
Membrane-bound Krebs cycle enzyme is
(a)Fumarase
(b)Cis-aconitase
(c)Succinic dehydrogenase
(d)Malate dehydrogenase
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: The Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle due to the formation of a tricarboxylic compound. The Krebs cycle consists of many enzymes, but the enzyme which is membrane-bound to the mitochondrial inner membrane is an enzyme that is also utilized in the Electron transport system (ETS).
Complete answer:
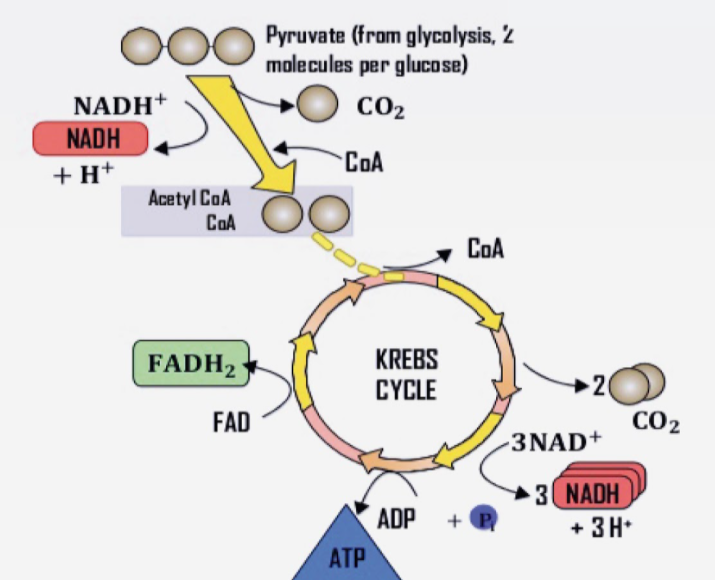
The enzyme that is membrane-bound in the Krebs cycle is succinic dehydrogenase. It catalyzes the reaction in which succinate is converted into fumarate in the Krebs cycle with the production of ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$. This enzyme is also found in ETS as part of Complex II which is an enzyme complex bound to the inner mitochondrial membrane. Succinate dehydrogenase is also known as succinate-coenzyme Q reductase.
Additional Information: Let us look at the Krebs cycle in detail.
Krebs cycle:
-The Krebs cycle starts with the condensation of the acetyl group with oxaloacetic acid(OAA) to give citric acid, hence it is also known as the citric acid cycle.
-This is followed by the synthesis of isocitric acid from citric acid.
-Successive steps of decarboxylation take place leading to the formation of $\alpha $-ketoglutaric acid and then succinyl-CoA.
-This succinyl-CoA is converted to succinic acid where a molecule of GTP is synthesized and finally it is converted to OAA allowing the cycle to continue.
-There are three points in this cycle where ${ NAD }^{ + }$ is converted to ${ NAD+H }^{ + }$.
-And there is one point where ${ FAD }^{ + }$ is converted to ${ FAD+H }^{ + }$.
So, the correct option is ‘Succinic dehydrogenase’.
Note: -There is a simultaneous synthesis of ATP from ADP during the conversion of GTP to GDP and this is known as substrate-level phosphorylation.
-Ubiquinone which is an electron carrier in ETS receives reducing equivalents from ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$ and this is the function of complex II
-When ${ NADH }_{ 2 }$ is oxidized there is a production of 3 molecules of ATP, but during oxidation of ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$, there is a production of 2 ATP.
Complete answer:
The enzyme that is membrane-bound in the Krebs cycle is succinic dehydrogenase. It catalyzes the reaction in which succinate is converted into fumarate in the Krebs cycle with the production of ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$. This enzyme is also found in ETS as part of Complex II which is an enzyme complex bound to the inner mitochondrial membrane. Succinate dehydrogenase is also known as succinate-coenzyme Q reductase.
Additional Information: Let us look at the Krebs cycle in detail.
Krebs cycle:
-The Krebs cycle starts with the condensation of the acetyl group with oxaloacetic acid(OAA) to give citric acid, hence it is also known as the citric acid cycle.
-This is followed by the synthesis of isocitric acid from citric acid.
-Successive steps of decarboxylation take place leading to the formation of $\alpha $-ketoglutaric acid and then succinyl-CoA.
-This succinyl-CoA is converted to succinic acid where a molecule of GTP is synthesized and finally it is converted to OAA allowing the cycle to continue.
-There are three points in this cycle where ${ NAD }^{ + }$ is converted to ${ NAD+H }^{ + }$.
-And there is one point where ${ FAD }^{ + }$ is converted to ${ FAD+H }^{ + }$.
So, the correct option is ‘Succinic dehydrogenase’.
Note: -There is a simultaneous synthesis of ATP from ADP during the conversion of GTP to GDP and this is known as substrate-level phosphorylation.
-Ubiquinone which is an electron carrier in ETS receives reducing equivalents from ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$ and this is the function of complex II
-When ${ NADH }_{ 2 }$ is oxidized there is a production of 3 molecules of ATP, but during oxidation of ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$, there is a production of 2 ATP.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




