
Name the chemical used to test starch.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: The chemical belongs to the group of halogens and is a non-metallic solid with a purple-black luster in the standard conditions but it melts to form a deep violet liquid when the temperature is around 144 degrees celsius.
Complete answer:
Iodine is used to test the presence of starch and this test is known as Starch-Iodine test. In this test, the presence of starch is detected by observing a change in color that is due to the formation of a complex. The reagents in this test are – a solution of $I_{2}$ (iodine) and KI (potassium iodide). The solution of these two chemicals in water is generally light orange-brown but when it is added to another solution or sample that contains starch, the light orange-brown color changes to deep blue. This change in color is due to the charge-transfer complexes. In the presence of potassium iodide, the iodine forms polyiodide ions like $I_{3}^{-}$ that act as charge donors and get embedded in the amylose helix forming a complex that is deep blue.
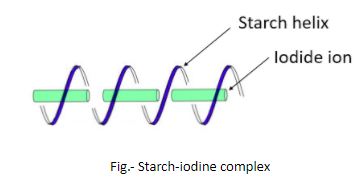
So, it is clear now that it is the amylose in the starch which is responsible for the formation of deep blue color by forming a complex with iodine. Iodine is a lustrous purple-black non-metallic solid belonging to the group of halogens.
Note: There is a limitation of this test that it cannot be performed in a very low pH environment because in such conditions, the hydrolysis of starch occurs and it prevents the formation of a starch-iodine complex that gives the blue color as an indication of the presence of starch.
Complete answer:
Iodine is used to test the presence of starch and this test is known as Starch-Iodine test. In this test, the presence of starch is detected by observing a change in color that is due to the formation of a complex. The reagents in this test are – a solution of $I_{2}$ (iodine) and KI (potassium iodide). The solution of these two chemicals in water is generally light orange-brown but when it is added to another solution or sample that contains starch, the light orange-brown color changes to deep blue. This change in color is due to the charge-transfer complexes. In the presence of potassium iodide, the iodine forms polyiodide ions like $I_{3}^{-}$ that act as charge donors and get embedded in the amylose helix forming a complex that is deep blue.

So, it is clear now that it is the amylose in the starch which is responsible for the formation of deep blue color by forming a complex with iodine. Iodine is a lustrous purple-black non-metallic solid belonging to the group of halogens.
Note: There is a limitation of this test that it cannot be performed in a very low pH environment because in such conditions, the hydrolysis of starch occurs and it prevents the formation of a starch-iodine complex that gives the blue color as an indication of the presence of starch.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




