
Name a non-metal which is liquid at room temperature.
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: It is a reddish-brown liquid that is extremely poisonous to humans. It falls in the halogen category and it is used to form a reagent that is used in Markovnikov's addition reaction.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In order to answer our question, we need to gain knowledge about bromine. Bromine is a nonmetal in the group 17 of the periodic table, and it is the third halogen. Bromine possesses properties that are more or less similar to other halogens like fluorine, chlorine and iodine. The electronic configuration of bromine is $[Ar]3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{2}}4{{p}^{5}}$. It has a deficiency of one electron to fulfil its octet configuration, so for this reason, it is a good oxidising agent, however a weaker oxidising agent than chlorine. Properties of bromine are intermediate between iodine and chlorine, for example, bromine is less reactive than chlorine and more reactive than iodine. Moreover, properties like ionisation energy, electron affinity ionic radius as well as bond length of bromine fall between chlorine and iodine. Bromine is reddish to brownish in colour and the reason for it is the transition of the electrons from the highest occupied antibonding orbital to the lowest vacant antibonding $\pi $ orbital. Bromine exists as a diatomic molecule $B{{r}_{2}}$ and its structure looks like:
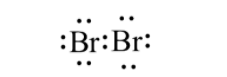
The molar mass of bromine is about $160g\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$. There are two stable isotopes of bromine which are possible which are $^{79}Br$ and $^{81}Br$. Both of them are the natural isotopes and they occur almost in equal percentage in nature. However, bromine is very toxic to humans. Liquid bromine can burn the skin of humans, whereas inhalation of the bromine gas may lead to breathing problems and adverse effects in the respiratory tract.
Hence, bromine is the non-metal which is liquid at normal room temperature.
Note: It is to be noted that the Van der waals force of attraction between the molecules increases down the group. So, chlorine is a gas, bromine a liquid and iodine a solid as their forces of attraction increase respectively.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In order to answer our question, we need to gain knowledge about bromine. Bromine is a nonmetal in the group 17 of the periodic table, and it is the third halogen. Bromine possesses properties that are more or less similar to other halogens like fluorine, chlorine and iodine. The electronic configuration of bromine is $[Ar]3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{2}}4{{p}^{5}}$. It has a deficiency of one electron to fulfil its octet configuration, so for this reason, it is a good oxidising agent, however a weaker oxidising agent than chlorine. Properties of bromine are intermediate between iodine and chlorine, for example, bromine is less reactive than chlorine and more reactive than iodine. Moreover, properties like ionisation energy, electron affinity ionic radius as well as bond length of bromine fall between chlorine and iodine. Bromine is reddish to brownish in colour and the reason for it is the transition of the electrons from the highest occupied antibonding orbital to the lowest vacant antibonding $\pi $ orbital. Bromine exists as a diatomic molecule $B{{r}_{2}}$ and its structure looks like:
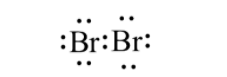
The molar mass of bromine is about $160g\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$. There are two stable isotopes of bromine which are possible which are $^{79}Br$ and $^{81}Br$. Both of them are the natural isotopes and they occur almost in equal percentage in nature. However, bromine is very toxic to humans. Liquid bromine can burn the skin of humans, whereas inhalation of the bromine gas may lead to breathing problems and adverse effects in the respiratory tract.
Hence, bromine is the non-metal which is liquid at normal room temperature.
Note: It is to be noted that the Van der waals force of attraction between the molecules increases down the group. So, chlorine is a gas, bromine a liquid and iodine a solid as their forces of attraction increase respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




