
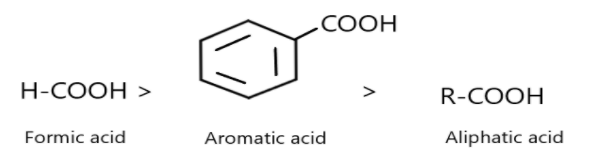
More the power of –I effect more will be acidity (opposite for +I effect). On the basis of the given statement check whether the given order is correct or not?

Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: We have already learnt that the inductive effect is a permanent effect that arises whenever an electron withdrawing group is attached to the carbon chain. This effect weakens with increasing distance from the substituent and becomes almost negligible after three carbon atoms.
Complete answer:
We know that the inductive effect arises when an electron withdrawing group (EWG) is attached to the carbon chain. For example- let us assume a carbon chain with chlorine attached at one end ${C_4} - {C_3} - {C_2} - {C_1} - Cl$. Since chlorine is more electronegative than carbon, the σ-electrons of $C - Cl$ bond are attracted towards chlorine and it acquires a small negative charge and ${C_1}$ acquires a small positive charge which will attract the σ-electrons of the other carbon atoms resulting in the more positive charge on carbon atoms and hence the displacement of these σ-electrons along a saturated carbon chain whenever an EWG is present is the inductive effect or I-effect.
This effect weakens with increasing distance from the substituent and becomes almost negligible after three carbon atoms. There are two types of inductive effects:
(a) $ - I\,effect$ and
(b) $ + I\,effect$
$ - I\,effect$ involves the permanent shifting of σ-electrons away from carbon atoms due to an atom or a group.
Example: $ - N{O_2} > - CN > - COOH > - F > - Cl > - Br > - I > - OH$
$ + I\,effect$ involves the permanent shifting of σ-electrons towards the carbon atom due to an atom or a group.
Example: ${(C{H_3})_3}C - > {(C{H_3})_2}CH - > C{H_3} - C{H_2} - > C{H_3}$
Groups that have $ + I\,effect$ increases the electron density on the molecule responsible for donating an electron and becomes basic whereas groups with$ - I\,effect$ decreases the electron density and molecules becomes acidic thereby becoming electron deficient.
As the number of $ - I\,groups$ increases, acidity also increases, opposite is the case of $ + I\, groups$.
Thus, the given order is correct as the formic acid is more stable and acidic due to stability of conjugate base whereas benzoic acid is stabilised due to resonance of ring structure and aliphatic acid possesses less acidity than the other two.
Note:
Inductive effect is responsible for the high melting point, high boiling point and greater dipole moment of polar compounds. This effect weakens with increasing distance from the substituent and becomes almost negligible after three carbon atoms, this is the key point to keep in mind about inductive effect.
Complete answer:
We know that the inductive effect arises when an electron withdrawing group (EWG) is attached to the carbon chain. For example- let us assume a carbon chain with chlorine attached at one end ${C_4} - {C_3} - {C_2} - {C_1} - Cl$. Since chlorine is more electronegative than carbon, the σ-electrons of $C - Cl$ bond are attracted towards chlorine and it acquires a small negative charge and ${C_1}$ acquires a small positive charge which will attract the σ-electrons of the other carbon atoms resulting in the more positive charge on carbon atoms and hence the displacement of these σ-electrons along a saturated carbon chain whenever an EWG is present is the inductive effect or I-effect.
This effect weakens with increasing distance from the substituent and becomes almost negligible after three carbon atoms. There are two types of inductive effects:
(a) $ - I\,effect$ and
(b) $ + I\,effect$
$ - I\,effect$ involves the permanent shifting of σ-electrons away from carbon atoms due to an atom or a group.
Example: $ - N{O_2} > - CN > - COOH > - F > - Cl > - Br > - I > - OH$
$ + I\,effect$ involves the permanent shifting of σ-electrons towards the carbon atom due to an atom or a group.
Example: ${(C{H_3})_3}C - > {(C{H_3})_2}CH - > C{H_3} - C{H_2} - > C{H_3}$
Groups that have $ + I\,effect$ increases the electron density on the molecule responsible for donating an electron and becomes basic whereas groups with$ - I\,effect$ decreases the electron density and molecules becomes acidic thereby becoming electron deficient.
As the number of $ - I\,groups$ increases, acidity also increases, opposite is the case of $ + I\, groups$.
Thus, the given order is correct as the formic acid is more stable and acidic due to stability of conjugate base whereas benzoic acid is stabilised due to resonance of ring structure and aliphatic acid possesses less acidity than the other two.
Note:
Inductive effect is responsible for the high melting point, high boiling point and greater dipole moment of polar compounds. This effect weakens with increasing distance from the substituent and becomes almost negligible after three carbon atoms, this is the key point to keep in mind about inductive effect.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




