
What is mostly present in our blood – carbaminohemoglobin or carboxyhemoglobin?
Answer
480.3k+ views
Hint: Haemoglobin is a protein, which is present in the red blood cells of the body. It is an iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein and ispresent in almost all vertebrates and tissues of some invertebrates. It carries oxygen, providing blood its red color. Though haemoglobin levels vary from one person to another, men generally consist of more haemoglobin than women.
Complete answer:
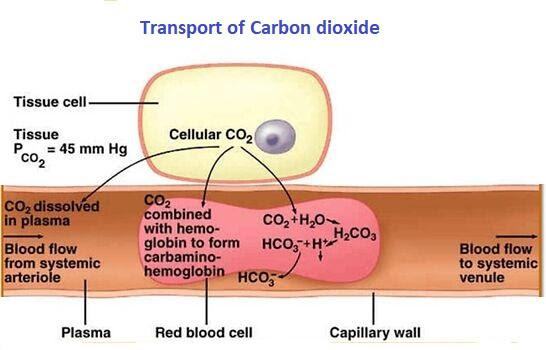
Haemoglobin carrying carbon dioxide is called carbaminohemoglobin and haemoglobin bound to carbon monoxide is called carboxyhemoglobin.
The binding of carbon dioxide to haemoglobin occurs as in the tissues, partial pressure of oxygen is lower and partial pressure of carbon dioxide is higher. Carbaminohaemoglobin is one of the configurations, where carbon dioxide exists in the blood. The chemical complex is formed after the release of oxygen by the haemoglobin to a cell. Around 23% of carbon dioxide produced in tissues is carried by haemoglobin in carbaminohemoglobin form. As oxygen begins entering the blood, carbon dioxide is unloaded at primary capillaries around the lungs.
In comparison with carbaminohemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin is a far more stable compound, because once carbon monoxide is formed, it does not leave haemoglobin, leading to a decrease in the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Carbon monoxide binds the sites on the haemoglobin molecule, which normally binds with oxygen and is not readily displaced from the molecule. This exposure to carbon monoxide results in cellular anoxia.
Note:
Carboxyhaemoglobin, being a stable complex, prevents normal complexing with oxygen. Carbaminohaemoglobin is not that stable complex, being one of the forms of carbon dioxide in the blood of the body. It is found in tissue capillaries, as carbon dioxide combines with free alpha groups of haemoglobin. Thus, carbaminohemoglobin is mostly present in the blood, in comparison with carboxyhemoglobin.
Complete answer:

Haemoglobin carrying carbon dioxide is called carbaminohemoglobin and haemoglobin bound to carbon monoxide is called carboxyhemoglobin.
The binding of carbon dioxide to haemoglobin occurs as in the tissues, partial pressure of oxygen is lower and partial pressure of carbon dioxide is higher. Carbaminohaemoglobin is one of the configurations, where carbon dioxide exists in the blood. The chemical complex is formed after the release of oxygen by the haemoglobin to a cell. Around 23% of carbon dioxide produced in tissues is carried by haemoglobin in carbaminohemoglobin form. As oxygen begins entering the blood, carbon dioxide is unloaded at primary capillaries around the lungs.
In comparison with carbaminohemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin is a far more stable compound, because once carbon monoxide is formed, it does not leave haemoglobin, leading to a decrease in the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Carbon monoxide binds the sites on the haemoglobin molecule, which normally binds with oxygen and is not readily displaced from the molecule. This exposure to carbon monoxide results in cellular anoxia.
Note:
Carboxyhaemoglobin, being a stable complex, prevents normal complexing with oxygen. Carbaminohaemoglobin is not that stable complex, being one of the forms of carbon dioxide in the blood of the body. It is found in tissue capillaries, as carbon dioxide combines with free alpha groups of haemoglobin. Thus, carbaminohemoglobin is mostly present in the blood, in comparison with carboxyhemoglobin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




