
Methanogens belong to
(a)Dinoflagellates
(b)Slime moulds
(c)Eubacteria
(d)Archaebacteria
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: The most primitive monerans belong to methanogens. They are a single-celled organism domain. They are anaerobes that are facultative obligate. They lack well-defined cell nuclei and are thus prokaryotes. Methanobrevibacter smithii is an example of a methanogen.
Complete answer:
The division of species into three kingdoms, Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, and Eukaryotes, which were later referred to as domains, was proposed by Carl Woese. The archaebacteria are the group that consists, like methanogens, of primitive prokaryotic organisms. The cell wall lacks peptidoglycan and can transform methane gas into carbon dioxide and hydrogen. For the reduction of carbon dioxide, hydrogen serves as an electron donor.
Additional Information: -Archaebacteria belong to methanogens. They are autotrophs that obtain both energy and carbon from products of decomposition. They occur in marshy areas where, with the help of hydrogen, they convert formic acid and carbon dioxide to methane. In the processing of methane and fuel gas within gobar gas plants, this capability is commercially exploited e.g., Methanobacterium, Methanococcus.
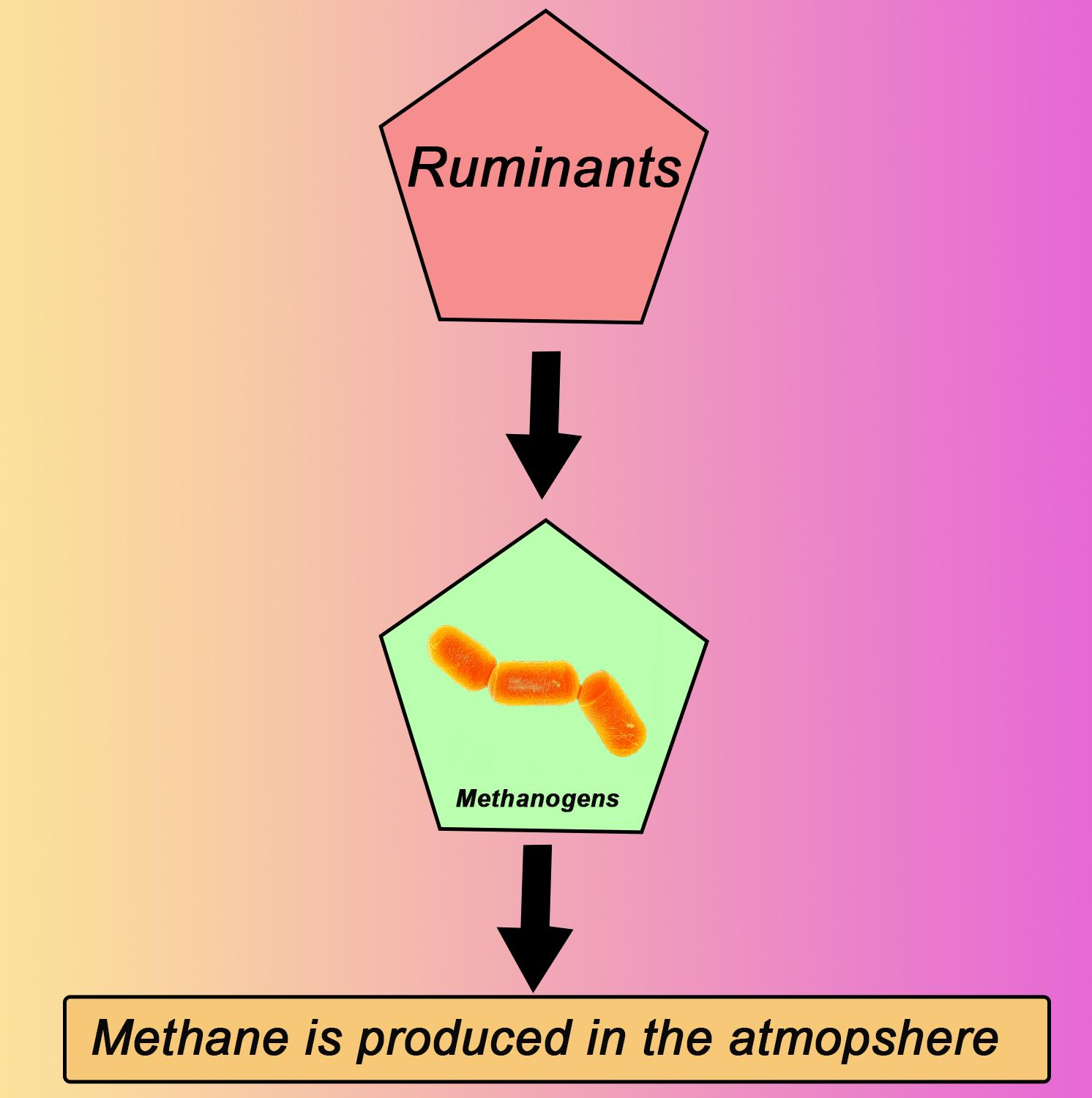
Some of the methanogens reside inside the rumen of herbivorous animals that chew their cuds as symbionts. These archaebacteria are useful for the fermentation of cellulose by ruminants.
-Methanogens are often found in animal guts, deep aquatic sediment layers, hydrothermal vents, and wetlands.
They are essential, as in the flatulence in humans, for the methane in the belches of ruminants and the marsh gas of the wetlands. Methanogens, which generate methane rather than absorb it, should not be confused with methanotrophs.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Archaebacteria’.
Note: Methanogens are microorganisms that in hypoxic conditions emit methane as a metabolic byproduct. They are prokaryotic and belong to the Archaea domain. The biological production of methane, also called methanogenesis, in marine sediments is normally limited to where sulfates are reduced, below the top layers. Moreover, populations of methanogenic archaea play an invaluable role in the treatment of anaerobic wastewater. Some are extremophiles, located kilometers below the surface in settings such as hot springs and submarine hydrothermal vents as well as in the "solid" rock of the Earth's crust.
Complete answer:
The division of species into three kingdoms, Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, and Eukaryotes, which were later referred to as domains, was proposed by Carl Woese. The archaebacteria are the group that consists, like methanogens, of primitive prokaryotic organisms. The cell wall lacks peptidoglycan and can transform methane gas into carbon dioxide and hydrogen. For the reduction of carbon dioxide, hydrogen serves as an electron donor.
Additional Information: -Archaebacteria belong to methanogens. They are autotrophs that obtain both energy and carbon from products of decomposition. They occur in marshy areas where, with the help of hydrogen, they convert formic acid and carbon dioxide to methane. In the processing of methane and fuel gas within gobar gas plants, this capability is commercially exploited e.g., Methanobacterium, Methanococcus.
Some of the methanogens reside inside the rumen of herbivorous animals that chew their cuds as symbionts. These archaebacteria are useful for the fermentation of cellulose by ruminants.
-Methanogens are often found in animal guts, deep aquatic sediment layers, hydrothermal vents, and wetlands.
They are essential, as in the flatulence in humans, for the methane in the belches of ruminants and the marsh gas of the wetlands. Methanogens, which generate methane rather than absorb it, should not be confused with methanotrophs.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Archaebacteria’.
Note: Methanogens are microorganisms that in hypoxic conditions emit methane as a metabolic byproduct. They are prokaryotic and belong to the Archaea domain. The biological production of methane, also called methanogenesis, in marine sediments is normally limited to where sulfates are reduced, below the top layers. Moreover, populations of methanogenic archaea play an invaluable role in the treatment of anaerobic wastewater. Some are extremophiles, located kilometers below the surface in settings such as hot springs and submarine hydrothermal vents as well as in the "solid" rock of the Earth's crust.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




