
Mention the shape and draw a diagram of \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_3}\] .
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint:First determine the number of bonding domains and lone pair of electrons present on the central atom. Then calculate the steric number. From the steric number, determine the type of hybridization and geometry.
Complete answer:
The chemical formula \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_3}\] represents xenon trioxide.
The central atom is a xenon atom. Xenon is a noble gas element or inert gas element.
The atomic number of xenon is 54 and its electronic configuration is \[\left[ {{\text{Kr}}} \right]4{d^{10}}5{s^2}5{p^6}\].
The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and its electronic configuration is \[\left[ {{\text{He}}} \right]2{s^2}2{p^4}\].
Thus, an oxygen atom has six valence electrons.
In the xenon trioxide molecule, the central xenon atom forms three double bonds with three oxygen atoms. Thus, there are three \[{\text{Xe = O}}\] double bonds in one molecule of xenon trioxide.
Thus, the number of bonding domains is 3. The central xenon atom has one lone pair of electrons. Thus, the steric number for the central xenon atom in xenon trioxide is 4. The steric number of four is associated with tetrahedral electron pair geometry due to \[s{p^3}\] hybridization. Since one lone pair of electrons is present, the molecular geometry is pyramidal.
The diagram of xenon trioxide is shown below:
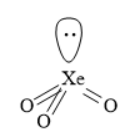
Structure of Xenon Trioxide
Note:
Steric number is the total number of bonding domains and lone pair of electrons present on the central atom. You can use the steric number to predict the type of hybridization and the molecular geometry.
Complete answer:
The chemical formula \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_3}\] represents xenon trioxide.
The central atom is a xenon atom. Xenon is a noble gas element or inert gas element.
The atomic number of xenon is 54 and its electronic configuration is \[\left[ {{\text{Kr}}} \right]4{d^{10}}5{s^2}5{p^6}\].
The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and its electronic configuration is \[\left[ {{\text{He}}} \right]2{s^2}2{p^4}\].
Thus, an oxygen atom has six valence electrons.
In the xenon trioxide molecule, the central xenon atom forms three double bonds with three oxygen atoms. Thus, there are three \[{\text{Xe = O}}\] double bonds in one molecule of xenon trioxide.
Thus, the number of bonding domains is 3. The central xenon atom has one lone pair of electrons. Thus, the steric number for the central xenon atom in xenon trioxide is 4. The steric number of four is associated with tetrahedral electron pair geometry due to \[s{p^3}\] hybridization. Since one lone pair of electrons is present, the molecular geometry is pyramidal.
The diagram of xenon trioxide is shown below:

Structure of Xenon Trioxide
Note:
Steric number is the total number of bonding domains and lone pair of electrons present on the central atom. You can use the steric number to predict the type of hybridization and the molecular geometry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




