
Name the process of ethanol to ethene conversion and reactants used.
(A) Hydrogenation of ethane in the presence of concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$
(B) Dehydration of ethanol in the presence of concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$
(C) Oxidation of ethanol in presence of concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$
(D) Reduction of ethanol in the presence concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we should know the definition of the hydrogenation process, dehydration process, oxidation process and the reduction process. We should know the role of concentrated sulfuric acid which will help us come to a conclusion easily.
Complete step by step solution:
It is very important to know the definition of the process of hydrogenation, dehydration, oxidation and reduction.
Hydrogenation is the process of addition of hydrogen to a molecule or a compound in presence of certain catalysts such as platinum/palladium.
Dehydration is the process of removal of hydrogen from a molecule or compound.
Oxidation is the reaction where the molecules lose its electrons whereas, the reduction is the reaction the molecule gains electrons.
A most important point to remember is that Concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$ can act as a dehydrating agent and very rarely as an oxidizing agent. Ethanol is oxidized to aldehyde not to ethane that too in the presence of dichromate or pyridine.
When ethanol is treated with concentrated sulfuric acid at $C{H_3} - C{H_2}$, ethane is formed.
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}OH\xrightarrow[{{{170}^ \circ }C}]{{Conc.{H_2}S{O_4}}}C{H_2} = C{H_2} + {H_2}O\]
Mechanism:
Step 1: protonation of alcohol: on the addition of a proton to alcohol protonated alcohol is formed
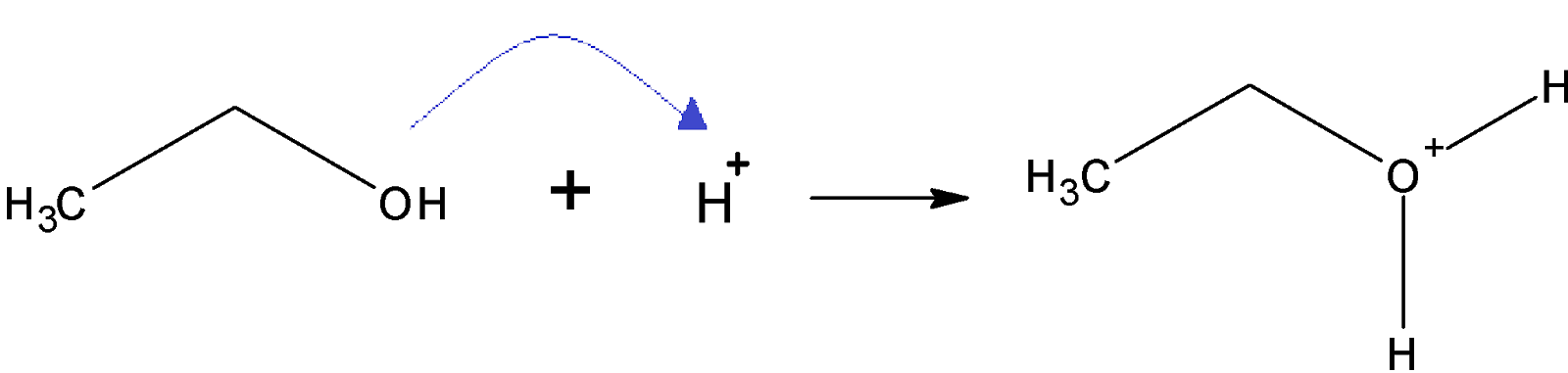
Step 2: elimination of water molecule: removal of a water molecule from the protonated alcohol gives a stable carbonium ion.
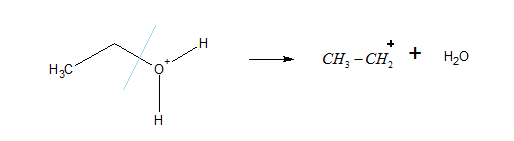
Step 3: Carbonium loses hydrogen to give a stable carbonium ion.
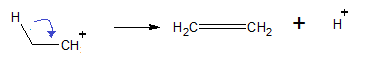
Thus, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: The reaction of alcohol is treated with concentrated sulfuric is very sensitive to reaction conditions such as temperature. If the same reaction is carried out at room temperature the product formed will be ethyl hydrogen sulfate.
Complete step by step solution:
It is very important to know the definition of the process of hydrogenation, dehydration, oxidation and reduction.
Hydrogenation is the process of addition of hydrogen to a molecule or a compound in presence of certain catalysts such as platinum/palladium.
Dehydration is the process of removal of hydrogen from a molecule or compound.
Oxidation is the reaction where the molecules lose its electrons whereas, the reduction is the reaction the molecule gains electrons.
A most important point to remember is that Concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$ can act as a dehydrating agent and very rarely as an oxidizing agent. Ethanol is oxidized to aldehyde not to ethane that too in the presence of dichromate or pyridine.
When ethanol is treated with concentrated sulfuric acid at $C{H_3} - C{H_2}$, ethane is formed.
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}OH\xrightarrow[{{{170}^ \circ }C}]{{Conc.{H_2}S{O_4}}}C{H_2} = C{H_2} + {H_2}O\]
Mechanism:
Step 1: protonation of alcohol: on the addition of a proton to alcohol protonated alcohol is formed

Step 2: elimination of water molecule: removal of a water molecule from the protonated alcohol gives a stable carbonium ion.

Step 3: Carbonium loses hydrogen to give a stable carbonium ion.
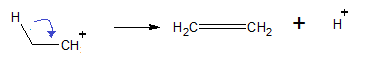
Thus, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: The reaction of alcohol is treated with concentrated sulfuric is very sensitive to reaction conditions such as temperature. If the same reaction is carried out at room temperature the product formed will be ethyl hydrogen sulfate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




