
Name the commonly found purines in nucleic acid.
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: Nucleic acid is the most important biomolecule present in the living organism. Nucleic acid is of two types DNA and RNA. DNA is the master molecule that controls the growth, development and functioning of the cell. RNA is the major molecule for the synthesis of proteins. Purines are the nitrogenous bases present in DNA and RNA.
Complete answer:
The nucleic acid is found in the nucleus of the cell. It is found in the cytoplasm of the prokaryotic cells. DNA and RNA are the most important nucleic acid. The DNA and RNA are made up of nitrogenous bases, ribose and deoxyribose sugar and a phosphate molecule.
Let us discuss the structure of the nitrogenous bases.
The nitrogenous bases are the nitrogen-containing biomolecules. They are the monomer that forms the building blocks of nucleic acids. These bases are linked to the sugar backbone. The bases form bond between each other and are responsible to form a double-stranded ladder-like structure of the DNA.
There are two types of nitrogenous bases. These bases are complementary to each other and form a covalent bond between them.
i) Purines- The purine bases are the two fused ring structures (imidazole and pyrimidine) in which the amino group is present. They are heterocyclic aromatic compounds. There are two purine bases- Adenine and guanine. They are water-soluble.
ii) Pyrimidine-These are simple ring structures. The pyrimidines are three in number. Cytosine and thymine are present in DNA and cytosine and uracil in the case of RNA. The structure of purines and pyrimidine and the bond is as follows-
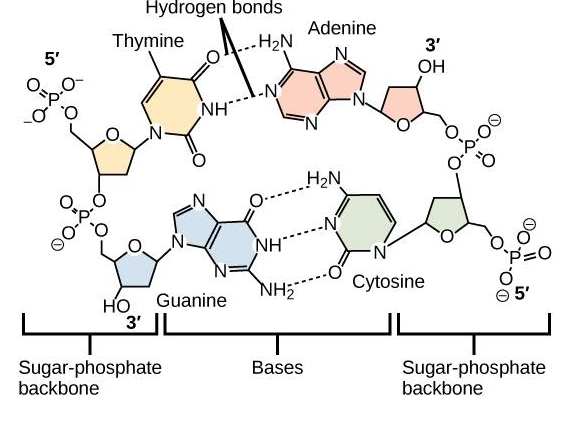
The commonly found purines are adenine and guanine.
Note: The pairing takes place between the purines and pyrimidine. Adenine forms a double bond with thymine/ uracil. Guanine forms a triple bond with cytosine. They are called complementary bases.
Complete answer:
The nucleic acid is found in the nucleus of the cell. It is found in the cytoplasm of the prokaryotic cells. DNA and RNA are the most important nucleic acid. The DNA and RNA are made up of nitrogenous bases, ribose and deoxyribose sugar and a phosphate molecule.
Let us discuss the structure of the nitrogenous bases.
The nitrogenous bases are the nitrogen-containing biomolecules. They are the monomer that forms the building blocks of nucleic acids. These bases are linked to the sugar backbone. The bases form bond between each other and are responsible to form a double-stranded ladder-like structure of the DNA.
There are two types of nitrogenous bases. These bases are complementary to each other and form a covalent bond between them.
i) Purines- The purine bases are the two fused ring structures (imidazole and pyrimidine) in which the amino group is present. They are heterocyclic aromatic compounds. There are two purine bases- Adenine and guanine. They are water-soluble.
ii) Pyrimidine-These are simple ring structures. The pyrimidines are three in number. Cytosine and thymine are present in DNA and cytosine and uracil in the case of RNA. The structure of purines and pyrimidine and the bond is as follows-

The commonly found purines are adenine and guanine.
Note: The pairing takes place between the purines and pyrimidine. Adenine forms a double bond with thymine/ uracil. Guanine forms a triple bond with cytosine. They are called complementary bases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




