
Monocot root differs from dicot root in having
A. Open vascular bundles
B. Scattered vascular bundles
C. Well developed pith
D. Radially arranged vascular bundles
Answer
602.1k+ views
Hint: The plants which bear seeds having only one cotyledon are known as monocots whereas those having two cotyledons in their seeds are known as dicots.
Complete answer
Monocot roots differ from dicot roots in having a well-developed pith. The major differences between the monocot and dicot roots are as follows:
So, the correct answer is ‘Well developed pith'.
Note:
Pith or the medulla is the centremost region in a monocot root. It is made up of soft and spongy parenchymatous cells. It consists of round or angular cells with intercellular spaces between them. It is meant for the storage and transport of nutrients to the plants. It is present in the stem as well. It is rich in starch and serves as food, for example, a sago palm tree. The pith wood also helps in the cleaning of watch parts.
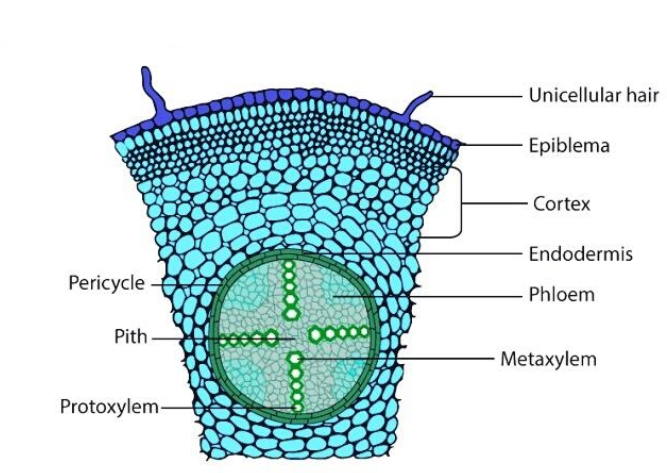
DICOT
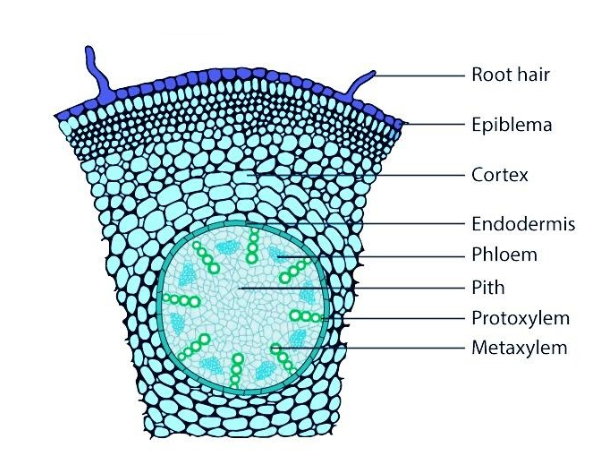
MONOCOT
Complete answer
Monocot roots differ from dicot roots in having a well-developed pith. The major differences between the monocot and dicot roots are as follows:
| Feature | Dicot root | Monocot root |
| Cortex | It is comparatively narrower. | It is very wide. |
| Cork | It is conspicuous and replaces the epiblema, cortex, and some part of endodermis. It can easily be seen on older roots. | Cork is absent. Epiblema peels off leaving behind cortex and endodermis. The older roots have a special covering known as exodermis. |
| Endodermis | It is relatively thinner with thick and prominent Casparian stripes. | The endodermal cells are highly thickened and possess Casparian strips at younger stages only. |
| Passage cells | They are absent. | They are present |
| Pericycle | It leads to formation of lateral roots along with cork cambium and vascular cambium. | It only forms lateral roots and not cambium. |
| Vascular bundles | They possess 2-5 bundles of xylem and phloem. | They possess eight or more than eight vascular bundles. The xylem vessels are round to oval in shape. |
| Secondary growth | It is present and takes place with the help of cork cambium and vascular cambium. | It is completely absent. |
| Pith | It is either completely absent or very small. | They have a well-developed pith in the center. |
So, the correct answer is ‘Well developed pith'.
Note:
Pith or the medulla is the centremost region in a monocot root. It is made up of soft and spongy parenchymatous cells. It consists of round or angular cells with intercellular spaces between them. It is meant for the storage and transport of nutrients to the plants. It is present in the stem as well. It is rich in starch and serves as food, for example, a sago palm tree. The pith wood also helps in the cleaning of watch parts.

DICOT

MONOCOT
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




