
How is Methoxyethane prepared from:
(a) Methyl iodide (b) Diazomethane
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: For the preparation of ethyl methyl ether from methyl iodide or diazomethane look for the reagents and bases that will be needed to in order to introduce the ethoxy group with the methyl group (this methyl group will come from methyl iodide or diazomethane).
Complete step by step solution:
Methoxyethane is also called ethyl methyl ether. It is clear colourless gas with an odour of medicine. Its boiling point is very low (7.6 $ ^{ o }{ C }$).Water is more dense than Methoxyethane but the vapours of Methoxyethane are heavier than air. Since it is highly flammable therefore on a prolonged exposure to heat or fire, the containers containing the Methoxyethane may explode violently. If it is inhaled, it may cause asphyxiation or dizziness. It is a Lewis base because of the presence of two lone pairs on the oxygen atom in its structure. Its structure is shown below:
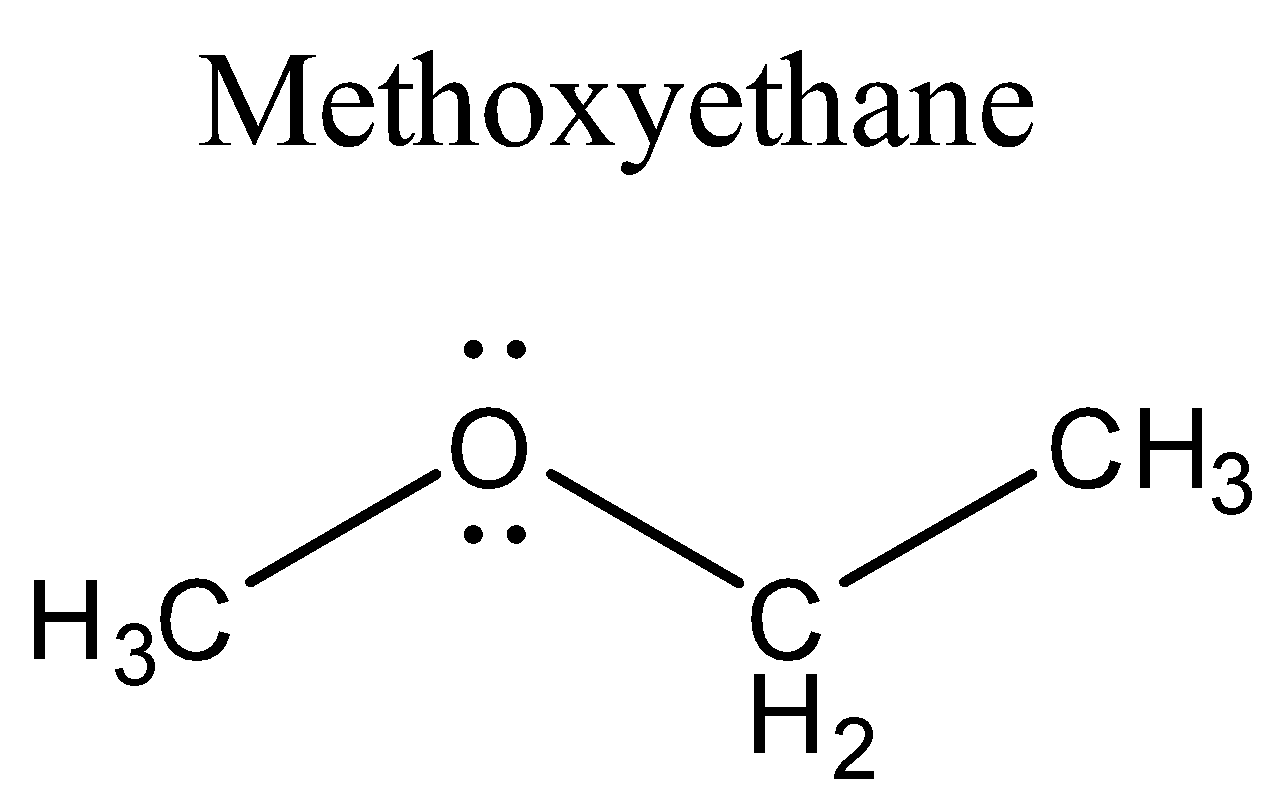
It reacts with Lewis acids and forms salts (acid-base reaction).
-Preparation of ethyl methyl ether (Methoxyethane) from methyl iodide :
The methyl iodide is heated with alcoholic sodium ethoxide in order to form ethyl methyl ether. The reaction is given below:
$ \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }ONa(s) \\ Sodium\quad methoxide \end{matrix}+\begin{matrix} { CH }_{ 3 }-I(l) \\ Methyl\quad iodide \end{matrix}\xrightarrow { \triangle } \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }O{ CH }_{ 3 }(g) \\ ethyl\quad methyl\quad ether \end{matrix}+\begin{matrix} NaI(s) \\ Sodium\quad iodide \end{matrix}$
This reaction is a $ { S }_{ N }2$ substitution reaction where the base sodium ethoxide is attacking the methyl iodide such that the leaning group (iodide ion) leaves.
-Preparation of ethyl methyl ether from diazomethane :
Ethyl alcohol is treated with diazomethane in presence of fluoroboric acid in order to produce ethyl methyl ether. The reaction is given below:
$ \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }-OH(l) \\ Ethanol \end{matrix}+\begin{matrix} { CH }_{ 2 }{ N }_{ 2 }(l) \\ Diazomethane \end{matrix}\xrightarrow [ \triangle ]{ HB{ F }_{ 4 } } \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }O{ CH }_{ 3 }(g) \\ Ethyl\quad methyl\quad ether \end{matrix}+\begin{matrix} { N }_{ 2 }(g) \\ Nitrogen \end{matrix}$
Hence ethyl methyl ether can be prepared from both diazomethane and methyl iodide.
Note: Methoxyethane or more appropriately 1-Methoxyethane is the IUPAC name of the compound ethyl methyl ether. For the preparation of ethyl methyl ether from diazomethane, instead of a fluoroboric acid (which acts as an acid catalyst) we can use acids such as $Sn{ Cl }_{ 2 }$, $B{ F }_{ 3 }-OEt$ or silica.
Complete step by step solution:
Methoxyethane is also called ethyl methyl ether. It is clear colourless gas with an odour of medicine. Its boiling point is very low (7.6 $ ^{ o }{ C }$).Water is more dense than Methoxyethane but the vapours of Methoxyethane are heavier than air. Since it is highly flammable therefore on a prolonged exposure to heat or fire, the containers containing the Methoxyethane may explode violently. If it is inhaled, it may cause asphyxiation or dizziness. It is a Lewis base because of the presence of two lone pairs on the oxygen atom in its structure. Its structure is shown below:

It reacts with Lewis acids and forms salts (acid-base reaction).
-Preparation of ethyl methyl ether (Methoxyethane) from methyl iodide :
The methyl iodide is heated with alcoholic sodium ethoxide in order to form ethyl methyl ether. The reaction is given below:
$ \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }ONa(s) \\ Sodium\quad methoxide \end{matrix}+\begin{matrix} { CH }_{ 3 }-I(l) \\ Methyl\quad iodide \end{matrix}\xrightarrow { \triangle } \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }O{ CH }_{ 3 }(g) \\ ethyl\quad methyl\quad ether \end{matrix}+\begin{matrix} NaI(s) \\ Sodium\quad iodide \end{matrix}$
This reaction is a $ { S }_{ N }2$ substitution reaction where the base sodium ethoxide is attacking the methyl iodide such that the leaning group (iodide ion) leaves.
-Preparation of ethyl methyl ether from diazomethane :
Ethyl alcohol is treated with diazomethane in presence of fluoroboric acid in order to produce ethyl methyl ether. The reaction is given below:
$ \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }-OH(l) \\ Ethanol \end{matrix}+\begin{matrix} { CH }_{ 2 }{ N }_{ 2 }(l) \\ Diazomethane \end{matrix}\xrightarrow [ \triangle ]{ HB{ F }_{ 4 } } \begin{matrix} { C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }O{ CH }_{ 3 }(g) \\ Ethyl\quad methyl\quad ether \end{matrix}+\begin{matrix} { N }_{ 2 }(g) \\ Nitrogen \end{matrix}$
Hence ethyl methyl ether can be prepared from both diazomethane and methyl iodide.
Note: Methoxyethane or more appropriately 1-Methoxyethane is the IUPAC name of the compound ethyl methyl ether. For the preparation of ethyl methyl ether from diazomethane, instead of a fluoroboric acid (which acts as an acid catalyst) we can use acids such as $Sn{ Cl }_{ 2 }$, $B{ F }_{ 3 }-OEt$ or silica.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




