
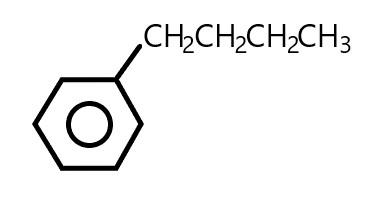
How would you name the following aromatic hydrocarbon?

Answer
542.7k+ views
Hint: The international union of pure and applied chemistry (IUPAC) is an organization which is used for naming organic chemical compounds. To write the name of any compound we have to follow some rule of IUPAC nomenclature. The most ideal aromatic compound is benzene which is represented as:
Complete step by step answer:
For IUPAC nomenclature of substituted benzene compounds, the substituent is placed as prefix to the word benzene. If the benzene is di or tri substituted, the position of substituents is defined by the numbering the carbon atoms of the ring such that substituents are located at the lowest numbers possible.
Details of rules for IUPAC nomenclature of aromatic compounds is given below:
Identify the principal functional group and secondary functional group. Principal group gets the lowest locant.
When a substituent is such, which when taken together with the benzene ring gives a special name to the molecule, then it is named as a derivative of that molecule.
When a functional group is present in the side chain attached to the benzene ring, then it is named as a phenyl derivative of that aliphatic compound.
In the trivial system of nomenclature the terms ortho, meta, para are used as prefixes to indicate the relative positions $1,2;1,3;1,4$ respectively.
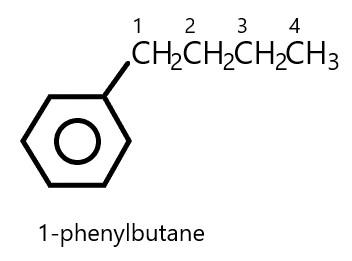
Now, using these rules we will write the name of our aromatic hydrocarbon. The side chain which is attached to the benzene is butane i.e.$C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}$
According to rule number $3$, when Butane is attached to the benzene ring it will become \[1 - phenylbutane\] so, it is a phenyl derivative.
Note: While writing any name of the organic compounds the rules of IUPAC should be remembered. Keep in mind that there is a difference between common name and IUPAC name. Common name is the name which we use in our daily life but IUPAC name is at international level.

Complete step by step answer:
For IUPAC nomenclature of substituted benzene compounds, the substituent is placed as prefix to the word benzene. If the benzene is di or tri substituted, the position of substituents is defined by the numbering the carbon atoms of the ring such that substituents are located at the lowest numbers possible.
Details of rules for IUPAC nomenclature of aromatic compounds is given below:
Identify the principal functional group and secondary functional group. Principal group gets the lowest locant.
When a substituent is such, which when taken together with the benzene ring gives a special name to the molecule, then it is named as a derivative of that molecule.
When a functional group is present in the side chain attached to the benzene ring, then it is named as a phenyl derivative of that aliphatic compound.
In the trivial system of nomenclature the terms ortho, meta, para are used as prefixes to indicate the relative positions $1,2;1,3;1,4$ respectively.
Now, using these rules we will write the name of our aromatic hydrocarbon. The side chain which is attached to the benzene is butane i.e.$C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}$

According to rule number $3$, when Butane is attached to the benzene ring it will become \[1 - phenylbutane\] so, it is a phenyl derivative.

Note: While writing any name of the organic compounds the rules of IUPAC should be remembered. Keep in mind that there is a difference between common name and IUPAC name. Common name is the name which we use in our daily life but IUPAC name is at international level.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




