
What is the molecular geometry of $ AsC{{l}_{3}} $ ?
(A) Tetrahedral.
(B) Trigonal Pyramidal.
(C) Trigonal Planar.
(D) T-Shaped.
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: We know that the molecular geometry of a molecule gives the general shape, bend angles, Torsional angles, bond lengths etc. the Propertius like polarity, reactivity, Colour, state of matter etc. can be determined by knouting the molecular geometry of the molecule.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have a basic ideology that molecular geometry is determined with the help of some special techniques named as spectroscopic and diffraction methods, example: X Rays , NMR, $ 1R, $ Raman spectroscopy etc. The geometry of individual molecules is discussed below;
To determine the molecular geometry of arsenic trichloride, $ AsC{{l}_{3}} $ , we must take a look at its Lewis structure. One arsenic trichloride molecule will have a total of $ 26 $ valence electrons $ -~5~ $ from the arsenic atom and $ 7 $ from each of the three chlorine atoms.
The arsenic atom will be bonded to the three chlorine atoms through single bonds that account for 6 of the $ 24 $ valence electrons. Each of the chlorine atoms will have three lone pairs, which will bring the number of valence electrons used to $ 24. $
The remaining two valence electrons will be placed on the arsenic atom as a lone pair.
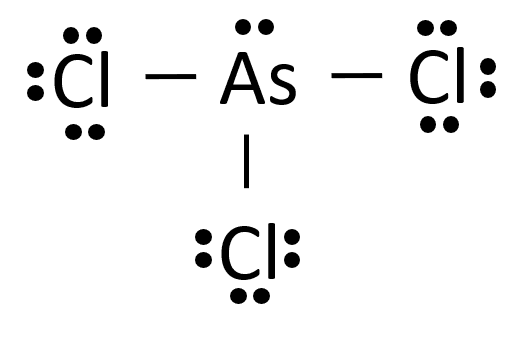
According to Theory, the geometry of $ AsC{{l}_{3}} $ is trigonal planar.
The correct answer is option (C).
Note :
Remember that $ VSEPR $ is a short form of the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. This theory. Can predict the geometry of many molecules, especially those belonging to the p block, in theory, the geometry of a molecule atom. The geometry of a molecule depends upon the number of valence shell electrons around the central atom. The pairs of electrons try to occupy minimum repulsion and maximal distance orientation in space.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have a basic ideology that molecular geometry is determined with the help of some special techniques named as spectroscopic and diffraction methods, example: X Rays , NMR, $ 1R, $ Raman spectroscopy etc. The geometry of individual molecules is discussed below;
To determine the molecular geometry of arsenic trichloride, $ AsC{{l}_{3}} $ , we must take a look at its Lewis structure. One arsenic trichloride molecule will have a total of $ 26 $ valence electrons $ -~5~ $ from the arsenic atom and $ 7 $ from each of the three chlorine atoms.
The arsenic atom will be bonded to the three chlorine atoms through single bonds that account for 6 of the $ 24 $ valence electrons. Each of the chlorine atoms will have three lone pairs, which will bring the number of valence electrons used to $ 24. $
The remaining two valence electrons will be placed on the arsenic atom as a lone pair.

According to Theory, the geometry of $ AsC{{l}_{3}} $ is trigonal planar.
The correct answer is option (C).
Note :
Remember that $ VSEPR $ is a short form of the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. This theory. Can predict the geometry of many molecules, especially those belonging to the p block, in theory, the geometry of a molecule atom. The geometry of a molecule depends upon the number of valence shell electrons around the central atom. The pairs of electrons try to occupy minimum repulsion and maximal distance orientation in space.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




