
What is nitrogen fixation and name two microbes which bring about the same.
Answer
501.9k+ views
Hint: Nitrogen is one of the important and abundant gases found in the environment along with oxygen and carbon-dioxide. Nitrogen contains the higher percentage that is $79\% $ in the atmosphere compared to other gases. Nitrogen is crucial to plants as it helps in structure formation and photosynthesis. Plants obtain nitrogen indirectly from microbes which convert atmospheric nitrogen into plant usage.
Complete answer:
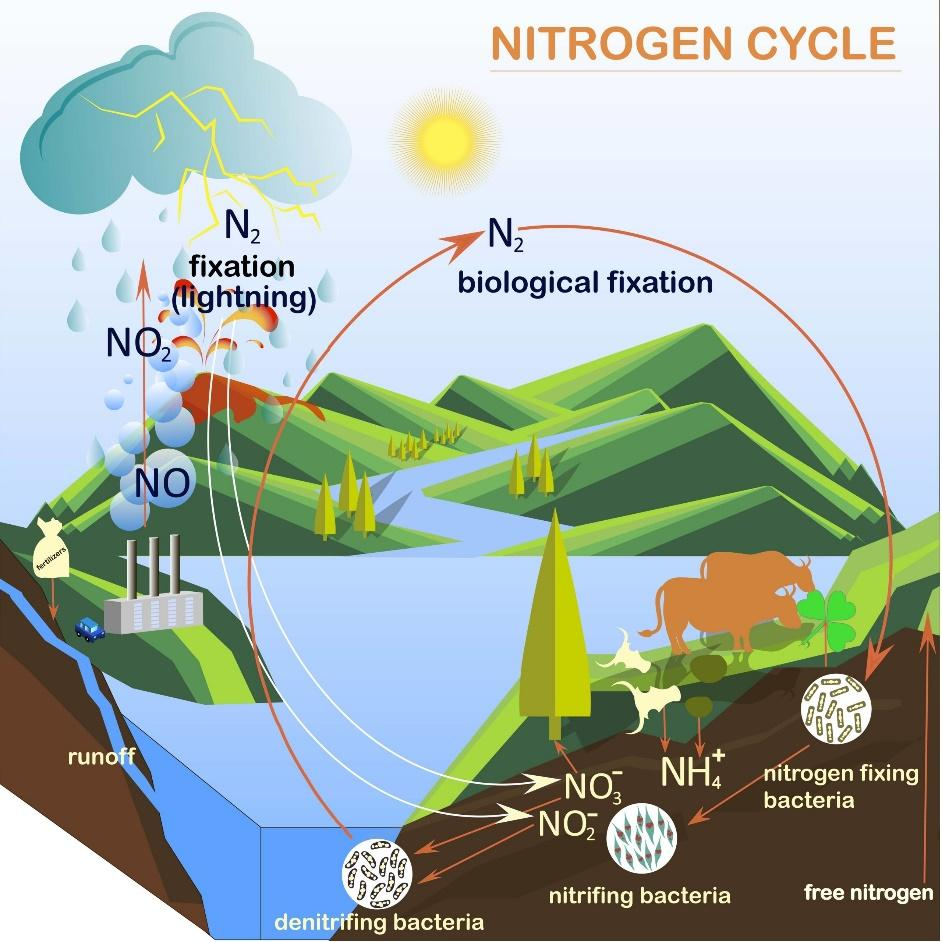
Nitrogen fixation is defined as converting the nitrogen into ammonia by some usage of chemical and biological processes. Nitrogen cycle evolves different processes assimilated together into organic compounds for uptake of plants specifically by certain microorganisms as part of nitrogen cycle.
In nature mostly nitrogen is extracted from the atmosphere by microorganisms to form ammonia, nitrites and nitrates that can be used in plants. Nitrogen is changed into ammonia which is related to nitrogenous compounds in soil and aquatic conditions.
Atmospheric nitrogen is basically in dinitrogen, a non-reactive molecule which is useless until too few microorganisms. Biological nitrogen fixation is crucial to life because organic compounds like-proteins, amino acids nucleoside and triphosphates. Nitrogen fixation is carried out by organisms or they are called nitrogen-fixation microbes as their role is to convert nitrogen into nitrogen forms. Such microbes are- diazotrophs like bacteria. Example- Azotobacter and archaea.
Note:
Two microbes which undergo fixation are-free living and cyanobacteria or blue-green algae. Examples of bacteria which convert the nitrogen to ammonia are- Nostoc, Anabaena, Clostridium and also some plants maintain a symbiotic relationship with microbes such as Rhizobium which is associated with leguminous plants.
Complete answer:
Nitrogen fixation is defined as converting the nitrogen into ammonia by some usage of chemical and biological processes. Nitrogen cycle evolves different processes assimilated together into organic compounds for uptake of plants specifically by certain microorganisms as part of nitrogen cycle.
In nature mostly nitrogen is extracted from the atmosphere by microorganisms to form ammonia, nitrites and nitrates that can be used in plants. Nitrogen is changed into ammonia which is related to nitrogenous compounds in soil and aquatic conditions.
Atmospheric nitrogen is basically in dinitrogen, a non-reactive molecule which is useless until too few microorganisms. Biological nitrogen fixation is crucial to life because organic compounds like-proteins, amino acids nucleoside and triphosphates. Nitrogen fixation is carried out by organisms or they are called nitrogen-fixation microbes as their role is to convert nitrogen into nitrogen forms. Such microbes are- diazotrophs like bacteria. Example- Azotobacter and archaea.

Note:
Two microbes which undergo fixation are-free living and cyanobacteria or blue-green algae. Examples of bacteria which convert the nitrogen to ammonia are- Nostoc, Anabaena, Clostridium and also some plants maintain a symbiotic relationship with microbes such as Rhizobium which is associated with leguminous plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




