
n-butane and isobutane are:
(A) Same compound
(B) Allotropes
(C) Isomers
(D) Structural isomers
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: We should know about the terms allotropes, isomerism and its types. Also, we should know how to draw the structures, the IUPAC nomenclature of these structures and the common names used for them.
Complete step by step answer:
n-butane has chemical formula $ {C_4}{H_{10}} $ and isobutane has chemical formula $ {C_4}{H_{10}} $ . So we observe that the chemical formulas for both are the same. Thus, allotropes option is eliminated. Now we will check the order in which they are placed.
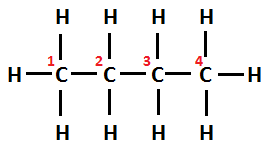
Structural formula of n-butane can be written as $ C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_3} $
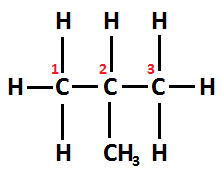
Whereas, Structural formula of isobutane can be written as $ C{H_3} - CH(C{H_3}) - C{H_3} $ . Its IUPAC name is Methylprop-2-ene.
Since the chain varies due to the position of the carbon atom, thus it is an example of a structural isomer.
So, option D. structural isomer is the correct option to the given question.
Note:
Complete step by step answer:
n-butane has chemical formula $ {C_4}{H_{10}} $ and isobutane has chemical formula $ {C_4}{H_{10}} $ . So we observe that the chemical formulas for both are the same. Thus, allotropes option is eliminated. Now we will check the order in which they are placed.
Structural formula of n-butane can be written as $ C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_3} $

Whereas, Structural formula of isobutane can be written as $ C{H_3} - CH(C{H_3}) - C{H_3} $ . Its IUPAC name is Methylprop-2-ene.

Since the chain varies due to the position of the carbon atom, thus it is an example of a structural isomer.
So, option D. structural isomer is the correct option to the given question.
Note:
| Serial number | Allotropes | Isomers |
| 1. | They have different chemical formulas. | They have the same chemical formula. |
| 2. | They are species of the same element. For example, oxygen $ {O_2} $ and ozone $ {O_3} $ . | They are composed of different elements, for example $ {C_4}{H_8} $ is an example of but-1-ene and but-2-ene. |
| 3. | They always have different structures. | They may or may not have the same structures. |
| 4. | It is observed in metals, nonmetals and metalloids. | Isomerism is generally observed in inorganic molecules and hydrocarbons. |
| 5. | We can’t specify the type. For carbon, there are eight allotropes. | Types: structural isomers and stereoisomers. |
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




