
Name the plant growth hormone which is synthesized at the shoot tip. Explain the fact that the shoot of a plant bends towards the light during its growth. Why?
Answer
506.4k+ views
Hint: The plants contain several hormones like auxins, gibberellins, cytokinin which are responsible for cell growth, development, elongation, preventing senescence, preventing dormancy etc. The primary plant hormones help in maintaining the physiological functions in the plant.
Complete answer:
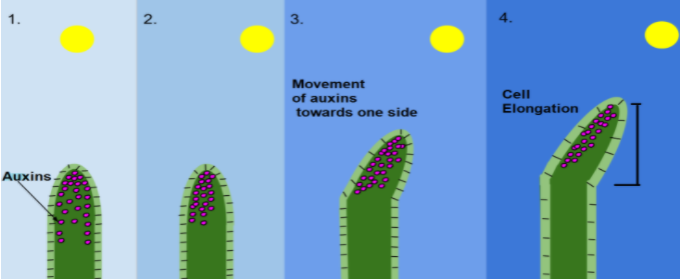
Shoot tips consist of highly dividing meristematic cells at the tip of all branches and stem. This is the region where the cells divide for the elongation of the stem. The plants elongate so that they can get maximum sunlight. This cell division is regulated by the phytohormone called the auxins. This hormone is transported down the shoot so that it can inhibit the growth of axillary buds. Auxins are the key regulator of growth in plant cells. They play a vital role in growth, development, elongation, differentiation root and shoot tropism, the transition of flowering etc.
One of the important functions of Auxin is tropic movement in plants. Let us discuss the trophic movement in response to light.
The plant’s exhibit phototropism which means that it bends towards the direction of light. This bending is majorly for growth. For example, sunflowers. This bending is regulated by the phytohormone called auxin.
During the presence of sunlight, the Auxins in the stem start moving towards the area which is away from light. Thus, the auxin concentration in this region increases due to which growth takes place. Whereas the area of low auxin concentration exhibits no growth. This results in the bending of the stem towards sunlight.
Note: The chemical structure of auxin is represented as IAA or Indole 3-Acetic acid. It was isolated by Kenneth V. Thimann. There are five naturally occurring auxins. Synthetic auxins are also used for initiating growth and development in plants.
Complete answer:
Shoot tips consist of highly dividing meristematic cells at the tip of all branches and stem. This is the region where the cells divide for the elongation of the stem. The plants elongate so that they can get maximum sunlight. This cell division is regulated by the phytohormone called the auxins. This hormone is transported down the shoot so that it can inhibit the growth of axillary buds. Auxins are the key regulator of growth in plant cells. They play a vital role in growth, development, elongation, differentiation root and shoot tropism, the transition of flowering etc.
One of the important functions of Auxin is tropic movement in plants. Let us discuss the trophic movement in response to light.
The plant’s exhibit phototropism which means that it bends towards the direction of light. This bending is majorly for growth. For example, sunflowers. This bending is regulated by the phytohormone called auxin.
During the presence of sunlight, the Auxins in the stem start moving towards the area which is away from light. Thus, the auxin concentration in this region increases due to which growth takes place. Whereas the area of low auxin concentration exhibits no growth. This results in the bending of the stem towards sunlight.

Note: The chemical structure of auxin is represented as IAA or Indole 3-Acetic acid. It was isolated by Kenneth V. Thimann. There are five naturally occurring auxins. Synthetic auxins are also used for initiating growth and development in plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




