
What is the minimum area of the triangle formed by any tangent to the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ with the coordinate axis.
Answer
498k+ views
Hint: The standard form equation of the ellipse is given by $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$.The coordinates of any point lying on the ellipse is represented by $(a\cos \theta ,b\sin \theta )$. The equation of the tangent at this point on the ellipse is given by $\dfrac{x}{a}\cos \theta + \dfrac{y}{b}\sin \theta = 1$.
To minimise the area of the triangle, we have to find the generalised form of the area formed using the tangent and ellipse and determine the condition to minimize the area.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given ellipse has the equation $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$.
Choose any point R on the ellipse, so the coordinates of the point R are represented as $R = (a\cos \theta ,b\sin \theta )$.
Let us draw the tangent at this point R on the ellipse, such that the tangent meets the y-axis at point Q and meets x-axis at point P.
The given figure represents the above ellipse and the mentioned tangent:
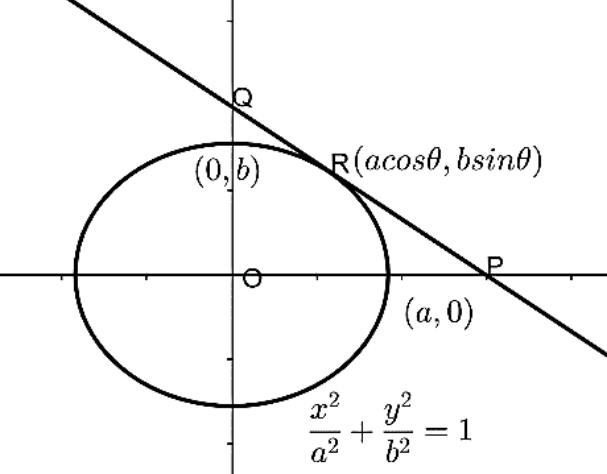
Now, the parametric form of the equation of the tangent at the point $(a\cos \theta ,b\sin \theta )$ is given by $\dfrac{x}{a}\cos \theta + \dfrac{y}{b}\sin \theta = 1$.
The above equation can be written as
$\dfrac{x}{{\left( {\dfrac{a}{{\cos \theta }}} \right)}} + \dfrac{y}{{\left( {\dfrac{b}{{\sin \theta }}} \right)}} = 1$
So, the x and y coordinates of the above tangent equation are
$P = \left( {\dfrac{a}{{\cos \theta }},0} \right)$
$Q = \left( {0,\dfrac{b}{{\sin \theta }}} \right)$
Now, we get the three coordinates of the triangle formed by the tangent on the ellipse.
The triangle $\Delta QOP$has the coordinates,
$
P = \left( {\dfrac{a}{{\cos \theta }},0} \right) \\
Q = \left( {0,\dfrac{b}{{\sin \theta }}} \right) \\
O = \left( {0,0} \right) $
Find the area of the above triangle, using the formulae: $Area = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height$, where base is $\dfrac{a}{{\cos \theta }}$ and height is $\dfrac{b}{{\sin \theta }}$.
Area of $\Delta QOP = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left| {\dfrac{a}{{\cos \theta }} \times \dfrac{b}{{\sin \theta }}} \right|$
Since, $a$ and $b$ cannot be negative so modulus can be removed from them,
Area of $\Delta QOP = ab \times \left| {\dfrac{1}{{2\cos \theta \sin \theta }}} \right|$
Use the identity: $2\sin \theta \cos \theta = \sin 2\theta $
Area of $\Delta QOP = ab \times \left| {\dfrac{1}{{\sin 2\theta }}} \right|$
To reduce the area of the triangle $\Delta QOP$, we need to reduce the value of \[\left| {\dfrac{1}{{\sin 2\theta }}} \right|\].
Since, \[\left| {\sin 2\theta } \right| \leqslant 1\]
Taking the reciprocal, \[\left| {\dfrac{1}{{\sin 2\theta }}} \right| \geqslant 1\]
Since, the minimum value \[\left| {\dfrac{1}{{\sin 2\theta }}} \right|\]is 1, hence the minimum value of the area of $\Delta QOP$ is \[ab\].
The minimum area of the triangle formed by any tangent to the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ with the coordinate axis is \[ab\].
Note: The minimum value of \[\sin \theta \] can be $ - 1$ and the maximum value is $1$. So, the value of \[\sin \theta \] always lies between $ - 1$ and $1$, and can be represented as, \[ - 1 < \sin \theta < 1\] or \[\left| {\sin \theta } \right| \leqslant 1\].The equation of the form $\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1$ has $x$ intercept $a$, and $y$intercept is $b$.
To minimise the area of the triangle, we have to find the generalised form of the area formed using the tangent and ellipse and determine the condition to minimize the area.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given ellipse has the equation $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$.
Choose any point R on the ellipse, so the coordinates of the point R are represented as $R = (a\cos \theta ,b\sin \theta )$.
Let us draw the tangent at this point R on the ellipse, such that the tangent meets the y-axis at point Q and meets x-axis at point P.
The given figure represents the above ellipse and the mentioned tangent:

Now, the parametric form of the equation of the tangent at the point $(a\cos \theta ,b\sin \theta )$ is given by $\dfrac{x}{a}\cos \theta + \dfrac{y}{b}\sin \theta = 1$.
The above equation can be written as
$\dfrac{x}{{\left( {\dfrac{a}{{\cos \theta }}} \right)}} + \dfrac{y}{{\left( {\dfrac{b}{{\sin \theta }}} \right)}} = 1$
So, the x and y coordinates of the above tangent equation are
$P = \left( {\dfrac{a}{{\cos \theta }},0} \right)$
$Q = \left( {0,\dfrac{b}{{\sin \theta }}} \right)$
Now, we get the three coordinates of the triangle formed by the tangent on the ellipse.
The triangle $\Delta QOP$has the coordinates,
$
P = \left( {\dfrac{a}{{\cos \theta }},0} \right) \\
Q = \left( {0,\dfrac{b}{{\sin \theta }}} \right) \\
O = \left( {0,0} \right) $
Find the area of the above triangle, using the formulae: $Area = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height$, where base is $\dfrac{a}{{\cos \theta }}$ and height is $\dfrac{b}{{\sin \theta }}$.
Area of $\Delta QOP = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left| {\dfrac{a}{{\cos \theta }} \times \dfrac{b}{{\sin \theta }}} \right|$
Since, $a$ and $b$ cannot be negative so modulus can be removed from them,
Area of $\Delta QOP = ab \times \left| {\dfrac{1}{{2\cos \theta \sin \theta }}} \right|$
Use the identity: $2\sin \theta \cos \theta = \sin 2\theta $
Area of $\Delta QOP = ab \times \left| {\dfrac{1}{{\sin 2\theta }}} \right|$
To reduce the area of the triangle $\Delta QOP$, we need to reduce the value of \[\left| {\dfrac{1}{{\sin 2\theta }}} \right|\].
Since, \[\left| {\sin 2\theta } \right| \leqslant 1\]
Taking the reciprocal, \[\left| {\dfrac{1}{{\sin 2\theta }}} \right| \geqslant 1\]
Since, the minimum value \[\left| {\dfrac{1}{{\sin 2\theta }}} \right|\]is 1, hence the minimum value of the area of $\Delta QOP$ is \[ab\].
The minimum area of the triangle formed by any tangent to the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ with the coordinate axis is \[ab\].
Note: The minimum value of \[\sin \theta \] can be $ - 1$ and the maximum value is $1$. So, the value of \[\sin \theta \] always lies between $ - 1$ and $1$, and can be represented as, \[ - 1 < \sin \theta < 1\] or \[\left| {\sin \theta } \right| \leqslant 1\].The equation of the form $\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1$ has $x$ intercept $a$, and $y$intercept is $b$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




