
What minimum is to be pulled Contacts \[15\]. I’ll be force by the rod on one of the blocks \[20\]. A block of mass M is kept on a rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is\[\mu \]. The block is to be pulled by applying a force to it. What minimum force is needed to side the block? In which direction should this block force act? The friction coefficient, between the board and the floor block? In what motion should I be bored?
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: The coefficient of friction is a dimensionless scalar value. The coefficient of friction is a ratio of the force friction between two bodies and force pressing together. Friction does not depend on the amount of surface area in contact between moving bodies. Friction depends on the magnitude of the forces holding the bodies together. The coefficients of friction range from \[0\] to greater than 1.
Complete step-by-step solution:
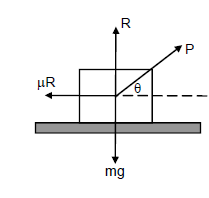
Let ‘\[P\] ’ be the force applied to at an angle \[\theta \] from the free body diagram.
\[R + P\sin \theta - mg = 0\]
\[R = - P\sin \theta + mg \to \left( 1 \right)\]
\[\mu R - P\cos \theta \to \left( 2 \right)\]
Equation \[\left( 1 \right)\mu \left( {mg - P\sin \theta } \right) - P\cos \theta = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \mu mg = \mu \rho \sin \theta - P\cos \theta \Rightarrow \rho = \dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\mu \sin \theta + \cos \theta }}\]
Applied force \[P\] should be minimum, when \[\mu \sin \theta + \cos \theta \] is maximum again, \[\mu \sin \theta + \cos \theta \] is maximum when its derivative is zero.
Therefore, \[d/d\theta \left( {\mu \sin \theta + \cos \theta } \right) = 0\]
\[\mu \cos \theta - \sin \theta = 0\]
\[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\mu \]
So,\[P = \dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\mu \sin \theta + \cos \theta }} = \dfrac{{\mu mg/\cos \theta }}{{\dfrac{{\mu \sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }} + \dfrac{{\cos \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}}} = \dfrac{{\mu mg\sec \theta }}{{1 + \mu \tan \theta }} = \dfrac{{\mu mg\sec \theta }}{{1 + {{\tan }^2}\theta }}\]
\[ = \dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\sec \theta }} = \dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\sqrt {\left( {1 + {{\tan }^2}\theta } \right)} }} = \dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\sqrt {1 + {\mu ^2}} }}\]
The minimum force is \[\dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\sqrt {1 + {\mu ^2}} }}\] at an angle \[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\mu \].
The block should move in the direction of the larger force. So, the block moves to the left side.
The friction coefficient between the board and floor is \[\mu \]. Therefore the maximum friction force which the floor can exert is \[\mu N\], when \[N\] is the normal reaction at the contact surface between the board and the floor.
Note:The static coefficient of friction is applied to motionless objects. The low value of the coefficient of friction is that the force required for sliding occurs is less than the force required when the coefficient of friction is high. The coefficients of friction range from \[0\] to greater than 1.
Complete step-by-step solution:

Let ‘\[P\] ’ be the force applied to at an angle \[\theta \] from the free body diagram.
\[R + P\sin \theta - mg = 0\]
\[R = - P\sin \theta + mg \to \left( 1 \right)\]
\[\mu R - P\cos \theta \to \left( 2 \right)\]
Equation \[\left( 1 \right)\mu \left( {mg - P\sin \theta } \right) - P\cos \theta = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \mu mg = \mu \rho \sin \theta - P\cos \theta \Rightarrow \rho = \dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\mu \sin \theta + \cos \theta }}\]
Applied force \[P\] should be minimum, when \[\mu \sin \theta + \cos \theta \] is maximum again, \[\mu \sin \theta + \cos \theta \] is maximum when its derivative is zero.
Therefore, \[d/d\theta \left( {\mu \sin \theta + \cos \theta } \right) = 0\]
\[\mu \cos \theta - \sin \theta = 0\]
\[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\mu \]
So,\[P = \dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\mu \sin \theta + \cos \theta }} = \dfrac{{\mu mg/\cos \theta }}{{\dfrac{{\mu \sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }} + \dfrac{{\cos \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}}} = \dfrac{{\mu mg\sec \theta }}{{1 + \mu \tan \theta }} = \dfrac{{\mu mg\sec \theta }}{{1 + {{\tan }^2}\theta }}\]
\[ = \dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\sec \theta }} = \dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\sqrt {\left( {1 + {{\tan }^2}\theta } \right)} }} = \dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\sqrt {1 + {\mu ^2}} }}\]
The minimum force is \[\dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\sqrt {1 + {\mu ^2}} }}\] at an angle \[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\mu \].
The block should move in the direction of the larger force. So, the block moves to the left side.
The friction coefficient between the board and floor is \[\mu \]. Therefore the maximum friction force which the floor can exert is \[\mu N\], when \[N\] is the normal reaction at the contact surface between the board and the floor.
Note:The static coefficient of friction is applied to motionless objects. The low value of the coefficient of friction is that the force required for sliding occurs is less than the force required when the coefficient of friction is high. The coefficients of friction range from \[0\] to greater than 1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




