } + \dfrac{9}{2}{P_ \circ }{V_ \circ }} \right) = \dfrac{9}{4}\dfrac{{{P_ \circ }{V_ \circ }}}{{nR}}$
Hence, the maximum temperature of gas during the process is option D. $\dfrac{9}{4}\dfrac{{{P_ \circ }{V_ \circ }}}{{nR}}$ .
Additional information:
The ideal gas law was made by combining the gas law and Avogadro law. The gas law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to volume and directly proportional to temperature whereas Avogadro's Law states that volume or pressure is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas.
Note:
The temperature of a gas is a measure of the average translational kinetic energy of the molecules in a process. The ideal gas equation relates with all the components like the pressure, volume, temperature, and also number of moles of an ideal gas. When we have to find the temperature of a particular line then one has to use the line equation formula.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




