
Methyl orange is used as an indicator. It shows colour changes in acid, base and neutral substance. Tabulate your results as follows:
Indicator Colour change inference Methyl orange No change --- -- Acid Yellow ---
| Indicator | Colour change | inference |
| Methyl orange | No change | --- |
| -- | Acid | |
| Yellow | --- |
Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint: Indicators are the substance that changes colour in the reaction. Colour change depends upon the pH. Indicators are used to determine the end point of the acid-base titration.
Complete step-by-step answer:Methyl orange is a weak base. Methyl orange indicator is used in the strong acid weak base titration.
The colour change of methyl orange depends upon the pH of the solution. In acidic medium means pH below $3.0$ it shows red colour. In the range $3.0 - 4.5$ pH, Methyl orange is of orange colour and in basic medium shows yellow colour.
The structure of methyl orange is as follows:
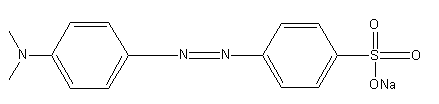
The change in methyl orange is represented as:
\[\mathop {{\text{HIn}}}\limits_{{\text{red}}} {\text{(aq)}}\, + \,{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\, \rightleftharpoons {H_3}{O^ + }{\text{(aq)}}\,{\text{ + }}{\mathop {\,{\text{In}}}\limits_{{\text{yellow}}} ^ - }(aq)\]
As the base is titrated with acid, initially in the basic medium methyl orange shows yellow colour. As the acid is added, concentration of acid increases, so the methyl orange remains in unionised form which is of red colour.
Methyl orange is of orange in acidic medium and
Results are tabulated as follows:
Note:Methyl orange shows different colours in acid, base and neutral substance. It changes colour from red to orange to yellow as the pH of the solution increases. As the pH decreases the colour changes from yellow to orange to red. Phenolphthalein, methyl blue, Erichrome blue are some of the indicators. At the end point, the base is completely neutralised with acid so both are present in equal amounts so, at the end point, sharp colour change is observed.
Complete step-by-step answer:Methyl orange is a weak base. Methyl orange indicator is used in the strong acid weak base titration.
The colour change of methyl orange depends upon the pH of the solution. In acidic medium means pH below $3.0$ it shows red colour. In the range $3.0 - 4.5$ pH, Methyl orange is of orange colour and in basic medium shows yellow colour.
The structure of methyl orange is as follows:

The change in methyl orange is represented as:
\[\mathop {{\text{HIn}}}\limits_{{\text{red}}} {\text{(aq)}}\, + \,{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\, \rightleftharpoons {H_3}{O^ + }{\text{(aq)}}\,{\text{ + }}{\mathop {\,{\text{In}}}\limits_{{\text{yellow}}} ^ - }(aq)\]
As the base is titrated with acid, initially in the basic medium methyl orange shows yellow colour. As the acid is added, concentration of acid increases, so the methyl orange remains in unionised form which is of red colour.
Methyl orange is of orange in acidic medium and
Results are tabulated as follows:
| Indicator | Colour change | inference |
| Methyl orange | No change | Neutral |
| Red | Acid | |
| Yellow | Base |
Note:Methyl orange shows different colours in acid, base and neutral substance. It changes colour from red to orange to yellow as the pH of the solution increases. As the pH decreases the colour changes from yellow to orange to red. Phenolphthalein, methyl blue, Erichrome blue are some of the indicators. At the end point, the base is completely neutralised with acid so both are present in equal amounts so, at the end point, sharp colour change is observed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




