
Molybdenum forms body-centred cubic crystals whose density is 10.3$g.c{m^{ - 3}}$. Calculate the edge length of the unit cell. The molar mass of Mo is 95.94$g.mo{l^{ - 1}}$.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: First find out the total number of atoms present in a bcc lattice. Then use the formula: $d = \dfrac{{z \times M}}{{{N_A} \times {a^3}}}$ to calculate the edge length of the unit cell, which can also be written as:
$a = \sqrt[3]{{\dfrac{{z \times M}}{{{N_A} \times d}}}}$
Formula used:
-Density of a unit cell: $d = \dfrac{{z \times M}}{{{N_A} \times {a^3}}}$ (A)
Where, d = density of the unit cell;
z = number of atoms present in the unit cell;
M = molar mass of the atom;
${N_A}$= Avogadro number;
a = side length of the unit cell.
Complete answer:
-First of all we need to see what a body centred cubic crystal (bcc) is.
In a body centred cubic unit cell or crystal atoms are present at each of its 8 corners and one atom is present at the body centre.
The total number of atoms present in a bcc crystal are:
(1)8 corner atoms × (1/8) contribution of each corner atom = 1 atom
(2)1 body centre atom
So, in total 2 atoms are present in a bcc crystal. It looks like:
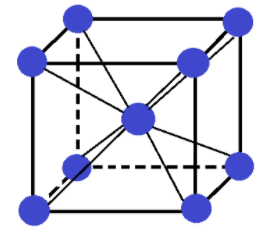
-The values for a Mo bcc structure given in the question are: d = 10.3$g.c{m^{ - 3}}$, M = 95.94$g.mo{l^{ - 1}}$ and we know that ${N_A}$= $6.023 \times {10^{23}}$. Also in the above discussion we just saw that for a bcc crystal z = 2.
Since we have d, M, ${N_A}$and z; we can find out the value of ‘a’ using the equation (A).
$d = \dfrac{{z \times M}}{{{N_A} \times {a^3}}}$
$10.3 = \dfrac{{2 \times 95.94}}{{6.023 \times {{10}^{23}} \times {a^3}}}$
${a^3} = \dfrac{{2 \times 95.94}}{{6.023 \times {{10}^{23}} \times 10.3}}$
= $\dfrac{{191.88}}{{62.0369 \times {{10}^{23}}}}$
= $3.092997 \times {10^{ - 23}}c{m^3}$
$a = \sqrt[3]{{3.092997 \times {{10}^{ - 23}}}}$
= $3.14 \times {10^{ - 8}}cm$
= 3.14 Å
So, the side of the cubic crystal is 3.14 Å.
Note:
In a bcc crystal or lattice there are only 2 atoms present and so it has a packing efficiency of 68%. Iron, chromium, tungsten and niobium also exhibit bcc structure.
$a = \sqrt[3]{{\dfrac{{z \times M}}{{{N_A} \times d}}}}$
Formula used:
-Density of a unit cell: $d = \dfrac{{z \times M}}{{{N_A} \times {a^3}}}$ (A)
Where, d = density of the unit cell;
z = number of atoms present in the unit cell;
M = molar mass of the atom;
${N_A}$= Avogadro number;
a = side length of the unit cell.
Complete answer:
-First of all we need to see what a body centred cubic crystal (bcc) is.
In a body centred cubic unit cell or crystal atoms are present at each of its 8 corners and one atom is present at the body centre.
The total number of atoms present in a bcc crystal are:
(1)8 corner atoms × (1/8) contribution of each corner atom = 1 atom
(2)1 body centre atom
So, in total 2 atoms are present in a bcc crystal. It looks like:

-The values for a Mo bcc structure given in the question are: d = 10.3$g.c{m^{ - 3}}$, M = 95.94$g.mo{l^{ - 1}}$ and we know that ${N_A}$= $6.023 \times {10^{23}}$. Also in the above discussion we just saw that for a bcc crystal z = 2.
Since we have d, M, ${N_A}$and z; we can find out the value of ‘a’ using the equation (A).
$d = \dfrac{{z \times M}}{{{N_A} \times {a^3}}}$
$10.3 = \dfrac{{2 \times 95.94}}{{6.023 \times {{10}^{23}} \times {a^3}}}$
${a^3} = \dfrac{{2 \times 95.94}}{{6.023 \times {{10}^{23}} \times 10.3}}$
= $\dfrac{{191.88}}{{62.0369 \times {{10}^{23}}}}$
= $3.092997 \times {10^{ - 23}}c{m^3}$
$a = \sqrt[3]{{3.092997 \times {{10}^{ - 23}}}}$
= $3.14 \times {10^{ - 8}}cm$
= 3.14 Å
So, the side of the cubic crystal is 3.14 Å.
Note:
In a bcc crystal or lattice there are only 2 atoms present and so it has a packing efficiency of 68%. Iron, chromium, tungsten and niobium also exhibit bcc structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




