
What is the name of the product of the hydrogenation of \[2 - methylpropanal\] ?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: We have to remember that in chemistry two reactions are mainly in organic concepts. The two reactions are oxidation and reduction reaction. The oxidation reaction is nothing but a chemical reaction from the reactant to produce the addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen or gain of electron in the product. The reduction reaction is nothing but a chemical reaction from the reactant to produce the addition of hydrogen or removal of oxygen or loss of electrons. The oxidation or reduction reaction plays a key role for converting one functional group to another functional group in the organic chemical reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
We must have to know that the hydrogenation is nothing but the reduction reaction in the chemistry.
The chemical for of \[2 - methylpropanal\] is
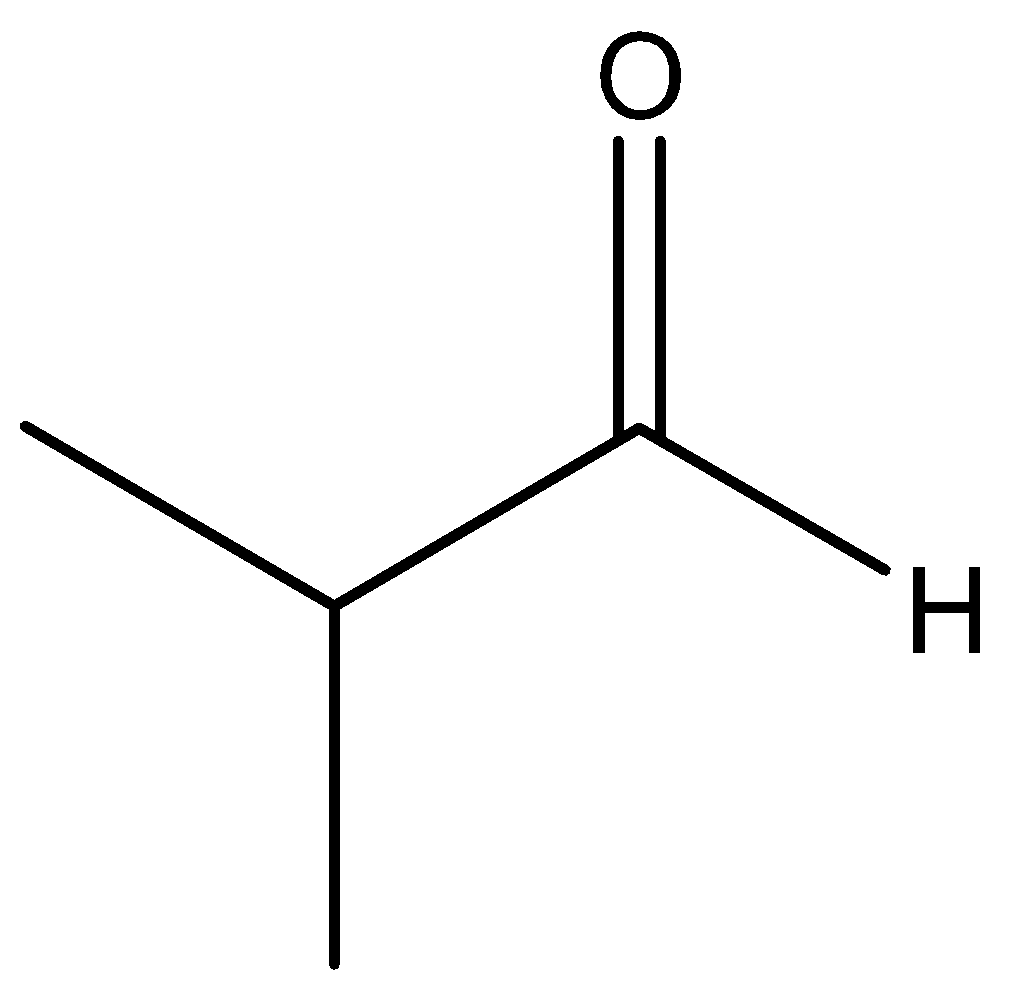
The function group present in the \[2 - methylpropanal\] is aldehyde. Reduction of the aldehyde group gives respect to alcohol. Maximum reduction of aldehyde gives primary alcohol in organic chemistry.
The hydrogenation of \[2 - methylpropanal\] , hydrogen attacks the carbonyl group in the molecule. Here, the carbonyl group is in the form of aldehyde, reduction of these aldehydes give \[2 - methylpropanol\] .
The reaction scheme of the above discussion is given below,
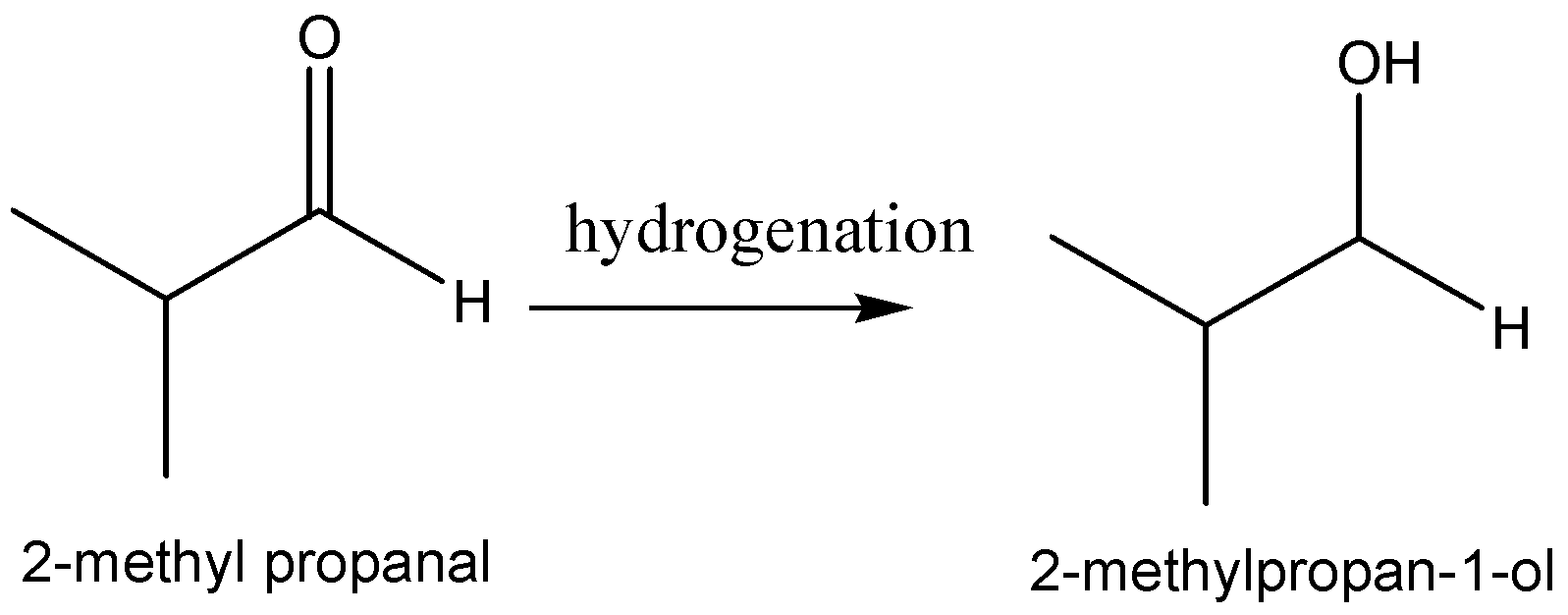
Hence, the product of the hydrogenation of \[2 - methylpropanal\] is \[2 - methylpropanal\].
Note: The hydrogenation means two hydrogen atoms are added in the reactant to give product after attacking these two hydrogens. The maximum two hydrogen are attacking in the electrophilic group in the reactant by using some specific reducing reagent. Here, lithium aluminium hydride or any metallic hydride used to convert aldehyde to alcohol group in \[2 - methylpropanal\] . The oxidation and reduction are the reversible reactions in organic chemistry. For example, the oxidation of primary alcohol is aldehyde. At the same time, the reduction of aldehyde is primary alcohol. Hence, the oxidation of primary alcohol and reduction of aldehyde is a reversible reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
We must have to know that the hydrogenation is nothing but the reduction reaction in the chemistry.
The chemical for of \[2 - methylpropanal\] is

The function group present in the \[2 - methylpropanal\] is aldehyde. Reduction of the aldehyde group gives respect to alcohol. Maximum reduction of aldehyde gives primary alcohol in organic chemistry.
The hydrogenation of \[2 - methylpropanal\] , hydrogen attacks the carbonyl group in the molecule. Here, the carbonyl group is in the form of aldehyde, reduction of these aldehydes give \[2 - methylpropanol\] .
The reaction scheme of the above discussion is given below,

Hence, the product of the hydrogenation of \[2 - methylpropanal\] is \[2 - methylpropanal\].
Note: The hydrogenation means two hydrogen atoms are added in the reactant to give product after attacking these two hydrogens. The maximum two hydrogen are attacking in the electrophilic group in the reactant by using some specific reducing reagent. Here, lithium aluminium hydride or any metallic hydride used to convert aldehyde to alcohol group in \[2 - methylpropanal\] . The oxidation and reduction are the reversible reactions in organic chemistry. For example, the oxidation of primary alcohol is aldehyde. At the same time, the reduction of aldehyde is primary alcohol. Hence, the oxidation of primary alcohol and reduction of aldehyde is a reversible reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




