
How do Mendel's experiments show that the Traits may be dominant or recessive?
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: The Mendel's experiments show that the Traits may be dominant or recessive by a genetic mix between two individuals who have homozygous genotypes, or genotypes that have completely dominant or completely recessive alleles, which result in opposite phenotypes for some of the genetic traits.
Complete answer:
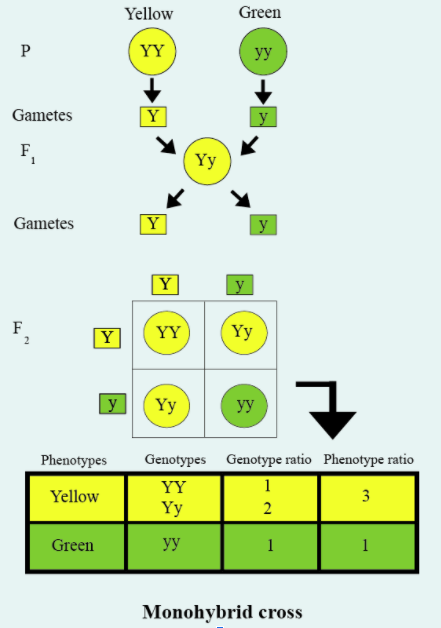
Mendel's experiments show that the Traits may be dominant or recessive by performing a monohybrid cross. Monohybrid cross between two pure breeding varieties always obtained hybrid progeny exhibiting one parental trait while the opposite trait was never expressed in the $F_1$ generation. It suggested that two alleles of a gene are often either dominant or recessive and the presence of the dominant allele in $F_1$ hybrids masks the expression of the recessive one.
Additional Information: Alleles are often either dominant or recessive. Dominant alleles show their effect even though the individual only has one copy of the allele (also referred to as being heterozygous). As an example, the allele for yellow seed is dominant, therefore you simply need one copy of the 'yellow seed' allele to possess yellow seed (although, with two copies you'll still have yellow seed). When the individuals have two copies of alleles then only the effects of recessive alleles are shown. As an example, the allele for green seed is recessive, therefore to possess green seed you would like to possess two copies of the ‘green seed' allele.
Note: If both alleles are dominant, it's called codominance. The resulting characteristic is because of both alleles being expressed equally. An example of this is the blood type AB which is the results of codominance of the A and B dominant alleles.
Complete answer:
Mendel's experiments show that the Traits may be dominant or recessive by performing a monohybrid cross. Monohybrid cross between two pure breeding varieties always obtained hybrid progeny exhibiting one parental trait while the opposite trait was never expressed in the $F_1$ generation. It suggested that two alleles of a gene are often either dominant or recessive and the presence of the dominant allele in $F_1$ hybrids masks the expression of the recessive one.
Additional Information: Alleles are often either dominant or recessive. Dominant alleles show their effect even though the individual only has one copy of the allele (also referred to as being heterozygous). As an example, the allele for yellow seed is dominant, therefore you simply need one copy of the 'yellow seed' allele to possess yellow seed (although, with two copies you'll still have yellow seed). When the individuals have two copies of alleles then only the effects of recessive alleles are shown. As an example, the allele for green seed is recessive, therefore to possess green seed you would like to possess two copies of the ‘green seed' allele.

Note: If both alleles are dominant, it's called codominance. The resulting characteristic is because of both alleles being expressed equally. An example of this is the blood type AB which is the results of codominance of the A and B dominant alleles.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

What is myopia and hypermetropia How are they corrected class 12 physics CBSE




