
Name the pores through which leaves exchange gases.
Answer
520.3k+ views
Hint:Leaves are green coloured structures which contain chlorophyll and they are responsible for making food by the process of photosynthesis.
Complete Answer:
The epidermis of leaves has small openings called stomata through which gas exchange. These are the small openings present on the inner surface of the leaves. They are bounded by the two guard cells. Stomata can be opened or closed depending on the turgidity of guard cells.
As the inner wall of a guard, the cell is thicker in comparison to the outer wall. Therefore, when the guard cell is filled with water, it becomes turgid, the outer wall bulges outward, drawing the inner wall with it and causing the stomata to enlarge. The closing and opening of the stomata also depend upon the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air. It is so because when carbon dioxide levels are below normal, i.e., about 0.03 percent, the guard cells become turgid and the stomata enlarge.
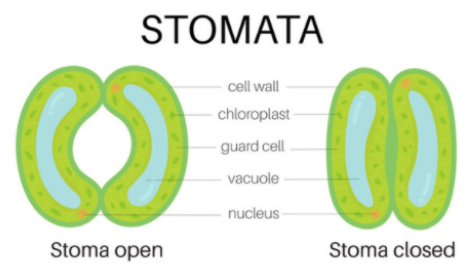
Stomata are mostly found in green aerial parts of plants, such as stem and particularly on the leaves. Stomata play a very important role as it provides direct pathways between leaves and the air. Carbon dioxide enters through the stomata while water and oxygen exit through it. Some of the main functions of stomata are as follows:
i. It opens and closes the pores in the leaves for an exchange of gases.
ii. It allows the plant to take in carbon dioxide and give out oxygen for photosynthesis.
Iii. Depending on the weather conditions, it closes or opens its pores to keep the moisture content developed.
Note:The loss of water in the form of water vapor from the stomata is termed as transpiration. It helps in the cooling of leaves.
Complete Answer:
The epidermis of leaves has small openings called stomata through which gas exchange. These are the small openings present on the inner surface of the leaves. They are bounded by the two guard cells. Stomata can be opened or closed depending on the turgidity of guard cells.
As the inner wall of a guard, the cell is thicker in comparison to the outer wall. Therefore, when the guard cell is filled with water, it becomes turgid, the outer wall bulges outward, drawing the inner wall with it and causing the stomata to enlarge. The closing and opening of the stomata also depend upon the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air. It is so because when carbon dioxide levels are below normal, i.e., about 0.03 percent, the guard cells become turgid and the stomata enlarge.

Stomata are mostly found in green aerial parts of plants, such as stem and particularly on the leaves. Stomata play a very important role as it provides direct pathways between leaves and the air. Carbon dioxide enters through the stomata while water and oxygen exit through it. Some of the main functions of stomata are as follows:
i. It opens and closes the pores in the leaves for an exchange of gases.
ii. It allows the plant to take in carbon dioxide and give out oxygen for photosynthesis.
Iii. Depending on the weather conditions, it closes or opens its pores to keep the moisture content developed.
Note:The loss of water in the form of water vapor from the stomata is termed as transpiration. It helps in the cooling of leaves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




