
Mono sodium acetylide reacts with an alkyl halide to form:
(A) An alkane
(B) An alkene
(C) an unsymmetrical higher alkyne
(D) a symmetrical higher alkyne
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: As we know that acetylene contains two hydrogen and two carbon in which carbon is attached with another carbon with triple bond if sodium is attached with acetylene then it will act as a nucleophile.
Complete step by step answer:
The mono sodium acetylide is prepared by sodium hydroxide (a strong base). When acetylene reacts with sodium hydroxide, this abstracts the hydrogen from acetylene because the acetylene proton is acidic due to \[sp\] hybridization of carbon thus, water eliminates and we get mono sodium acetylide which is represented as \[CH \equiv {C^ - }N{a^ + }\].
Now \[CH \equiv {C^ - }N{a^ + }\] contains a dipolar group (ylide) and acts as a nucleophile so it reacts with alkyl halide by \[S{N^2}\] (nucleophilic substitution reaction) process. The alkyl halide contains a halogen element which is a good leaving group that can easily leave when\[CH \equiv {C^ - }N{a^ + }\] attacks on it.
As we can see in the mechanism-
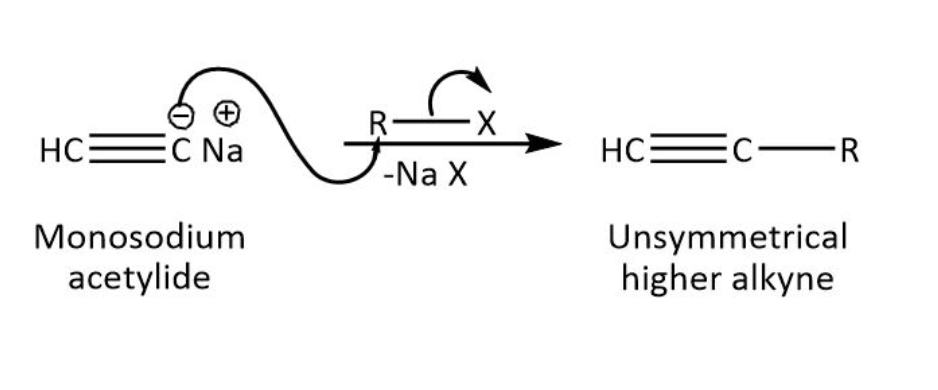
Therefore, the alkyl group is attached with the nucleophilic carbon by eliminating sodium halide.
Now the product is formed which contains an alkyne group and alkyl group so the correct option is option (C).
Note:
The symmetrical higher alkyne can also be prepared with the above mechanism but we have to take two equivalents of sodium hydroxide.
Complete step by step answer:
The mono sodium acetylide is prepared by sodium hydroxide (a strong base). When acetylene reacts with sodium hydroxide, this abstracts the hydrogen from acetylene because the acetylene proton is acidic due to \[sp\] hybridization of carbon thus, water eliminates and we get mono sodium acetylide which is represented as \[CH \equiv {C^ - }N{a^ + }\].
Now \[CH \equiv {C^ - }N{a^ + }\] contains a dipolar group (ylide) and acts as a nucleophile so it reacts with alkyl halide by \[S{N^2}\] (nucleophilic substitution reaction) process. The alkyl halide contains a halogen element which is a good leaving group that can easily leave when\[CH \equiv {C^ - }N{a^ + }\] attacks on it.
As we can see in the mechanism-

Therefore, the alkyl group is attached with the nucleophilic carbon by eliminating sodium halide.
Now the product is formed which contains an alkyne group and alkyl group so the correct option is option (C).
Note:
The symmetrical higher alkyne can also be prepared with the above mechanism but we have to take two equivalents of sodium hydroxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




