
Why is the motion of a body with a constant speed around a circular path said to be accelerated?
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: Motion in a circular path with a constant speed is called uniform circular motion. It is very important to understand the difference between a scalar and a vector quantity. For example speed is a scalar quantity and velocity is a vector quantity. A body in acceleration means there is a change in velocity with time. As vector quantity can be said to be changing even if only the direction is being changed, keeping the magnitude constant.
Complete step by step answer:
Speed is a scalar quantity and velocity is a vector quantity. If the speed is constant, it doesn’t imply that the acceleration is zero but if the velocity is constant, it always implies that acceleration is zero or motion is non-accelerated. Let’s consider the following diagram for more clarity.
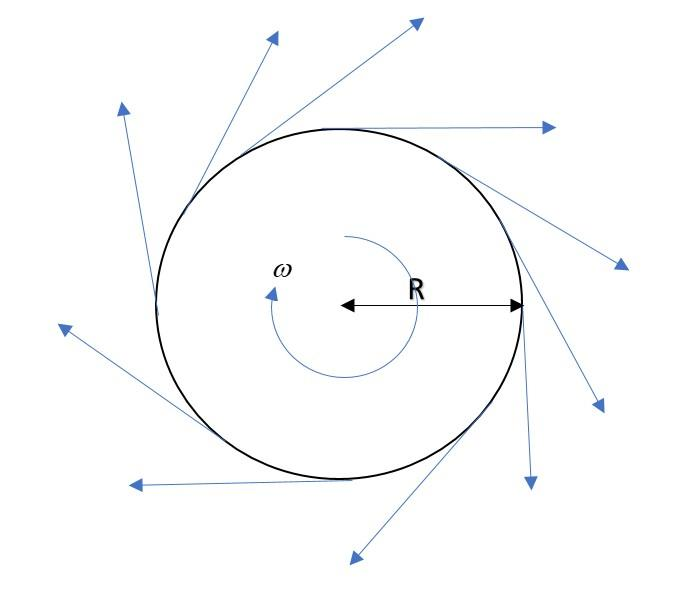
In the above figure, we can see that a particle when rotates in a circle, at each and every point of path, its direction changes which is shown by arrows and is always tangential to the circle at each point. Hence the direction is changing continuously and that also means that velocity is changing at every point. Thus we can say that the motion is accelerated.
The acceleration associated with this type of motion, called uniform circular motion is called centripetal acceleration and is given by $a_C = \omega R^2$, where R is the radius of circle and ‘$\omega$’ is the constant angular speed of the particle undergoing motion. This acceleration is directed radially inwards.
Note:
We can see that the magnitude of this acceleration is constant with time. One should always analyze the quantities with their directions and magnitude separately. For example the magnitude of centripetal acceleration is $\omega R^2$ but its direction is radially inwards (along the string). The direction of acceleration is also changing at every point.
Complete step by step answer:
Speed is a scalar quantity and velocity is a vector quantity. If the speed is constant, it doesn’t imply that the acceleration is zero but if the velocity is constant, it always implies that acceleration is zero or motion is non-accelerated. Let’s consider the following diagram for more clarity.

In the above figure, we can see that a particle when rotates in a circle, at each and every point of path, its direction changes which is shown by arrows and is always tangential to the circle at each point. Hence the direction is changing continuously and that also means that velocity is changing at every point. Thus we can say that the motion is accelerated.
The acceleration associated with this type of motion, called uniform circular motion is called centripetal acceleration and is given by $a_C = \omega R^2$, where R is the radius of circle and ‘$\omega$’ is the constant angular speed of the particle undergoing motion. This acceleration is directed radially inwards.
Note:
We can see that the magnitude of this acceleration is constant with time. One should always analyze the quantities with their directions and magnitude separately. For example the magnitude of centripetal acceleration is $\omega R^2$ but its direction is radially inwards (along the string). The direction of acceleration is also changing at every point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




