
Mention the steps involved in DNA fingerprinting.
Answer
542.4k+ views
Hint: This is a laboratory technique that is used to establish a nexus between biological evidence and a suspect in a criminal investigation. It is also used to establish links to paternity. The processes like Southern blotting, hybridization, autoradiography are involved in the steps of DNA fingerprinting.
Complete solution:
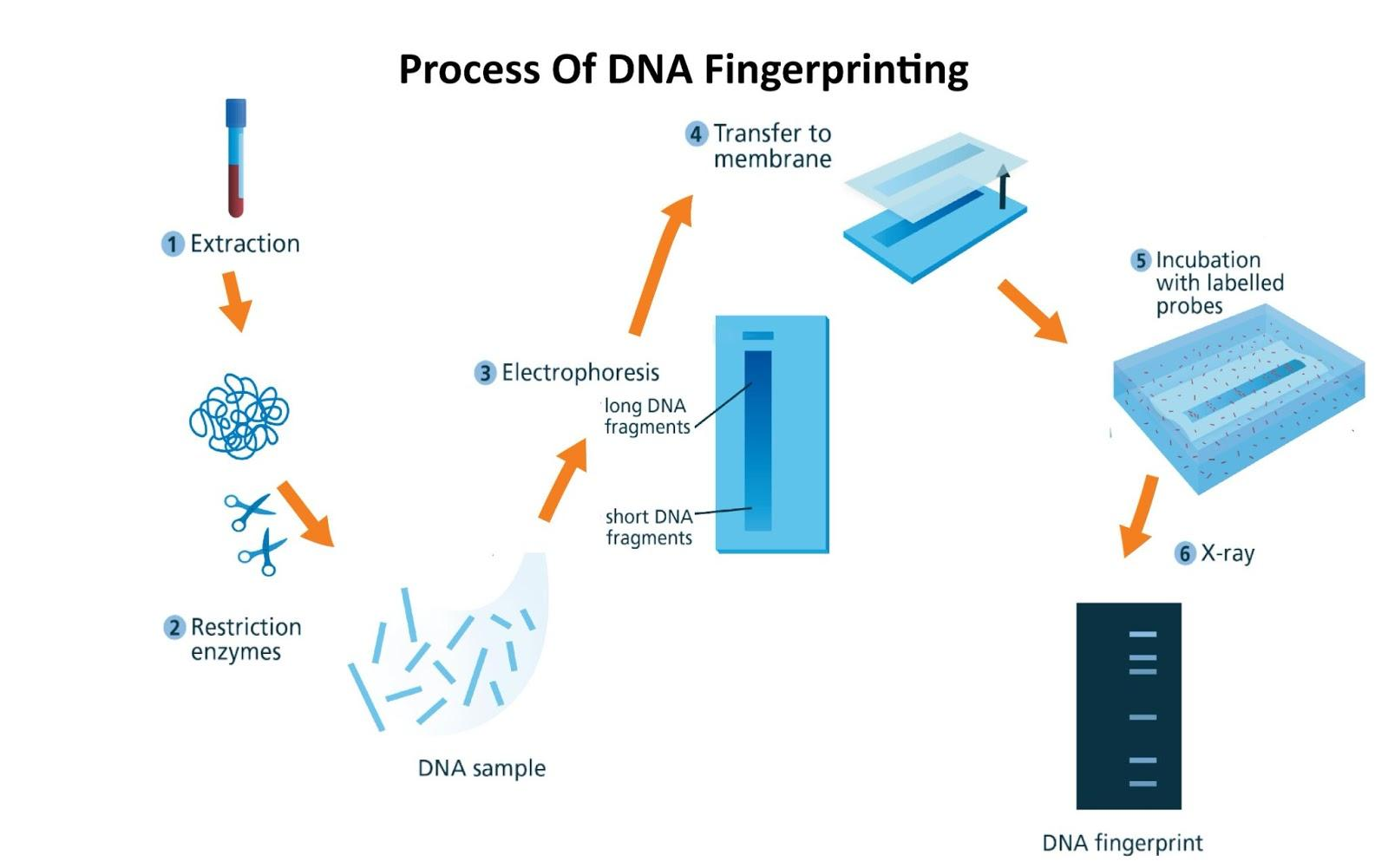
1. The DNA of the organism is extracted from its cell by doing centrifugation.
2. DNA is amplified with the help of the polymerase chain reaction technique.
3. DNA is fragmented with the help of the enzyme called Restriction endonuclease. This enzyme is also called molecular scissors as it helps in the cleavage of the DNA of any other molecules.
4. DNA fragments are separated by agarose gel electrophoresis.
5. The separated DNA fragments are visualized by the UV radiation after applying a dye called Ethidium bromide.
6. The DNA is transferred from the gel electrophoresis plate to the nitrocellulose plate or nylon membrane sheet. This process is called Southern blotting.
7. VNTR probes are now added which bund specific nucleotide sequences that are complementary to them. This is called hybridization.
8. The hybridized DNA fragments are detected by autoradiography. They are observed as dark bands in the X-Ray film.
Additional information:
DNA fingerprinting is a process that helps to identify DNA markers for inherited diseases. DNA fingerprinting technique was developed by Dr. Alec Jeffrey. VNTRs (Variable Number Tandem Repeats) are short repeating nucleotides.
DNA fingerprinting makes use of a technique that helps in making many copies of a short stretch of DNA and gel electrophoresis, a technique that separates DNA fragments based on their size. DNA sequencing, by contrast, uses more complicated techniques to specifically determine the sequence of letters in a piece of DNA.
Note:
-DNA fingerprinting technique is quite different from DNA sequencing. It's a process of finding the base pair sequence of the entire genome.
-Except for identical twins it is very unlikely that two people will have the same DNA pattern.
Complete solution:
1. The DNA of the organism is extracted from its cell by doing centrifugation.
2. DNA is amplified with the help of the polymerase chain reaction technique.
3. DNA is fragmented with the help of the enzyme called Restriction endonuclease. This enzyme is also called molecular scissors as it helps in the cleavage of the DNA of any other molecules.
4. DNA fragments are separated by agarose gel electrophoresis.
5. The separated DNA fragments are visualized by the UV radiation after applying a dye called Ethidium bromide.
6. The DNA is transferred from the gel electrophoresis plate to the nitrocellulose plate or nylon membrane sheet. This process is called Southern blotting.
7. VNTR probes are now added which bund specific nucleotide sequences that are complementary to them. This is called hybridization.
8. The hybridized DNA fragments are detected by autoradiography. They are observed as dark bands in the X-Ray film.
Additional information:
DNA fingerprinting is a process that helps to identify DNA markers for inherited diseases. DNA fingerprinting technique was developed by Dr. Alec Jeffrey. VNTRs (Variable Number Tandem Repeats) are short repeating nucleotides.
DNA fingerprinting makes use of a technique that helps in making many copies of a short stretch of DNA and gel electrophoresis, a technique that separates DNA fragments based on their size. DNA sequencing, by contrast, uses more complicated techniques to specifically determine the sequence of letters in a piece of DNA.
Note:
-DNA fingerprinting technique is quite different from DNA sequencing. It's a process of finding the base pair sequence of the entire genome.
-Except for identical twins it is very unlikely that two people will have the same DNA pattern.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




