
Monocot leaf can be distinguished from the dicot
(A)Stomata is equally distributed on both lower and upper epidermis
(B)Palisade cells on both upper and lower sides
(C)Several veins of nearly uniform size
(D)All of the above
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: Monocot leaf can be distinguished from the dicot in many ways like based on the distribution of tiny pores which help in gaseous exchange, the presence of leaf cells on both the cells, and many more.
Complete answer:
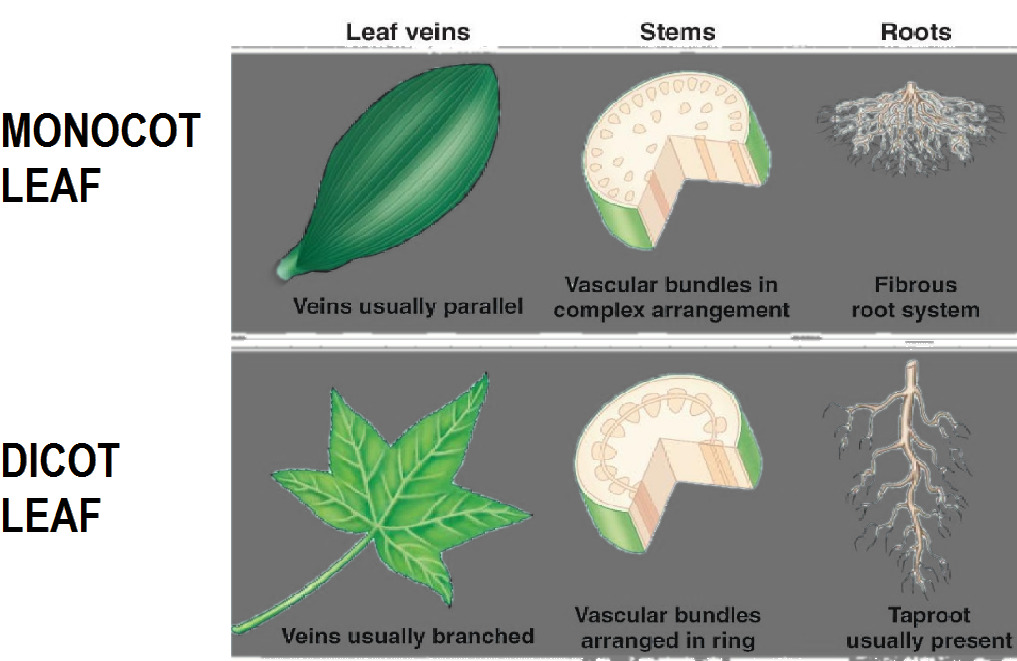
In monocots, as the leaf is mostly in an upright position, the stomata are distributed equally on both sides of the leaves. Palisade cells are the plant cells which are located on the leaves, right below the epidermis and cuticle. The mesophyll of a dicot leaf is differentiated into two distinct parts, the lower is spongy mesophyll and the upper is palisade. In monocot plant leaves no such differentiation is seen in mesophyll cells. In monocots, the veins which are present are near-uniform size but in dicots, the veins which are present have variation in size.
Additional Information:
There are many other differences between monocots and dicots. They are as follows:-
- One of the basic differences between them is that Embryo with a single cotyledon is present in monocots and dicot has Embryo with two cotyledons.
-In monocots, parallel venation is seen but in dicots, reticulate venation is seen.
-Secondary growth is absent in monocots but present in dicots.
-Flower parts are present in multiples of three in monocots but in dicots, flower parts are present in multiples of four or five.
-Fibrous roots are seen in monocots but in dicots, the taproot is seen.
So, the correct answer is ‘All of the above’.
Note: It is generally observed in monocots that parallel venations are found in nature but some monocots are exceptional cases that show reticulate venation. This type of exception can be seen in plant species that include Smilax and Colocasia. Similarly, in dicots reticulate venation is found but in some exceptions that include plant species like Calophyllum and Eryngium parallel venation is seen.
Complete answer:
In monocots, as the leaf is mostly in an upright position, the stomata are distributed equally on both sides of the leaves. Palisade cells are the plant cells which are located on the leaves, right below the epidermis and cuticle. The mesophyll of a dicot leaf is differentiated into two distinct parts, the lower is spongy mesophyll and the upper is palisade. In monocot plant leaves no such differentiation is seen in mesophyll cells. In monocots, the veins which are present are near-uniform size but in dicots, the veins which are present have variation in size.
Additional Information:
There are many other differences between monocots and dicots. They are as follows:-
- One of the basic differences between them is that Embryo with a single cotyledon is present in monocots and dicot has Embryo with two cotyledons.
-In monocots, parallel venation is seen but in dicots, reticulate venation is seen.
-Secondary growth is absent in monocots but present in dicots.
-Flower parts are present in multiples of three in monocots but in dicots, flower parts are present in multiples of four or five.
-Fibrous roots are seen in monocots but in dicots, the taproot is seen.
So, the correct answer is ‘All of the above’.
Note: It is generally observed in monocots that parallel venations are found in nature but some monocots are exceptional cases that show reticulate venation. This type of exception can be seen in plant species that include Smilax and Colocasia. Similarly, in dicots reticulate venation is found but in some exceptions that include plant species like Calophyllum and Eryngium parallel venation is seen.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




