
Monocot root differs from dicot in having
A. No vascular bundles
B. Well-developed pith
C. Radially arranged vascular bundles
D. Open vascular bundles
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Monocot trees can be defined as those trees in which the seed of the fruit has a single cotyledon. For example, corn. The dicot trees can be defined as those trees in which the seed of the fruit has two cotyledons. Examples include beans.
Step by step answer:Roots of Dicot tree and monocot tree can be different on the basis of activity of pericycle, the number of vascular bundles, and the presence of medulla.
In monocot root, the medulla is well developed, whereas, in dicot root, the pith is reduced, because of the extensions of xylem strands in the roots.
In the dicot root, a well-developed pith is absent but in the case of monocot root, a well-developed pith is present.
Again, in dicot roots, open vascular bundles are present in roots which are radially arranged.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B. Well-developed pith.
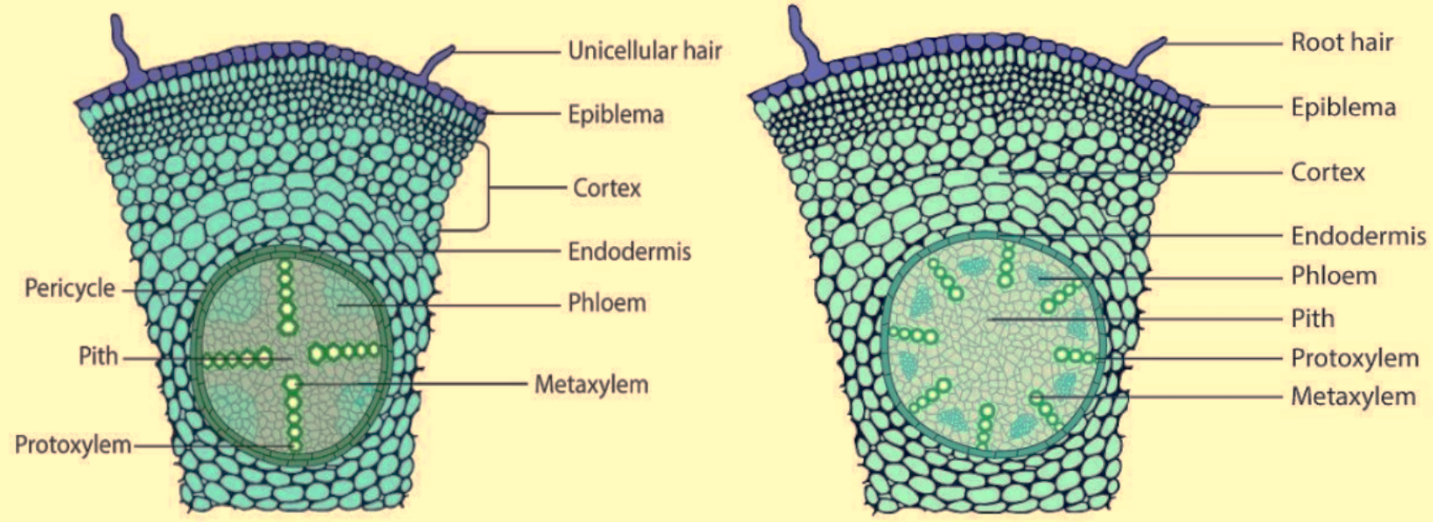
Note: The vascular bundle means the presence of xylem and phloem. The xylem helps in the transportation of water and minerals and the phloem helps in the transportation of food from source to sink. The source for the water is the root and for food is the leaves.
Step by step answer:Roots of Dicot tree and monocot tree can be different on the basis of activity of pericycle, the number of vascular bundles, and the presence of medulla.
In monocot root, the medulla is well developed, whereas, in dicot root, the pith is reduced, because of the extensions of xylem strands in the roots.
In the dicot root, a well-developed pith is absent but in the case of monocot root, a well-developed pith is present.
Again, in dicot roots, open vascular bundles are present in roots which are radially arranged.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B. Well-developed pith.

Note: The vascular bundle means the presence of xylem and phloem. The xylem helps in the transportation of water and minerals and the phloem helps in the transportation of food from source to sink. The source for the water is the root and for food is the leaves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




